Vanderbilt chemist Ben Brown awarded $2.375M to develop nonaddictive painkillers with AI
2024-01-19
When Ben Brown, research assistant professor of chemistry, thinks about the opioid epidemic, he views the problem on a molecular level. Painkillers used legitimately in medicine, such as oxycodone, are highly addictive, but better understanding of how their molecules interact with proteins in the body could lead to the formulation of nonaddictive alternatives, he said.
In May, the National Institute on Drug Abuse awarded Brown $1.5 million over five years to further his work in this area. Brown, faculty affiliate of the Vanderbilt Center for Addiction Research and the Center for Applied Artificial Intelligence in Protein Dynamics, is developing artificial intelligence that ...
National champion tree program finds new home
2024-01-19
The National Champion Tree Program started 83 years ago at American Forests to discover the largest, living trees in the United States. Now, the program is moving from the organization’s headquarters to a new home in the School of Natural Resources at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture (UTIA).
American Forests launched the Champion Tree Program in 1940. Its vision included establishing a nationwide laboratory for the study of forestry and trees. Being housed at Tennessee’s 1862 public land-grant university will advance the program’s understanding of big trees. “The National Champion Tree Program moving to UTIA means it can continue protecting ...
New AEM study evaluates potential disparities in restraint use in the emergency department at a minority-serving safety-net hospital
2024-01-19
Des Plaines, IL — A new study that contributes additional data to a growing body of evidence demonstrating disparities in restraint use in the emergency department (ED) has been published in the January issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM). The study, titled Disparities in use of physical restraints at an urban, minority-serving hospital emergency department evaluates the association between race/ethnicity and the use of restraints in an ED population ...
CRISPR off-switches: A path towards safer genome engineering?
2024-01-19
Using CRISPR, an immune system bacteria use to protect themselves from viruses, scientists have harnessed the power to edit genetic information within cells. In fact, the first CRISPR-based therapeutic was recently approved by the FDA to treat sickle cell disease in December 2023. That therapy is based on a highly studied system known as the CRISPR-Cas9 genetic scissor.
However, a newer and unique platform with the potential to make large-sized DNA removals, called Type I CRISPR or CRISPR-Cas3, waits in the wings for potential therapeutic use.
A new study from Yan Zhang, ...
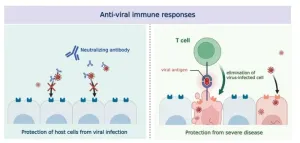
Evolution of the human immune system in the post-Omicron era
2024-01-19
It has been 4 years since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be eradicated and new variants are continuously emerging. Despite the extensive immunization programs, breakthrough infections (infection after vaccination) by new variants are common. New research suggests that human immune responses are also changing in order to combat the never-ending emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Specifically, it has been discovered the immune system that encountered breakthrough infection by the Omicron variant acquires enhanced immunity against future versions of the Omicron.
A team of South Korean scientists ...
First therapeutic target for preserving heart function in patients with pulmonary hypertension
2024-01-19
A team led by Dr. Guadalupe Sabio at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid has discovered a possible therapeutic target for pulmonary hypertension.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, identifies the first therapeutic target that can be modulated to preserve cardiac function in pulmonary hypertension, providing hope in the fight against this rare but fatal disease for which there is currently no cure.
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of elevated blood pressure in the arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. This increased pulmonary blood pressure puts the heart under continuous strain ...
Endless biotechnological innovation requires a creative approach
2024-01-19
Scientists working on biological design should focus on the idiosyncrasies of biological systems over optimisation, according to new research.
In a study, published today in Science Advances, researchers from the Universities of Bristol and Ghent have shown how exploring the unknown may be the crucial step needed to realise the continual innovation needed for the biotechnologies of the future.
Recognising the role of open-endedness in achieving this goal and its growing importance in fields like computer science and evolutionary biology, the team mapped out how open-endedness is linked to bioengineering practice today and what would be required to achieve it in ...
The secret life of CD4+ T cells: from helpers to melanoma fighters
2024-01-19
In the study led by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and published in Science Immunology, the researchers found that CD4+ T cells, traditionally called ‘helper T cells’ for their role in aiding the activation of other immune cells, are remarkably effective in controlling melanoma.
University of Melbourne’s Dr Emma Bawden, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Doherty Institute and lead author of the study, said this discovery challenges the conventional understanding of the role of CD4+ T cells in cancer immunity.
“Our ...
Study says ice age could help predict oceans’ response to global warming
2024-01-19
A team of scientists led by a Tulane University oceanographer has found that deposits deep under the ocean floor reveal a way to measure the ocean oxygen level and its connections with carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the last ice age, which ended more than 11,000 years ago.
