New oviraptor dinosaur from the US Hell Creek Formation lived at the end of the Age of Dinosaurs and weighed about the same as an average woman
2024-01-24
New oviraptor dinosaur from the US Hell Creek Formation lived at the end of the Age of Dinosaurs and weighed about the same as an average woman
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0294901
Article Title: A new oviraptorosaur (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the end-Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of North America
Author Countries: USA, Canada
Funding: Funding for histology processing provided to HNW by Oklahoma State University for Health Sciences. Funding to GFF provided by the Royal Society (Grant NIF\R1\191527) and a Banting Fellowship ...
Galápagos penguin is exposed to and may accumulate microplastics at high rate within its food web, modelling suggests
2024-01-24
Modelling shows how microplastics may bioaccumulate in the Galápagos Islands food web, with Galápagos penguins most affected, according to a study published January 24, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Karly McMullen from the University of British Columbia, Canada, under the supervision of Dr. Juan José Alava and Dr. Evgeny A. Pakhomov of the Institute for the Ocean and Fisheries, University of British Columbia, Canada, and colleagues.
We know that microplastics are building up in our oceans, but the extent of the damage to marine organisms is still being assessed. Here, McMullen and colleagues focused ...
Obesity spiked in children during COVID-19 lockdowns—only the youngest bounced back
2024-01-24
Obesity among primary school children in the UK spiked during the COVID-19 lockdown, with a 45% increase between 2019/20 and 2020/21 among 4-5-year-olds, according to a study published on January 24, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Iván Ochoa-Moreno from the University of Southampton, UK, and colleagues. The authors estimated that without reversals, increased obesity rates in Year 6 children alone will cost society an additional £800 million in healthcare.
During the first year of the pandemic, school closures dramatically altered the routines of young children. Cancellation of organized sports, ...
Risk of death during heatwaves in Brazil linked to socioeconomic factors
2024-01-24
A new study suggests that heatwaves are exacerbating socioeconomic inequalities in Brazil, with people who are female, elderly, Black, Brown, or who have lower educational levels potentially facing greater risk of death during heatwaves. Djacinto Monteiro dos Santos of Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 24, 2024.
As climate change progresses, heatwaves are becoming hotter, longer, and more frequent in many regions ...
DNA from preserved feces reveals ancient Japanese gut environment
2024-01-24
DNA from ancient feces can offer archaeologists new clues about the life and health of Japanese people who lived thousands of years ago, according to a study published January 24, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Luca Nishimura and Ituro Inoue from the National Institute of Genetics, Japan, Hiroki Oota from The University of Tokyo, Mayumi Ajimoto from Wakasa History Museum, and colleagues.
Fossilized feces, also known as coprolites, can preserve an array of genetic material from the digestive tracts ...
A virus that infected the first animals hundreds of millions of years ago has become essential for the development of the embryo
2024-01-24
At least 8% of the human genome is genetic material from viruses. It was considered ‘junk DNA’ until recently, but its role in human development is now known to be essential
Researchers at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) describe for the first time the role of these viruses in a key process in development, when cells become pluripotent few hours after fertilization
The finding, published in Science Advances, is relevant for regenerative medicine and for the creation of artificial ...
City of Hope, TGen researchers develop machine-learning tool to detect cancer earlier via liquid biopsy
2024-01-24
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), a precision medicine research organization that is part of City of Hope, have developed and tested an innovative machine-learning approach that could one day enable the earlier detection of cancer in patients by using smaller blood draws. The study was published today in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“A huge body of evidence shows that cancer caught at later stages kills people. This new technology gets us closer to a world ...
Gene behind heart defects in Down syndrome identified
2024-01-24
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 19:00hrs GMT 24 January 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Gene behind heart defects in Down syndrome identified
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL have identified a gene that causes heart defects in Down syndrome, a condition that results from an additional copy of chromosome 21.
Reducing the overactivity of this gene partially reversed these defects in mice, setting the scene for potential future therapies for heart conditions in people with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome ...
Moving humanoid robots outside research labs: the evolution of the iCub3 avatar system
2024-01-24
Genova (Italy), 24 January 2024 - Over the past four years, the research team at the Artificial and Mechanical Intelligence (AMI) lab at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) in Genova (Italy) has developed advanced avatar technologies, known as the iCub3 system, in continuous testing with real-world scenarios. The system was utilized to enable a human operator to remotely visit locations 300 km away, to entertain the public at events and television appearances, and ...
