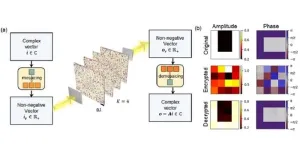
Optical computing boost with diffractive network advance
2024-01-22
State-of-the-art neural networks heavily rely on linear operations, such as matrix-vector multiplications and convolutions. While dedicated processors like GPUs and TPUs exist for these operations, they have limitations in terms of power consumption and bandwidth. Optics is better suited for such operations because of its inherent parallelism, large bandwidth, and computation speed.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NN), also known as diffractive networks, constitute an emerging optical computing architecture. ...
Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) to lead $40 Million initiative for AFIRM Consortium
2024-01-22
Winston Salem, NC – January 22, 2024 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, part of Wake Forest University School of Medicine, has been selected to lead the Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine (AFIRM) Consortium. The project - a $40 million, five year-long award from the Defense Health Agency (DHA) - will focus on taking regenerative medicine solutions for battlefield injuries to the next level, and ultimately to the general public.
Regenerative medicine is a science that takes advantage of the body's natural abilities to restore or replace damaged tissue and organs. WFIRM has managed two prior AFIRM consortia since ...
Argonne National Laboratory flexes capabilities with receipt of four nuclear innovation vouchers
2024-01-22
A decade that began with a global shutdown is a third of the way done. Its finale — a major deadline for reducing U.S. carbon emissions to slow climate change — approaches at the usual clip. With the decade’s halfway mark in view, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) awarded seven new vouchers to companies and national laboratories working to develop and commercialize clean nuclear energy projects. Nuclear energy is considered central to efforts to minimize carbon emissions and still reliably meet rising ...
Strategy to boost prostate cancer treatment efficacy devised at Rutgers Health
2024-01-22
Rutgers researchers can predict which patients will benefit from a popular prostate cancer drug – and have devised a strategy that may make the treatment work longer.
“This work should help doctors know which patients’ prostate cancers will and won’t respond to the androgen deprivation therapy enzalutamide, which can slow prostate cancer growth by disrupting androgen receptor signaling,” said Antonina Mitrofanova, associate professor of Biomedical and Health Informatics, associate dean for research at the Rutgers School of Health Professions, researcher at Rutgers Cancer ...
Salad in space? New study says it's not a healthy choice
2024-01-22
Lettuce and other leafy green vegetables are part of a healthy, balanced diet — even for astronauts on a mission.
It’s been more than three years since the National Aeronautics and Space Administration made space-grown lettuce an item on the menu for astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Alongside their space diet staples of flour tortillas and powdered coffee, astronauts can munch on a salad, grown from control chambers aboard the ISS that account for the ideal temperature, amount of water and light ...
Sexual minority young people in Canada more likely to experience harmful police contact
2024-01-22
Toronto, ON – While there has been much public scrutiny and research on police interactions and violence towards sexual minorities in the United States, there is a gap in the current literature on how sexual minorities fare with law enforcement contact in Canada. A new study published in the Annals of Epidemiology aims to fill this research gap by examining the relationship between sexual orientation and experiences with police contact, including intrusion and harassment from the police, in Canada.
Among a sample of 940 adolescents and young adults across Canada, the study found that the prevalence of police contact was highest among persons ...
University Hospitals OBGYN and urologist Joseph Welles Henderson, MD, named InterStim™ Center of Excellence
2024-01-22
CLEVELAND -- Joseph Welles Henderson, MD, of University Hospitals has been named an InterStim™ Center of Excellence by Medtronic (NYSE: MDT), the world’s largest medical device manufacturer. The designation is awarded to caregivers who have demonstrated particular expertise in the use of the InterStim™ system to treat overactive bladder, as well as non-obstructive urinary retention and chronic fecal incontinence.
Dr. Henderson is an OBGYN and urologist, and specializes in female pelvic medicine and reconstruction ...
Thinning of brain region may signal dementia risk 5-10 years before symptoms
2024-01-22
SAN ANTONIO, Jan. 22, 2024 — A ribbon of brain tissue called cortical gray matter grows thinner in people who go on to develop dementia, and this appears to be an accurate biomarker of the disease five to 10 years before symptoms appear, researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (also called UT Health San Antonio) reported.
The researchers, working with colleagues from The University of California, Davis, and Boston University, conducted an MRI brain imaging study published ...