The findings, published in Science Advances, help explain the role oceans played in past glacial melting cycles and could improve predictions of how ocean carbon cycles will respond to global warming.
Oceans adjust atmospheric CO2 as ice ages transition to warmer climates by releasing the greenhouse ...
From snack to science: Innovative grant brings popcorn into the classroom
2024-01-19
URBANA, Ill. — In a few years, popcorn could become a standard element in science classrooms across Illinois and the nation. With funding from a new USDA grant, a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign crop scientist and collaborating educators are developing a popcorn-based curriculum to reinforce concepts around agricultural science, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, computer science, genomics, research methods, and more for 4-H and high school students.
The funding may be new, but Tony Studer has proselytized ...
The case of a patient with multiple myeloma cured after hepatitis treatment reveals that this cancer can be caused by viruses, and opens up new treatment options
2024-01-19
Hepatitis C and B viruses are one of the causes of this type of cancer –a most frequent on in blood–, and the pathologies that precede it, known as gammopathies.
Early identification of an infection with these viruses can help doctors to prescribe appropriate treatment and prevent it from leading to malignant pathologies.
The research has been discussed in an editorial article in the journal Haematologica
A few years ago, a patient was cured of multiple myeloma after being treated for hepatitis C, astounding researchers from the group led by Joaquín ...
Why family businesses get more from women leaders
2024-01-19
Family businesses account for more than 70 percent of global GDP, and survey data shows that they are much friendlier to female leadership: up to 55 percent have at least one woman on their board and 70 percent are considering a woman for their next CEO. Experts have attributed this outlier gender parity to an emphasis on long-term strategies or family values. But a new study, published in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, suggests that women’s success as leaders in family businesses is deeply rooted in how employees interpret their leadership style.
“Family firms tend to focus on being inclusive ...
Wobbling particles in the sky
2024-01-19
The atmosphere contains many tiny solid particles. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) and the University of Göttingen in collaboration with the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) in France and the university of Gothenburg, Sweden, now studied how such non-spherical particles settle in air. For this, they used a new precision apparatus equipped with high-speed cameras and a novel particle injection mechanism. Using a 3D-printer, they created particles of different shapes resembling discs of thickness as low as 50 micrometer and rods of length as high as 880 micrometers. Thanks to this setup, they could observe that particles ...
Hiring globally mobile, highly specialized workers after their firm’s failure can be a strategic move, despite a loss of legitimacy
2024-01-19
New research published in Global Strategy Journal identifies globally mobile workers with highly specialized skills as a strategic hiring strategy, due to the workers’ legitimacy and mobility after being laid off by a failure of their former employer. The study shows that laid-off workers experience comparatively high legitimacy loss if they worked in the unit or geographical location where other workers were suspected of being responsible for the corporation’s failure. As a result, their bargaining position with a prospective employer is weaker, even if their special skills ...
New study demonstrates the importance of diverse social ties to entrepreneurship, even in divided societies
2024-01-19
We’ve known for a decade that political affiliation increasingly affects Americans’ everyday lives, including where they live, whom they befriend, and whom they welcome as in-laws. A recent Cato Institute survey revealed that nearly a third of Americans worry that voicing their political views could even harm their employment. This intensifying political tribalism, especially during an election year, threatens to limit the social networks vital to entrepreneurs. However a new study, published in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, offers an example of how to connect across political entrenchment from a surprising ...
DNA origami folded into tiny motor
2024-01-19
Scientists have created the world’s first working nanoscale electromotor, according to research published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology. The science team designed a turbine engineered from DNA that is powered by hydrodynamic flow inside a nanopore, a nanometer-sized hole in a membrane of solid-state silicon nitride.
The tiny motor could help spark research into future applications such as building molecular factories for useful chemicals or medical probes of molecules inside the bloodstream to detect diseases such as cancer.
“Common macroscopic machines become inefficient at the nanoscale,” said ...
How firms frame training programs for gig workers boosts promotion and uptake of the programs, strengthening the bond between worker and company
2024-01-19
General skills training programs for those hired under flexible arrangements can strengthen the relationship between firm and worker, thus benefiting both groups. But for that to happen, the programs need to have strong buy-in from both managers and workers. A new study published in Strategic Management Journal found the use of relational terms to frame training programs is key: Such phrasing makes managers more likely to promote the programs and increases uptake among the gig or contract workers.
The research team included Thomaz Teodorovicz of Copenhagen Business School, Sérgio Lazzarini of Western ...