Retinal imaging and genetics data used to predict future disease risk
2024-01-24
Mass Eye and Ear physician-researchers show that retinal imaging can help predict a person’s risk of developing ocular, neuropsychiatric, cardiac, metabolic, and pulmonary diseases.
The team also identified genetic loci associated with retinal thinning, which could help develop personalized treatment plans and future therapies for eye diseases such as glaucoma and macular degeneration.
The retina is said to provide a window into a person’s systemic health. In a new study published January 24th in Science Translational Medicine, physician-researchers from Mass ...
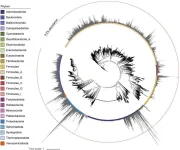
North China fossils show eukaryotes first acquired multicellularity 1.63 billion years ago
2024-01-24
In a study published in Science Advances on Jan. 24, researchers led by Prof. ZHU Maoyan from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported their recent discovery of 1.63-billion-year-old multicellular fossils from North China.
These exquisitely preserved microfossils are currently considered the oldest record of multicellular eukaryotes. This study is another breakthrough after the researchers’ earlier discovery of decimeter-sized eukaryotic fossils in the Yanshan area ...
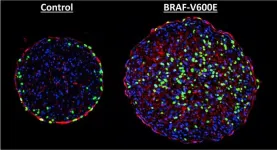
Harnessing skin cancer genes to heal hearts
2024-01-24
DURHAM, N.C. – Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that one of the most dangerous mutations found in skin cancers might moonlight as a pathway to mending a broken heart.
The genetic mutation in the protein BRAF, a part of the MAPK signaling pathway that can promote cell division, is one of the most common and most aggressive found in melanoma patients. In a new study, researchers show that introducing this mutation to rat heart tissue grown in a laboratory can induce growth.
Repairing ...
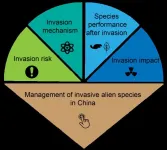
Special Feature calls attention to biological invasion research in China
2024-01-24
This month, the Ecological Society of America spotlights the challenge posed by invasive alien species in China with the release of a Special Feature, “Management of Biological Invasions in China,” in the latest issue of its journal Ecological Applications.
Accelerating rates of biological invasion have led to growing concerns about the destructive impacts of invasive alien species, or IAS, on the environment and human societies. This is especially true in China, which has witnessed a surge in ...
Researchers add a ‘twist’ to classical material design
2024-01-24
Researchers with the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University and the DOE's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) grew a twisted multilayer crystal structure for the first time and measured the structure’s key properties. The twisted structure could help researchers develop next-generation materials for solar cells, quantum computers, lasers and other devices.
“This structure is something that we have not seen before – it was a huge surprise to me,” said Yi Cui, a professor at Stanford and SLAC and paper co-author. “A new quantum electronic property could appear ...
The costly, unintended consequences produced by the National Flood Insurance Program
2024-01-24
Since the creation of the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) in 1968, the U.S. government has paid over $51 billion to cover flood losses. Almost half of these payouts went to just 25 counties, among the fastest-growing counties by population. A new paper published in the Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists examines whether insuring people against potential flood losses contributes directly to population growth in flood-prone areas. In “Does the National Flood Insurance Program Drive Migration ...
Tiny vibrating bubbles could lead to better water treatment
2024-01-24
Fresh research into the physics of vibrating nanobubbles reveals that they do not heat up as much as previously thought.
Vibrating nanobubbles have surprising uses as ultrasound contrast agents in cancer diagnosis. They can also be forced to collapse - destroying nearby microscopic contaminants - for waste-water treatment and surface cleaning of delicate microfluidic devices.
The stiffness of a nanobubble as it vibrates is strongly related to their internal temperature, and being able to understand ...
Self-powered movable seawall for tsunami protection and emergency power generation
2024-01-24
With over 2,780 fishing ports and 993 commercial and industrial ports, Japan faces the challenge of safeguarding these important coastal assets from the destructive forces of tsunamis. A promising solution lies in the form of a movable barrier system, where gates rising from the seafloor act as barriers, protecting ports against tsunamis, storm surges and high waves. However, during natural disasters, power outages may disrupt the electricity needed to operate the gate.
To address this, researchers led by Professor Hiroshi Takagi from Tokyo Institute of Technology have proposed ...
Groundwater levels are sinking ever faster around the world
2024-01-24
At the beginning of November, The New York Times ran the headline, “America is using up its groundwater like there’s no tomorrow.” The journalists from the renowned media outlet had published an investigation into the state of groundwater reserves in the United States. They came to the conclusion that the United States is pumping out too much groundwater.
