Childhood vitamin D deficiency was likely prevalent during industrialization in England
2024-01-31
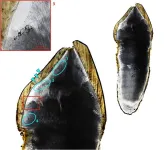
Evidence from teeth reveals that vitamin D deficiency during childhood was likely a major issue in industrialized England, according to a study published January 31, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anne Marie Snoddy of the University of Otago, New Zealand and colleagues.
The 18th and 19th centuries AD were a period of industrialization and urbanization in England. This was also a time of increasing incidence of health issues like vitamin D deficiency (VDD) and associated conditions like rickets, potentially linked to changing social practices ...
Archaeological evidence of seasonal vitamin D deficiency discovered
2024-01-31
Rickets ran rife in children following the Industrial Revolution, but University of Otago-led research has found factory work and polluted cities aren’t entirely to blame for the period’s vitamin D deficiencies.
In a Marsden funded study, just published in PLOS One, researchers from Otago, Durham University, University of Edinburgh, University of Brighton, and University of Queensland, sampled teeth from a cemetery site in industrial era England, looking for microscopic markers of nutritional disease.
Lead author Dr Annie Sohler-Snoddy, Research ...
Jennifer J. Raab named President and CEO of The New York Stem Cell Foundation
2024-01-31
NEW YORK, NY (January 31, 2024) – The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) announced today that, following a nationwide search, its Board of Directors has named Hunter College President Emerita Jennifer J. Raab as its next President and Chief Executive Officer, effective this month.
NYSCF is one of the world’s leading nonprofit stem cell organizations, raising and investing more than $450 million since its founding in 2005 to accelerate cures for the major diseases of our time through stem cell research. The foundation conducts its own pioneering research at the NYSCF Research Institute laboratories in Manhattan, informs and convenes scientists and ...
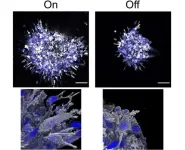
A new way to visualize brain cancer
2024-01-31
Brigham and MIT researchers uncovered never-before-seen details in human brain tissue with new, inexpensive microscopy technology.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Researchers have developed a new microscopy technology called decrowding expansion pathology (dExPath) to analyze brain tissue.
By pulling proteins apart with dExPath, researchers can stain proteins in tissue that could not be accessed before, highlighting nanometer sized structures or even cell populations that were previously hidden.
This “super-resolution imaging” technology ...
AI can predict brain cancer patients’ survival
2024-01-31
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can predict whether adult patients with brain cancer will survive more than eight months after receiving radiotherapy treatment.
The use of the AI to successfully predict patient outcomes would allow clinicians to be better informed for planning the next stage of treatment and refer patients to potentially life-saving treatment quicker.
This is the first use of AI to predict short-term and long-term survivors within eight-months of radiotherapy.
The paper published recently in Neuro-Oncology shows how researchers ...
Fermentation revolution? Trash becomes treasure as bio-waste yields valuable acetone and isopropanol
2024-01-31
In a major stride towards sustainable industrial fermentation, a team of researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in The Netherlands, has unveiled pioneering advancements in the purification of isopropanol and acetone from the fermentation of waste gases. The study, published in SCI's Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, introduces novel processes that promise to elevate the efficiency and viability of large-scale production.
Isopropanol and acetone have a combined global market of $10 billion. Both chemicals are important industry solvents and isopropanol ...
The hottest catalog of the year: the most comprehensive list of slow-building solar flares yet
2024-01-31
Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the Sun’s atmosphere and is released as electromagnetic radiation. Lasting anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours, flares usually reach temperatures around 10 million degrees Kelvin. Because of their intense electromagnetic energy, solar flares can cause disruptions in radio communications, Earth-orbiting satellites and even result in blackouts.
Although flares have been classified based on the amount of energy they emit at their peak, there has not been significant study into differentiating ...
Researchers uncover potential non-opioid treatment for chronic pain
2024-01-31
Among the most difficult types of pain to alleviate is neuropathic pain, pain that is usually caused by damage to nerves in various body tissues, including skin, muscle and joints. It can cause patients to suffer feelings like electric shocks, tingling, burning or stabbing. Diabetes, multiple sclerosis, chemotherapy drugs, injuries and amputations have all been associated with neuropathic pain, which is often chronic, sometimes unrelenting and affects millions of people worldwide. Many of the available pain medications are only moderately effective at treating this type of pain and often come with serious ...