How do human capital and pro-market institutions shape ambitious entrepreneurship in good and crisis times?
2024-01-19
Scholars and policymakers have highlighted the positive impact of human capital on entrepreneurial activity. Vast attention has also been directed to the beneficial role of pro-market institutions for entrepreneurship. A new article published in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal shows that the positive relation between pro-market institutions and growth aspirations is weaker for entrepreneurs with general human capital (higher education), but stronger for those with specific human capital (start-up or investment experience). ...
Important to involve both parents in breastfeeding
2024-01-19
The most important support person for women to succeed in their ambition to breastfeed is the new mother’s partner. The partner also needs to be included through more support from healthcare professionals.
Together with Region Sörmland, Uppsala University has implemented a breastfeeding support programme. It provides new parents with structured breastfeeding support throughout the healthcare chain. The study is presented in an article published in the International Breastfeeding Journal. Interviews were conducted to investigate how the partner perceived the support in both the breastfeeding support group and in a control group that had ...
RIT’s Moumita Das elected as American Physical Society fellow
2024-01-19
Rochester Institute of Technology Professor Moumita Das, from the School of Physics and Astronomy, has been elected an American Physical Society Fellow for her exceptional contributions to physics.
The APS Fellowship Program was created to recognize members who have made advances in physics through original research and publication, innovative contributions in the application of physics to science and technology, or teaching or service in the activities of the organization. No more than one half of 1 percent of the APS membership, excluding students, is recognized with fellowship. Only four people from Das’s field worldwide were ...
New research center to explore how ‘untapped Kingdom’ of fungi can change our world
2024-01-19
A new research centre focused on harnessing the positive powers of fungi is being established at Cranfield University with a £7.2 million injection of funding from Research England.
Fungi are one of the most diverse kingdoms in all living organisms and have an estimated global monetary value of 54.57 trillion US dollars. Long used for food and medicine, only a small proportion of classified fungi species has been studied in detail and developed for industrial use – leaving an estimated three million species yet to be discovered and evaluated. To date, research of fungi has largely focused on mitigating negative effects like disease, toxins and food loss.
The ...
University of Houston joins SMART Hub, a $5 million Department of Defense consortium
2024-01-19
To tackle the challenges of a shrinking wireless spectrum, the University of Houston has joined the Spectrum Management with Adaptive and Reconfigurable Technology (SMART) Hub – a Department of Defense Spectrum Innovation Center to conduct multifaceted spectrum research to meet national defense needs. The center, led by Baylor University, is a collection of researchers, engineers and economic and policy experts looking to enact a paradigm shift in the use and management of the wireless spectrum.
SMART Hub will develop next-generation technologies for unprecedented spectrum agility, to revolutionize ...
Occupational sitting time, leisure physical activity, and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality
2024-01-19
About The Study: In this study involving 481,000 individuals over a mean follow-up period of nearly 13 years, individuals who predominantly engaged in sitting at work exhibited a higher risk of mortality from all causes and cardiovascular disease compared with those who predominantly did not sit. Individuals who predominantly sit at work would need to engage in an additional 15 to 30 minutes of physical activity per day to mitigate this increased risk and reach the same level of risk as individuals who predominantly do not sit at work.
Authors: Chi-Pang Wen, M.D., Ph.D., of the National Health Research ...
Timing of maternal COVID-19 vaccine and antibody concentrations in infants born preterm
2024-01-19
About The Study: In this prospective cohort study of 220 pregnant individuals with preterm and full-term deliveries, receipt of three or more compared with two doses of COVID-19 vaccine before delivery resulted in 10-fold higher cord anti-Spike antibody levels. Maternal antibody concentration appeared more important than delivery gestational age in determining cord anti-Spike antibody levels. The number of doses and timing considerations for COVID-19 vaccine in pregnancy should include individuals at risk for preterm delivery.
Authors: Alisa Kachikis, M.D., M.S., of the University ...
When are opioid prescription limits effective in reducing prescription length?
2024-01-19
Study analyzed a West Virginia policy that tailored duration limits to a patient’s clinical setting
Researchers found a 27-57% reduction in prescription length with the tailored policy
Additional research is needed on potential consequences of limits, such as use of illicit opioids for pain relief
CHICAGO --- Many states have passed new laws that place restrictions on the duration of first-time opioid prescriptions to help address the opioid epidemic.
While most laws are one-size-fits-all, policies more tailored to the patient, such as their age or clinical setting (outpatient clinic, emergency room, etc.), were more effective ...
[1] ... [1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
[1439]
1440
[1441]
[1442]
[1443]
[1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
[1448]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.