Corning uses neutrons to reveal ‘atomic rings’ help predict glass performance
2024-01-23
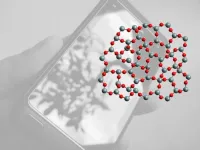
Glass is being used in a wider range of high-performance applications, including those for consumers and industry, military and aerospace electronics, coatings and optics. Because of the extreme precision demanded for use in products such as mobile phones and jet aircraft, glass substrates must not change their shape during the manufacturing process.
Corning Incorporated, a manufacturer of innovative glass, ceramics and related materials, invests a tremendous amount of resources into studying the stability of different types of glass. Recently, Corning researchers found that understanding the stability ...
CT-based radiomics deep learning to predict lymph node metastasis in tumors
2024-01-23
Tsukuba, Japan—Nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, while rare, are primarily treated through surgery. The presence or absence of lymph node metastasis considerably influences the selection of surgical and other treatment approaches. Particularly controversial is the necessity of surgery for tumors smaller than 2 cm as current clinical guidelines provide no clear consensus. Existing methods for preoperative diagnosis of lymph node metastasis are inadequate.
To address the aforementioned challenge, the Tsukuba team has created a predictive model by integrating radiomics features extracted from CT and MRI images using artificial intelligence ...
Researchers find new multiphoton effect within quantum interference of light
2024-01-23
An international team of researchers from Leibniz University Hannover (Germany) and the University of Strathclyde in Glasgow (United Kingdom) has disproved a previously held assumption about the impact of multiphoton components in interference effects of thermal fields (e.g. sunlight) and parametric single photons (generated in non-linear crystals). "We experimentally proved that the interference effect between thermal light and parametric single photons also leads to quantum interference with the background field. For this reason, the background cannot simply be neglected and subtracted from calculations, as ...
Anxiety and depression symptoms after the Dobbs abortion decision
2024-01-23
About The Study: In this analysis of survey data from 718,000 participants from December 2021 to January 2023, residence in states with abortion trigger laws (anticipatory bans that would go into effect should Roe v Wade be overturned) compared with residence in states without such laws was associated with a small but significantly greater increase in anxiety and depression symptoms after the Dobbs v Jackson decision in June 2022.
Authors: Benjamin Thornburg, B.S., of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.25599)
Editor’s ...
Cancer diagnoses after recent weight loss
2024-01-23
About The Study: Health professionals with weight loss within the prior two years had a significantly higher risk of cancer during the subsequent 12 months compared with those without recent weight loss in this study that included 157,000 participants. Cancer of the upper gastrointestinal tract was particularly common among participants with recent weight loss compared with those without recent weight loss.
Authors: Brian M. Wolpin, M.D., M.P.H., of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
USPSTF statement on screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children
2024-01-23
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children 5 years or younger without signs or symptoms. Speech and language delays and disorders can pose significant problems for children and their families. Evidence suggests that school-aged children with speech or language delays may be at increased risk of learning and literacy disabilities, including difficulties with reading and writing. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this updated recommendation ...
Discovering the physics behind 300-year-old firefighting methods
2024-01-23
WASHINGTON, Jan. 23, 2024 – Today, water pressure technology is ubiquitous, and any person who showers, waters a garden, or fights fires is benefiting from the technology devised to harness it. In the 17th and 18th centuries, though, a steady stream of water not punctuated by pressure drops was a major breakthrough.
In 1666, when bucket brigades were the best line of defense, the Great Fire of London burned almost all of the city’s tightly packed, wooden structures. The disaster destroyed hundreds of thousands of homes and dozens of churches, demonstrating the need for better firefighting methods and equipment.
One landmark advancement was the ...
Long-term follow up pinpoints side effects of treatments for prostate cancer patients
2024-01-23
A 10-year follow up study of nearly 2,500 U.S. men who received prostate cancer treatment will help inform decision making in terms of treatments and side effects for a diverse population.
The CEASAR (Comparative Effectiveness Analysis of Surgery and Radiation for Localized Prostate Cancer) study, coordinated by Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC), is a multisite research study conducting long-term follow up on men who were diagnosed with localized prostate cancer between 2011 and 2012.
Researchers have now followed the same cohort of men for more than a decade, administering a series of questionnaires ...