John Theurer Cancer Center (JTCC) physician co-authors clinical research on innovative oral leukemia therapy
2024-01-31
Researchers at Hackensack Meridian’s John Theurer Cancer Center (JTCC), are part of a published Phase 3 study reporting on the equivalent safety and effectiveness in the oral treatment of blood cancers–such as myelodysplastic syndrome and/or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia–to its previously inpatient, intravenous treatment counterparts.
John Theurer Cancer Center is part of the NCI-designated Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center at Georgetown University.
Dr. James K. McCloskey, M.D., led JTCC’s ...
UC Irvine scientists make breakthrough in quantum materials research
2024-01-31
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 31, 2024 — Researchers at the University of California, Irvine and Los Alamos National Laboratory, publishing in the latest issue of Nature Communications, describe the discovery of a new method that transforms everyday materials like glass into materials scientists can use to make quantum computers.
“The materials we made are substances that exhibit unique electrical or quantum properties because of their specific atomic shapes or structures,” said Luis A. Jauregui, professor of physics & astronomy ...
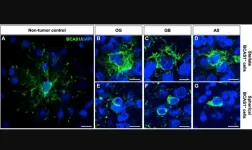
BCAS1 defines a heterogeneous cell population in diffuse glioma patients
2024-01-31
“[...] this is the first study describing a BCAS1+ cell population in a large cohort of diffuse glioma patients.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 31, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 24, 2024, entitled, “BCAS1 defines a heterogeneous cell population in diffuse gliomas.”
Oligodendrocyte precursor markers have become of great interest to identify new diagnostic and therapeutic targets for diffuse gliomas, since state-of-the-art studies point towards immature oligodendrocytes as a possible source of gliomagenesis. Brain enriched myelin associated ...
Microgreens made to order: Italian scientists have tailored iodine and potassium content of radishes, peas, rocket and chard
2024-01-31
In a significant development for personalised nutrition, researchers in Italy have cultivated microgreens with bespoke nutritional profiles to serve individual dietary requirements.
The study, published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture (doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13222), provides a blueprint for the soilless cultivation of nutritionally enriched plants in a commercial greenhouse setting.
Co-authors Massimiliano D’Imperio and Francesco Serio, both at the Institute of Sciences of Food Production (ISPA) National Council ...
How to make bright quantum dots even brighter
2024-01-31
Quantum dots are a kind of artificial atom: just a few nanometres in size and made of semiconductor materials, they can emit light of a specific colour or even single photons, which is important for quantum technologies. The discoverers and pioneers of the commercial production of quantum dots were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2023. In recent years, quantum dots made of perovskites have attracted particular attention. Perovskites belong to a class of materials that have a similar structure to the mineral perovskite ...
Method combines artificial intelligence and satellite imagery to map crop-livestock integration systems
2024-01-31
Crop-livestock integration (CLI) systems combine the growing of crops in rotation or consortium, especially grain crops such as soybeans, corn and sorghum, and forage plants used to feed cattle and pigs, with the raising of livestock, typically beef cattle. The crops provide most of the cash income, while the livestock has food available during the dry season and facilitates seed management. CLI improves soil fertility, raises yields and helps rehabilitate degraded areas while reducing the use of pesticides, mitigating the risk of erosion and the seasonality of production, and lowering ...
Pedestrian injuries from falls versus motor vehicle collisions: are we lacking critical policy and interventions?
2024-01-31
January 31, 2024—Using Emergency Medical Services (EMS) data, researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health compared the national burden of pedestrian injuries from motor vehicles to that of pedestrian falls occurring on streets and sidewalks and found that the probability of a pedestrian suffering a severe injury is higher for motor vehicle collisions as compared to falls. Yet, the public health burden of the number of pedestrians injured from a fall – severe or otherwise - is significantly higher compared to the number of pedestrians injured by a motor ...
Treatment of aggressive breast cancer: discovery of a new protein involved in the development of metastases
2024-01-31
A protein found abundantly in breast cancers that are refractory to conventional treatments is thought to cause the development of metastasis. Targeting it would prevent metastatic spread and therefore increase patients survival. These are the findings of a study conducted by a French-American team and led by a biologist at CNRS1. The study, the results of which appear on 31st January in Cell Discovery, aims to better understand the mechanisms at play in the development of primary tumours in aggressive ...
Worldwide prevalence and disability from mental disorders across childhood and adolescence
2024-01-31
About The Study: In this analysis using data from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease study, there was a high prevalence of mental disorders affecting children and youths, indicating that more than 1 of 10 (or 293 million) individuals ages 5 to 24 globally live with a diagnosable mental disorder. In terms of burden, around one-fifth of all disease-related disability (considering all causes) was attributable to mental disorders among this population. Additionally, this age period encompasses about one-fourth of the mental disorder burden across the entire life course.