Zeng researching techniques for achieving supply chain security for the Internet of Things
2024-01-22
Qiang Zeng, Associate Professor, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "Towards Lifetime Supply Chain Security for Internet of Things: Testing an Update Before Trusting It."
The global Internet of Things (IoT) market size is expected to rise substantially by 2029. IoT devices are manufactured by various companies around the world, and thus, should not be trusted by default. Zeng aims to ensure lifetime supply chain security of IoT devices. To attain this objective, he is proposing to test an IoT device and every firmware update through ...
Arafin conducting research aimed at securing chiplet-based semiconductor manufacturing from untrusted supply chains
2024-01-22
Md Tanvir Arafin, Assistant Professor, Cybersecurity Engineering, received funding for the project: "Securing Chiplet-based Semiconductor Manufacturing from Untrusted Supply Chains."
Monolithic integrated circuit (IC) design is reaching the physical limit to accommodate the ever-increasing demand of cramming more transistors in a chip. To address this, novel design primitives that move from monolithic design practices to heterogeneous integration of IC primitives in a 2.5 or 3D structure have emerged. ...
Good and bad news for people with low back pain
2024-01-22
Low back pain is a major cause of disability around the globe, with more than 570 million people affected. In the United States alone, health care spending on low back pain was $134.5 billion between 1996 and 2016, and costs are increasing.
"The good news is that most episodes of back pain recover, and this is the case even if you have already had back pain for a couple of months," University of South Australia Professor Lorimer Moseley says.
"The bad news is that once you have had back pain for more than a few months, the chance ...
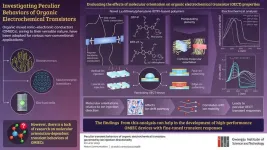
GIST researchers investigate strange transient responses of organic electrochemical transistors
2024-01-22
Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors (OMIECs) are a highly sought-after class of materials for non-conventional applications, such as bioelectronics, neuromorphic computing, and bio-fuel cells, owing to their two-in-one electronic and ionic conduction properties. To ensure a much wider acceptance of these fascinating materials, there is a need to diversify their properties and develop techniques that allow application-specific tailoring of the features of OMIEC-based devices. A crucial aspect of this process is to develop strategies for evaluating the various properties of these ...
Protein discovery could help solve prostate cancer drug resistance
2024-01-22
SPOKANE, Wash. – Researchers have identified a receptor protein known as CHRM1 as a key player in prostate cancer cells’ resistance to docetaxel, a commonly used chemotherapy drug to treat advanced cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. The discovery opens the door to new treatment strategies that could overcome this resistance. This could ultimately help extend the lives of those with prostate cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer deaths among men.
Led by a team of scientists at Washington State University, ...
Improvement of social isolation and loneliness and excess mortality risk in people with obesity
2024-01-22
About The Study: The findings of this study of 398,000 UK Biobank participants support the improvement of social isolation and loneliness in people with obesity to decrease obesity-related excess risk of mortality.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52824)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
In utero exposure to maternal COVID-19 vaccination and offspring neurodevelopment at 12 and 18 months
2024-01-22
About The Study: The results of this study including 2,261 and 1,940 infants ages 12 and 18 months, respectively, suggest that COVID-19 vaccination was safe during pregnancy from the perspective of infant neurodevelopment to 18 months of age. Additional longer-term research should be conducted to corroborate these findings and buttress clinical guidance with a strong evidence base.
Authors: Eleni G. Jaswa, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5743)
Editor’s ...
Scientists advance affordable, sustainable solution for flat-panel displays and wearable tech
2024-01-22
Key takeaways:
A new 3D-printable material called “supramolecular ink” replaces costly scarce metals with inexpensive, Earth-abundant materials.
The organic material requires far less energy to manufacture than conventional methods.
It could also enhance the sustainability of 3D-printable wearable devices, lighting technologies, and luminescent art and sculpture.
A research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has developed “supramolecular ink,” a new technology for use in OLED (organic light-emitting ...
Innovate UK, the Urban Future Lab, and Greentown Labs announce the Year 4 cohort for their Global Incubator Programme
2024-01-22
Commencing in January, the Urban Future Lab (UFL) at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, in collaboration with Greentown Labs, will serve as the supportive entry point in the U.S. for the fourth cohort of Innovate UK’s Global Incubator Programme: Clean Growth edition. This initiative is specifically designed to foster and assist the establishment of innovative climate technology companies demonstrating significant potential for international scalability into new markets.
The annual program extends the opportunity to eight U.K.-based businesses, enabling them to explore the U.S. market and gain access to esteemed mentors over a six-month period.
