EHR workload continues to grow for primary care physicians
2024-01-22
The study evaluated recent trends in primary care physicians’ (PCPs) electronic health record (EHR) workload. Prior to and early in the COVID-19 pandemic, PCPs spent more time in the EHR and received more messages than physicians in other specialties, but it is unclear if the pandemic further accelerated the growth of PCPs’ EHR workload. Researchers observed EHR usage of 141 academic PCPs practicing family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics within the University of Wisconsin-Madison health system, which cares for nearly 300,000 primary care patients per year. This longitudinal study compared the amount of time participating ...
Clear and open communication with care teams could improve the birthing experience for Black people
2024-01-22
This study explored the perspectives of Black birthing people on how better communication with care teams may have improved their birth experiences. Researchers interviewed 30 non-Hispanic Black, English-language–proficient, low-income birthing people in the Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, area, all of whom were insured by Medicaid. All gave birth to preterm infants before 34 weeks gestation, or before 36 weeks gestation to birthing people with a modifiable risk factor such as high blood pressure. The interviews uncovered three main themes regarding the quality of communication with their care teams and the effect on their experiences: ...
A simple three-question screening tool may help to identify precarious employment among primary care patients
2024-01-22
Precarious employment, defined by temporary contracts, unstable employment, or job insecurity, is increasingly common and is associated with inconsistent access to health insurance, lower incomes, and greater exposure to physical hazards and psychological stress. A team of researchers in Toronto, Canada, created and tested a new three-question screening tool to help primary care clinics identify these patients. The screener included the following three questions: 1) non-standard employment (Are you currently employed in a casual, short-term, or temporary position?); 2) violations of occupational health ...
Primary care physicians and urologists work together to provide optimal care for men with low-risk prostate cancer
2024-01-22
This study considers the perspectives of primary care physicians (PCPs) and urologists on what facilitates and what creates barriers to active surveillance (AS) care for men with low-risk prostate cancer. Researchers conducted in-depth, semi-structured interviews with 19 PCPs (9 female, 4 in community practices, 15 in academic medical centers) and 15 urologists (3 female, 5 in private practice, 3 in academic medical centers) between June 2020 and March 2021. Their goal was to assess interviewees’ knowledge of AS, what factors they felt influence adherence to follow-up ...
Patients who obtained telemedicine medication abortions (TeleMAB) through primary care have positive feelings about their experience
2024-01-22
This study explores patients’ experiences and perspectives on obtaining telemedicine medication abortions (TeleMAB) through their primary care health system. Researchers conducted in-depth phone interviews with 14 English, Spanish, and/or Portuguese-speaking patients, ranging in age from 26 to 42, who received a TeleMAB between July 2020 and December 2021 from a large primary care safety-net community health system in Massachusetts. Thirteen of the interviewees provided demographic information. All 13 identified as female, and 10 had children ...
An update on a 2015 report shows that gabapentinoid usage in the U.S. has continued to climb
2024-01-22
Gabapentinoids are commonly prescribed for an array of off-label conditions, including management of chronic pain. Updating their 2015 report on gabapentinoid usage in the U.S., researchers used the 2002–2021 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to investigate the proportion of the adult population using gabapentinoids, medications, and diagnoses associated with users, and the likelihood of starting, stopping, or continuing gabapentinoids. They found that gabapentinoid use has increased from 4.0% in 2015 to 4.7% in 2021. ...
The serious risks and high costs of monoclonal antibodies may outweigh the benefits for patients with Alzheimer dementia
2024-01-22
Researchers performed a meta-analysis of randomized trial studies that compared the use of amyloid-reducing monoclonal antibodies (MABs) in patients with Alzheimer dementia at a dose consistent with that used in Phase 3 or FDA approval trials with the use of a placebo. Their purpose was to evaluate clinically meaningful benefits and harms of MABs to these patients. For inclusion in this meta-analysis, the RCT studies had to include adult participants with cognitive impairment or Alzheimer disease of any severity and report at least one clinically relevant benefit or harm to participants after at least one year. The research team identified 19 such publications that evaluated ...
Annals of Family Medicine January/February 2024 Tip Sheet
2024-01-22
EHR Workload Continues to Grow for Primary Care Physicians
The study evaluated recent trends in primary care physicians’ (PCPs) electronic health record (EHR) workload. Prior to and early in the COVID-19 pandemic, PCPs spent more time in the EHR and received more messages than physicians in other specialties, but it is unclear if the pandemic further accelerated the growth of PCPs’ EHR workload. Researchers observed EHR usage of 141 academic PCPs practicing family medicine, internal medicine, and general pediatrics within the University of Wisconsin-Madison health system, which ...