Maternal autistic traits and adverse birth outcomes
2024-01-23
About The Study: In this study of 87,000 women, higher level of maternal autistic traits was associated with increased risk of adverse birth outcomes, particularly very preterm birth. Acknowledging the risks and providing tailored and timely antenatal care support to women with a high level of autistic traits in the general population, particularly women with autistic traits within the clinical range, regardless of formal diagnosis, is warranted.
Authors: Mariko Hosozawa, M.D., Ph.D., of the National Center for Global Health ...
Patient self-assessment of walking ability and fracture risk in older adults
2024-01-23
About The Study: Self-reported walking limitations were associated with increased risk of fracture in this study of 238,000 participants age 45 and older. These findings suggest that walking ability should be sought by clinicians to identify high-risk candidates for further assessment.
Authors: Dana Bliuc, Ph.D., of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52675)
Editor’s ...
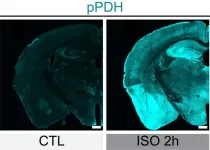
New technology lets researchers track brain cells’ “off switches”
2024-01-23
For decades, scientists have studied the intricate activity patterns in human and animal brains by observing when different groups of brain cells turn on. Equally important to understanding the brain and related diseases, however, is knowing how long those neurons stay active and when they turn off again.
Now, scientists at Scripps Research have developed a new technology that lets them track when, after a burst of activity, brain cells shut off—a process known as inhibition. The technique, published in Neuron on January 23, 2024, provides a new way to study not only the normal functioning ...
Study suggests that unintentional weight loss is a signal to see a doctor
2024-01-23
Boston – Unintentional weight loss is associated with an increase in the risk of a cancer diagnosis within the coming year, according to a study from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
“If you are losing weight and you aren’t trying to lose weight by making changes in your exercise routine or diet, people should see their doctor to consider possible causes,” says lead investigator Brian Wolpin, MD, MPH, Director of the Gastrointestinal Cancer Center at Dana-Farber and Director of the Hale Family Center for Pancreatic Cancer Research. “There are ...
New research guides mathematical model-building for gene regulatory networks
2024-01-23
AMES, Iowa — Over the last 20 years, researchers in biology and medicine have created Boolean network models to simulate complex systems and find solutions, including new treatments for colorectal cancer.
“Boolean network models operate under the assumption that each gene in a regulatory network can have one of two states: on or off,” says Claus Kadelka, a systems biologist and associate professor of mathematics at Iowa State University.
Kadelka and undergraduate student researchers recently published a study that ...
Reflecting on your legacy could make you more philanthropic, new research finds
2024-01-23
People have a tendency to leave their wealth to family members and other loved ones. However, Andrew Carnegie, a famously wealthy industrialist, once said “I would as soon leave to my son a curse as the almighty dollar.” Indeed, Carnegie donated over 90% of his fortune to charity. New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science shows that people can be spurred to look beyond close relationships in favor of philanthropy by having them reflect on their legacy. The researchers called this phenomenon the “Andrew Carnegie ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation awarded NIH grant to develop allograft-rejection-on-a-chip model
2024-01-23
(LOS ANGELES) – January 23, 2024 - Vadim Jucaud, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, has been awarded a grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop a functional organ-on-a-chip to model allogeneic transplant rejection. Such a model would allow the study of allograft tolerance and may ultimately lead to reducing organ transplant rejections without needing immunosuppressive drugs.
Organ transplantation is a lifesaving procedure for patients with end-stage organ disease. Over 145,000 organs per year are transplanted worldwide from organ donors to recipients. For these so-called allografts, ...
A neurological disease paradigm shift
2024-01-23
One of the things that makes developing effective treatments for Parkinson’s disease so challenging is its complexity. While some forms are caused by genetics, others have environmental factors, and patients can show a wide range of symptoms of varying severity. Diagnosis of Parkinson’s is also currently made very late, after the disease may have been in the brain for a decade or more.
In a paper published in The Lancet Neurology, a group of scientists argue that this complexity demands a new way of classifying the disease for research purposes, one based not on clinical diagnosis but biology. The authors have called their biological model ...
No sex difference in concussion recovery among college athletes
2024-01-23
A new large, national study of collegiate student-athletes in the United States dispels a long-held belief about concussions, finding that women and men recover from sport-related head injuries within the same time frame.
Women and men’s recovery patterns ...