"We’re ...
KIER Accelerates Carbon-Neutral Technological Innovation through International Collaboration with Horizon Europe
2024-01-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) promotes active collaborations with prominent European institutions, including leading 'Research & Technology Organisations (RTO), prestigious universities, and small & medium-sized enterprises (SME). KIER has consistently stressed the importance of international collaborations in developing evolving and advanced green technologies. As a consequence, the consortium entitled "Scalable High-power Output and Low-Cost MAde-to-measure Tandem Solar Modules Enabling Specialized PV Applications (SOLMATES)", in which KIER participated and worked as a partner with 13 other ...
Groundbreaking discovery enables cost-effective and eco-friendly green hydrogen production
2024-01-22
A breakthrough technology has been developed that enables the production of green hydrogen in a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner, bringing us closer to a carbon-neutral society by replacing expensive precious metal catalysts.
Led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, a joint research team has successfully developed a bifunctional water electrolysis catalyst for the high-efficiency and stable production of high-purity green hydrogen.
The newly-developed catalyst exhibits exceptional durability even in highly corrosive acidic environments. ...
Navigating the ‘big little leap’ to kindergarten
2024-01-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – No matter how well children are prepared for kindergarten, their transition to the classroom during the first few months plays a key role in their success, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that kids who made a more successful transition in the first 10-14 weeks of kindergarten scored higher than others on tests of academic and social-behavioral skills at the end of the school year.
Important parts of the transition – what the researchers called a “big little leap” – included making new friends, ...
Bad to the bone: UMass Amherst engineer aims to prevent fractures in cancer patients
2024-01-22
Bad to the Bone: UMass Amherst Engineer Aims to Prevent Fractures in Cancer Patients
National Cancer Institute funds research to assess if the treatment of cancer metastasis in patients is as damaging as the disease
AMHERST, Mass. – For some patients whose cancer has spread to their bones, the ensuing treatment can be more physically damaging than the original disease, leading to increased bone loss and fracture. Stacyann Bailey, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has received a two-year grant from the National Cancer Institute to study the complex relationship between drugs used to treat metastatic cancer ...
Breakthrough research enhances stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells
2024-01-22
A team of researchers from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, jointly led by Professors Sung-Yeon Jang, Jungki Ryu, and Ji-Wook Jang, in collaboration with Professor Sang Kyu Kwak from Korea University, have achieved remarkable advancements in the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells. Their groundbreaking work not only paves the way for the commercialization of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), but also offers significant potential in green hydrogen production technology, ensuring long-term operation with high efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered attention due to their reduced toxicity and broad light absorption ...
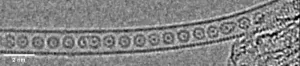
Scientists trap krypton atoms to form one-dimensional gas
2024-01-22
For the first time, scientists have successfully trapped atoms of krypton (Kr), a noble gas, inside a carbon nanotube to form a one-dimensional gas.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used advanced transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods to capture the moment when Kr atoms joined together, one by one, inside a “nano test tube” container with diameter half a million times smaller than the width of a human hair. The research has been published in the journal of the American Chemical Society.
The behaviour of atoms has been studied by scientists ever since it was hypothesized that ...
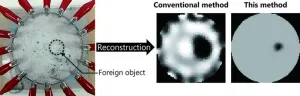
Hybrid machine learning method boosts resolution of electrical impedance tomography for structural imaging
2024-01-22
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-destructive imaging technique used to visualize the interior of materials. In this method, an electric current is injected between two electrodes, creating an electric field, and other electrodes measure distortions caused by the presence of foreign objects inside the material. Compared to other imaging methods, such as X-ray imaging, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, EIT has the advantages of being low cost and less cumbersome as it does not require large magnets or radiation. Therefore, it holds great potential as a non-destructive structural health monitoring ...
New study finds liquid laundry detergent packet exposure burden among young children remains; increase in exposures among older children, teens, and adults
2024-01-22
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – A new study conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of the Abigail Wexner Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and the Central Ohio Poison Center investigated trends in calls to poison centers across the country for exposures to liquid laundry detergent packets. The study investigators identified declines in the number, rate and severity of liquid laundry detergent packet exposures among children younger than 6 years. However, the exposure burden remained high. Additionally, exposures have increased among older children, teens and adults.
The study, published in Clinical Toxicology, found that in the most recent ...
[1] ... [1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
[1429]
1430
[1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.