Authors: Christian Kieling, M.D., Ph.D., of the Universidade ...
1 of 10 veterans diagnosed with dementia may instead have cognitive decline from cirrhosis
2024-01-31
RICHMOND, Va. (Jan. 31, 2024) – As many as 10% of older U.S. veterans diagnosed with dementia may suffer instead from reversible cognitive decline caused by advanced liver disease, according to an analysis from the Virginia Commonwealth University’s School of Medicine and the Richmond VA Medical Center.
It can be difficult for physicians to differentiate dementia from the cognitive decline caused by cirrhosis, called hepatic encephalopathy. If undetected, patients may not receive appropriate treatment that can reverse or halt the impairment. ...
Leisure-time physical activity and falls with and without injuries among older women
2024-01-31
About The Study: Participation in leisure-time physical activity at the recommended level or above was associated with lower odds of both non-injurious and injurious falls in this study of 7,100 older women. Brisk walking and both moderate and moderate-vigorous leisure-time physical activity were associated with lower odds of non-injurious falls.
Authors: Wing S. Kwok, B.App.Sc., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Oxford scientists launch ambitious roadmap for circular carbon plastics economy
2024-01-31
Researchers from the Oxford Martin Programme on the Future of Plastics, University of Oxford, have outlined ambitious targets to help deliver a sustainable and net zero plastic economy. In a paper published in Nature, the authors argue for a rethinking of the technical, economic, and policy paradigms that have entrenched the status-quo, one of rising carbon emissions and uncontrolled pollution.
Currently the global plastics system results in over 1 gigatonnes per annum (Gt/annum) of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions which is the same as the total combined emissions ...
Molecule can quickly, and briefly, boost white blood cell counts
2024-01-31
New Haven, Conn. — Treatment with a molecule known as A485 can quickly and temporarily increase levels of white blood cells, a critical part of the body’s immune system, an effect that is difficult to deliver with currently available pharmaceuticals, a new Yale study finds.
In an experiment, the researchers found that exposure to the molecule in mice caused white blood cells to mobilize from the bone marrow, a response that could inform future treatment for patients who need a boost in immune activity, the researchers say.
The findings were reported Jan. 31 in the journal ...
When and how immune cells decide to form pathogen memories
2024-01-31
Unexpected findings have emerged about how and when certain infection-killing white blood cells decide to form memories about their encounters with a pathogen.
It has been known for decades that these cells can turn themselves into durable memory cells that can survive a long time after an initial infection is cleared. They are prepared to quickly recognize and eliminate future intrusions by the same kind of pathogen.
That is one reason people are resistant to some infectious diseases after exposure to or recovery from the illness. Vaccinations also work this ...
Whole blood transfusion improves survival during traumatic bleeding
2024-01-31
(Boston)—Significant bleeding due to traumatic injury is the number one cause of preventable deaths in the U.S., with the majority of deaths occurring within six hours. Emerging evidence suggests that the transfusion of whole blood (blood that is not separated into parts) is associated with a survival benefit compared to the traditional use of blood component transfusion (red blood cells, plasma, and platelets) in these patients.
A new study from researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of ...
Combination drug therapy shows promise for a treatment-resistant cancer
2024-01-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
A combination of two cancer drugs could be effective against malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs) — soft tissue tumors that are stubbornly resistant to chemotherapy and radiation — according to a laboratory study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
Both drugs interfere with cell growth and replication but have different mechanisms of action. Used together, they suppressed the growth of MPNSTs in mouse models of human disease, the researchers found. The findings were published ...
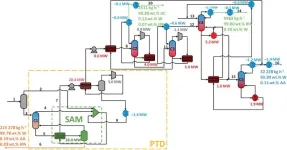
Decarbonizing the world’s industries
2024-01-31
Harmful emissions from the industrial sector could be reduced by up to 85% across the world, according to new research.
The sector, which includes iron and steel, chemicals, cement, and food and drink, emits around a quarter of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions - planet-warming gases that result in climate change and extreme weather.
This new study, led by the University of Leeds as part of its contribution to the UK Energy Research Centre (UKERC), found that decarbonising the sector is technically possible with a mix of “high and low-maturity” technologies - those that are tried and tested, along with upcoming tech that is not yet ready to be used in industry.
Lead ...
[1] ... [1413]
[1414]
[1415]
[1416]
[1417]
[1418]
[1419]
[1420]
1421
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
[1429]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.