But the US isn’t an isolated case. “The rest of the world is also squandering groundwater like there’s no tomorrow,” says Hansjörg Seybold, Senior Scientist in the Department of Environmental Systems Science at ETH Zurich. He is coauthor ...
$1.2 million grant awarded to LSU LCMC Health Cancer Center to help break down barriers to cervical cancer prevention
2024-01-24
NEW ORLEANS (Jan. 24, 2024) – A research team from LSU LCMC Health Cancer Center has been awarded a $1.5 million grant to eliminate barriers from cervical cancer prevention. The five-year program combines a $1.2 million award from the American Cancer Society and $75,000 a year for five years investment from LSU Health New Orleans.
Louisiana has one of the highest cervical cancer death rates in the country. Cervical cancer rates are higher in predominantly African American communities represented in both urban (New Orleans) and rural areas of Louisiana. Black women in Louisiana are diagnosed with and die from cervical cancer at a significantly ...
Off-road autonomy: U-M's Automotive Research Center funded with $100 million through 2028
2024-01-24
Images
The U.S. Army has extended its long-running relationship with the University of Michigan's Automotive Research Center, reaching a new five-year, agreement of up to $100 million to boost work on autonomous vehicle technologies.
This potentially doubles the federal government's financial investment with ARC since the last agreement, reached in 2019. Following its 1994 launch, the ARC has served as a source of technology and first-in-class modeling and simulation for the Army's fleet of vehicles—the largest such fleet in the world.
"We are driving the development of modern mobility systems with our advanced modeling ...
Atmospheric pressure changes could be driving Mars’ elusive methane pulses
2024-01-24
New research shows that atmospheric pressure fluctuations that pull gases up from underground could be responsible for releasing subsurface methane into Mars’ atmosphere; knowing when and where to look for methane can help the Curiosity rover search for signs of life.
“Understanding Mars’ methane variations has been highlighted by NASA’s Curiosity team as the next key step towards figuring out where it comes from,” said John Ortiz, a graduate student at Los Alamos National Laboratory who led the research team. “There are several challenges associated with meeting that goal, ...
New pieces in the puzzle of first life on Earth
2024-01-24
Microorganisms were the first forms of life on our planet. The clues are written in 3.5 billion-year-old rocks by geochemical and morphological traces, such as chemical compounds or structures that these organisms left behind. However, it is still not clear when and where life originated on Earth and when a diversity of species developed in these early microbial communities. Evidence is scarce and often disputed. Now, researchers led by the University of Göttingen and Linnӕus University in Sweden have uncovered key findings about the earliest forms of life. In rock ...
Post pandemic, US cardiovascular death rate continues upward trajectory
2024-01-24
Ann Arbor, January 24, 2024 – New research confirms what public health leaders have been fearing: the significant uptick in the cardiovascular disease (CVD) death rate that began in 2020 has continued. The continuing trend reverses improvements achieved in the decade before the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce mortalities from heart disease and stroke, the leading causes of death in the United States. The findings are reported in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier.
Investigators from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ...
New model predicts how shoe properties affect a runner’s performance
2024-01-24
A good shoe can make a huge difference for runners, from career marathoners to couch-to-5K first-timers. But every runner is unique, and a shoe that works for one might trip up another. Outside of trying on a rack of different designs, there’s no quick and easy way to know which shoe best suits a person’s particular running style.
MIT engineers are hoping to change that with a new model that predicts how certain shoe properties will affect a runner’s performance.
The simple model incorporates ...
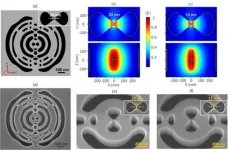
Sub-wavelength confinement of light demonstrated in indium phosphide nanocavity
2024-01-24
WASHINGTON — As we transition to a new era in computing, there is a need for new devices that integrate electronic and photonic functionalities at the nanoscale while enhancing the interaction between photons and electrons. In an important step toward fulfilling this need, researchers have developed a new III-V semiconductor nanocavity that confines light at levels below the so-called diffraction limit.
“Nanocavities with ultrasmall mode volumes hold great promise for improving a wide range of photonic ...
[1] ... [1427]
[1428]
[1429]
[1430]
[1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
1435
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
[1439]
[1440]
[1441]
[1442]
[1443]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.