New study published in Nature Scientific Reports shows industry-leading performance for Waymark Signal in predicting avoidable ER and hospital utilization
2024-01-23
Waymark, the Medicaid provider enablement company, today published a peer-reviewed study in Nature’s Scientific Reports comparing the performance of Waymark SignalTM, the company’s proprietary machine learning technology, to conventional Medicaid risk models. The study found that Waymark Signal was 90 percent accurate in predicting avoidable emergency room (ER) and hospital utilization for patients receiving Medicaid — stronger performance than leading Medicaid risk models in the field.
Waymark ...
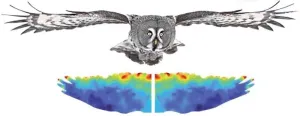
Uncovering the secrets behind the silent flight of owls
2024-01-23
Owls are fascinating creatures that can fly silently through some of the quietest places. Their wings make no noise while flying, enabling them to accurately locate their prey using their exceptional hearing ability while remaining undetected. This unique ability depends on many factors and has long been a hot research subject.
Studies have found associations between the ability to fly silently and the presence of micro-fringes in owl wings. These trailing-edge (TE) fringes play a crucial role in suppressing the noise produced by wing ...
Incheon National University researchers propose a web 3.0 streaming architecture and marketplace
2024-01-23
Web 3.0 is an internet paradigm that is based around blockchain technology, an advanced database mechanism. Compared to Web 2.0, the current internet paradigm, Web 3.0 provides some added advantages, such as transparency and decentralized control structures. This is because Web 3.0 is designed to work over trustless and permissionless networks. Unfortunately, owing to certain technical difficulties, the implementation of Web 3.0 media streaming requires modifications to the service architecture of existing media streaming services. These difficulties include the degradation ...
Major climate benefits with electric aircraft
2024-01-23
Aviation has grown considerably in recent decades and accounts for approximately 2 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions and some 4 percent of all climate change impacts annually. While aviation is an important contributor to climate change and other environmental problems, electrification is one option for reducing these environmental impacts. The first electric aircraft are already in operation today and are mainly small planes used for pilot training and short flights in the immediate area. This is the type of plane that was studied in the life cycle assessment.
“In the short-term future, battery-powered electric aircraft will probably mostly be used for shorter ...
Multi-generational toxicant exposures show cumulative, inherited health effects
2024-01-23
While exposure to a single substance like DDT has been shown to create inherited disease susceptibility, a recent study in animals found exposure to multiple different toxicants across generations can amplify those health problems.
In the study, published in the journal Environmental Epigenetics, an initial generation of pregnant rats was exposed to a common fungicide, then their progeny to jet fuel and the following generation to DDT. When those rats were then bred out to a fifth unexposed generation, the incidence of obesity as well as kidney and prostate diseases in those animals were compounded, ...
Childhood relationships, experiences may have good and bad effects on adult heart health
2024-01-23
Research Highlights:
Positive, warm relationships between caregiver and child were associated with higher odds of attaining ideal heart health at multiple points across a 20-year span of adulthood.
Meanwhile, experiencing childhood adversity such as abuse was associated with a lower chance of reaching optimal cardiovascular health in adulthood.
Lower annual income as an adult — $35,000 or less — may confound the health effects of childhood adversity.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, Jan. 23, 2024
DALLAS, Jan. 23, 2024 — Throughout adulthood, ...
As a carbon offset, cookstove emission credits are greatly overestimated
2024-01-23
The fastest growing type of offset on the global carbon market subsidizes the distribution of efficient cookstoves in developing countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but a new study finds that the credits overestimate the stoves’ carbon savings by a factor of 10.
The overestimation undermines efforts to counteract carbon emissions to slow climate change, since companies use these offsets to meet climate targets and to sell products labeled as “carbon neutral” instead of making real reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. It also undermines ...
APOE genetic variants linked to Alzheimer disease are also associated with the development of subclinical aterosclerosis
2024-01-23
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid have found that one of the most potent genetic risk factors for Alzheimer disease, apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4), is also associated with an increased risk of developing subclinical atherosclerosis in middle age. The study also demonstrates protection against subclinical atherosclerosis in people carrying the variant APOE2, which protects against Alzheimer disease.
The study, coordinated by Dr. Marta Cortés Canteli and CNIC General Director Dr. Valentín Fuster, sheds light on the role of APOE in the development of cardiovascular diseases ...
[1] ... [1419]
[1420]
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
1427
[1428]
[1429]
[1430]
[1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.