A quality improvement intervention links high-risk prenatal patients at safety-net health centers with primary care
2024-01-22
Researchers assessed the development and implementation of a quality improvement learning collaborative’s (QILC) intervention to link high-risk prenatal patients with primary care. The aims of the study were twofold: to identify any quantitative impact of the intervention on postpartum and primary care utilization for high-risk prenatal patients and to explore the Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) participants’ experiences of working with a QI collaborative.
Using information from patients’ charts and/or ...
A new drug candidate can shrink kidney cysts
2024-01-22
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most common form of polycystic kidney disease, can lead to kidney enlargement and eventual loss of function. The disease affects more than 12 million people worldwide, and many patients end up needing dialysis or a kidney transplant by the time they reach their 60s.
Researchers at MIT and Yale University School of Medicine have now found that a compound originally developed as a potential cancer treatment holds promise for treating ADPKD. The drug works by exploiting kidney cyst cells’ vulnerability to oxidative stress — a state ...
Bone marrow adipocytes provide early sign of progression from MGUS to multiple myeloma
2024-01-22
A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 16, 2024, entitled, “Bone marrow adipocytes provide early sign for progression from MGUS to multiple myeloma.”
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematological malignancy and is characterized by clonal expansion of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow. In spite of recent advances in the field of MM, the disease has remained incurable. MM is preceded by a premalignant state known as monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), with a risk of progression to MM of 1% per year. Establishing a scalable approach that refines ...
Dr. Blagosklonny’s battle with cancer (Part 1)
2024-01-22
On January 3, 2024, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center published a new brief report in Oncoscience (Volume 11), entitled, “My battle with cancer. Part 1.”
“In January 2023, diagnosed with numerous metastases of lung cancer in my brain, I felt that I must accomplish a mission. If everything happens for a reason, my cancer, in particular, I must find out how metastatic cancer can be treated with curative intent. This is my mission now, and the reason I was ever born. In January 2023, I understood the meaning of life, of my life. I was born to write this article. In this article, I argue that monotherapy with ...
Don’t blame the sharks: Research led by UMass Amherst reveals why more hooked tarpon are being eaten
2024-01-22
In wave-making research recently published in Marine and Coastal Fisheries, a team of researchers, led by biologists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has quantified the rate at which great hammerhead sharks are eating Atlantic tarpon hooked by anglers at Bahia Honda, Florida—one of the prime tarpon fishing spots in the Florida Keys.
Called the “depredation rate,” the team found that 15.3% of tarpon that were hooked by anglers and fought for more than five minutes were eaten while still on the line. But the researchers also show that this is not necessarily a sign that the ecosystem is out of balance. To the contrary, increased reports ...
Shallow soda lakes show promise as cradles of life on Earth
2024-01-22
Charles Darwin proposed that life could have emerged in a “warm little pond” with the right cocktail of chemicals and energy. A study from the University of Washington, published this month in Communications Earth & Environment, reports that a shallow “soda lake” in western Canada shows promise for matching those requirements. The findings provide new support that life could have emerged from lakes on the early Earth, roughly 4 billion years ago.
Scientists have known that under ...
Computing with the power of light
2024-01-22
The exponential demand for high computing power is far exceeding the capabilities of current electronic systems; however, engineers at the University of Pittsburgh are shining a light on new solutions.
Nathan Youngblood, principal investigator and assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Pitt’s Swanson School of Engineering, received a $552,166 Faculty Early Career Development Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and a $449,240 award from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) through its Young Investigator Program (YIP) to continue his pioneering work in phase-change materials and optical computing.
“Dr. ...
Cholangiocarcinoma: New organ-on-chip aims at accelerating research and personalized medicine
2024-01-22
Milano, January 22nd 2024 – It is only a few centimeters in size and can be held between two fingers, but in the micro-channels carved inside it, it’s hidden a three-dimensional and highly faithful model of a biliary tract cancer called cholangiocarcinoma, complete with its tumor microenvironment. This 3D model is built starting from a sample of patient’s cancer cells and thus it represents a patient-specific "organ-on-chip": a technology made possible only through a multidisciplinary approach that merges biomedicine, physics and engineering.
The innovative prototype is the result ...
Bioengineered material developed to rapidly stop bleeding in patients on blood thinners
2024-01-22
More than 11 million people in the United States take anticoagulation or antiplatelet medications, such as heparin or aspirin, to treat serious conditions like heart attack and stroke. However, these medications also put patients at risk of life-threatening bleeding in the case of injury or during surgery. To improve strategies for reducing blood loss, a team led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, developed a porous material that maximizes blood absorption and effectively activates clotting mechanisms, even in patients on anticoagulation or ...
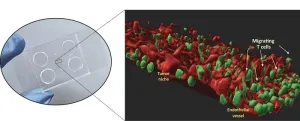
New biomarkers for active lupus nephritis discovered
2024-01-22
New biomarkers with improved diagnostic performance for early detection of lupus nephritis have been discovered in the University of Houston lab of Chandra Mohan, a pioneer in lupus research. Early identification of renal involvement in lupus and prompt treatment are essential in reducing the pain, suffering and eventual mortality it causes.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), commonly called lupus, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body attacks its own tissues and organs. Inflammation from the disease can impact many different parts of the body including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain and heart. Lupus nephritis is one ...
New research examines how assumptions affect motion capture technology
2024-01-22
Motion capture technology has applications in a wide range of fields, including entertainment, medicine, and sports, to name a few. But what if the measurements these systems were based on were rooted in social practices and biased assumptions, leading to errors that become ingrained over time?
This question is at the heart of new research co-authored by Mona Sloane, an assistant professor of data science and media studies at the University of Virginia.
Sloane and her co-authors — Abigal Jacobs, an assistant ...
Scientists identify mutations that cause inherited kidney disease
2024-01-22
Genetic changes or mutations can cause hereditary kidney disease, which can eventually lead to dialysis or the need for kidney transplantation. Identifying the cause of inherited kidney disease is the first step in identifying a treatment.
With that goal in mind, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the First Faculty of Medicine of Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic, have discovered a new genetic cause of inherited kidney disease.
The findings were recently published in Kidney International.
According to Anthony J. Bleyer, M.D., ...
How the brain responds to reward is linked to socioeconomic background
2024-01-22
MIT neuroscientists have found that the brain’s sensitivity to rewarding experiences — a critical factor in motivation and attention — can be shaped by socioeconomic conditions.
In a study of 12 to 14-year-olds whose socioeconomic status (SES) varied widely, the researchers found that children from lower SES backgrounds showed less sensitivity to reward than those from more affluent backgrounds.
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the research team measured brain activity as the children played a guessing game in which they earned extra money for each correct ...
New reagent improves the process of making sulfur-containing compounds that may be used in medicines
2024-01-22
During the past decade, there has been significant development of new sulfur containing compounds that are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and agricultural products. Sulfoximines, sulfonimidoyl fluorides and sulfonimidamides are types of sulfur-containing chemical compounds that have wide-ranging potential as therapeutic drugs. However, the synthesis process for these compounds is complex and has several limitations. In a new article published in Nature Chemistry, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers describe their ...
New candidate for universal memory is fast, low-power, stable and long-lasting
2024-01-22
We are tasking our computers with processing ever-increasing amounts of data to speed up drug discovery, improve weather and climate predictions, train artificial intelligence, and much more. To keep up with this demand, we need faster, more energy-efficient computer memory than ever before.
Researchers at Stanford have demonstrated that a new material may make phase-change memory—which relies on switching between high and low resistance states to create the ones and zeroes of computer data—an improved option for future AI and data-centric systems. ...
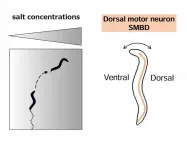
Follow the salt: connecting salt concentrations and motion in roundworms
2024-01-22
Joint research led by Ayaka Matsumoto and Yuichi Iino of the University of Tokyo demonstrated that temporal decrease in salt concentration leads to the activation of the neck motor neuron of roundworms only in a specific phase of its activity. The activation adjusts the roundworm's trajectory toward higher salt concentrations. The finding pinpoints the neural mechanism by which roundworms integrate sensory and motor information, a first step toward understanding the neural mechanisms of navigation in more complex animals. The findings were published in the journal Proceedings ...
Planetary Commons: Fostering global cooperation to safeguard critical Earth system functions
2024-01-22
“Stability and wealth of nations and our civilisation depends on the stability of critical Earth system functions that operate beyond national borders. At the same time, human activities push harder and harder on the planetary boundaries of these pivotal systems. From the Amazon rainforest to the Greenland ice masses, there are rising risks of triggering irreversible and unmanageable shifts in Earth system functioning. As these shifts affect people across the globe, we argue that tipping elements should be ...
[1] ... [1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
1429
[1430]
[1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.