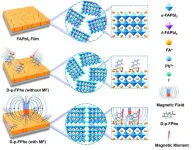
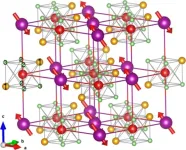
Highly oriented perovskite films induced by chiral molecules under magnetic-field control
2024-01-26
In the realm of clean energy, metal halide perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have emerged as a groundbreaking focus, capturing significant attention for their extraordinary advancements. In just over a decade, their certified power conversion efficiency (PCE) has skyrocketed to 26.1%, approaching the upper limits seen in traditional crystalline silicon cells. What sets PSCs apart is their potential to surpass the 30% PCE threshold [1].
The key to optimizing solar devices lies in the deposition of high-quality perovskite films. Achieving minimal defect density and exceptional homogeneity becomes crucial for enhancing device performance. One commonly employed strategy involves introducing ...
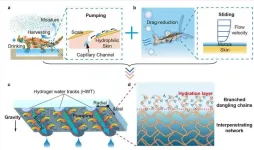
Bioinspired hydrogel pattern enhancing atmospheric water harvesting via directional droplet steering
2024-01-26
This study, led by Prof. Jiuhui Qu, Dr. Qinghua Ji, and Dr. Wei Zhang from Tsinghua University, focuses on addressing water scarcity by exploring atmospheric water harvesting. The water in the air originates from both natural and forced evaporation, with condensation being the final and crucial step in water harvesting. Condensation involves nucleation, growth, and shedding of water droplets, which are then collected. However, uncontrollable growth of condensed droplets leading to surface flooding is a pressing challenge due to insufficient driving forces, posing a threat to sustainable condensation.
To expedite this process and achieve orderly ...
App enhances nurses' care coordination competency for critically ill patients
2024-01-26
To improve the care coordination competency of nurses involved in the management of critically ill patients on life support, an electronic app—NCCCS—was developed by Associate Professor Chie Takiguchi of Toho University and Professor Tomoko Inoue of International University of Health and Welfare.
The NCCCS app utilizes the scoring system referred to as the Nurses' Care Coordinate Competency Scale (NCCCS), developed by Dr. Takiguchi et al. in 2017, and it is currently being translated into Chinese, Italian, Polish, and Persian. This app offers immediate feedback to nurses caring for critically ill patients on life ...
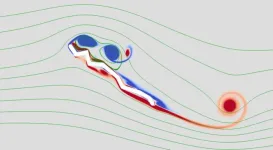
Dragonfly wings used to study relationship between corrugated wing structure and vortex motions
2024-01-26
Scientists from Hiroshima University undertook a study of dragonfly wings in order to better understand the relationship between a corrugated wing structure and vortex motions. They discovered that corrugated wings exhibit larger lift than flat wings.
Their work was published in the journal Physical Review Fluids on December 7, 2023.
The researchers set out to determine if the corrugation of a dragonfly's wing is a secret ingredient for boosting lift. While past research has largely zoomed in ...
Peach-palm waste and Trichoderma stromaticum: The potential of Cost-effective amylase production
2024-01-26
Amylases are among the most important biotechnological and industrial enzymes that can be applied in various sectors, such as food, pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, paper, and detergents.
The enzymes’ costs come from a range of factors including the quantity produced, the production process, the expense of its recovery, and the degree of purity at which it will be marketed, etc. The use of agro-industrial substrates and microorganisms brings the potential to low-cost enzyme production. Meanwhile, due to the ability to improve physical and chemical resistance to industrial environmental extremes, such as high temperature and pH, as well ...
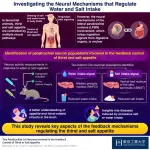
Decoding how the brain manages the appetite for salt and water
2024-01-26
Staying hydrated and consuming appropriate amounts of salt is essential for the survival of terrestrial animals, including humans. The human brain has several regions constituting neural circuits that regulate thirst and salt appetite, in intriguing ways.
Previous studies suggested that water or salt ingestion quickly suppresses thirst and salt appetite before the digestive system absorbs the ingested substances, indicating the presence of sensing and feedback mechanisms in digestive organs that help real-time thirst and salt appetite modulation in response to drinking ...
Immunocompromised patients and COVID infections: Who’s at risk?
2024-01-26
Early in the pandemic, clinicians noticed that certain immunocompromised patients were experiencing persistent SARS-CoV-2 infections, some lasting weeks to months at a time.
This raised concerns that one of these cases could be the source of an emerging viral variant that has benefited from an extended battle with the immune system.
A prospective study published in the journal Lancet Microbe provides more clarity on which patient populations are at higher risk for prolonged infections —and hints that this fear is likely unwarranted.
The ...
New tool improves the search for genes that cause diseases
2024-01-26
A new statistical tool developed by researchers at the University of Chicago improves the ability to find genetic variants that cause disease. The tool, described in a new paper published January 26, 2024, in Nature Genetics, combines data from genome wide association studies (GWAS) and predictions of genetic expression to limit the number of false positives and more accurately identify causal genes and variants for a disease.
GWAS is a commonly used approach to try to identify genes associated with a range of human traits, including most common diseases. Researchers compare genome sequences ...
Glacier melting destroys important climate data archive
2024-01-26
As part of the Ice Memory initiative, PSI researchers, with colleagues from the University of Fribourg and Ca’ Foscari University of Venice as well as the Institute of Polar Sciences of the Italian National Research Council (CNR), analysed ice cores drilled in 2018 and 2020 from the Corbassière glacier at Grand Combin in the canton of Valais. A comparison of the two sets of ice cores published in Nature Geoscience shows: Global warming has made at least this glacier unusable as a climate archive.
Reliable information about the past climate and air pollution can no longer be obtained from ...
Soap bark discovery offers a sustainability booster for the global vaccine market
2024-01-26
A valuable molecule sourced from the soapbark tree and used as a key ingredient in vaccines, has been replicated in an alternative plant host for the first time, opening unprecedented opportunities for the vaccine industry.
A research collaboration led by the John Innes Centre used the recently published genome sequence of the Chilean soapbark tree (Quillaja saponaria) to track down and map the elusive genes and enzymes in the complicated sequence of steps needed to produce the molecule QS-21.
Using transient expression techniques developed at the John Innes Centre, the team reconstituted the ...
Writing by hand may increase brain connectivity more than typing on a keyboard
2024-01-26
As digital devices progressively replace pen and paper, taking notes by hand is becoming increasingly uncommon in schools and universities. Using a keyboard is recommended because it’s often faster than writing by hand. However, the latter has been found to improve spelling accuracy and memory recall.
To find out if the process of forming letters by hand resulted in greater brain connectivity, researchers in Norway now investigated the underlying neural networks involved in both modes of writing.
“We ...
Computers are quick and reliable in counting seals
2024-01-26
Computers can count seals from aerial photographs with lightning speed and reliability. Based on their spatial patterns, the tiny dots on the aerial images can even be assigned to one of the two major species of seals in the Wadden Sea. That is shown in the thesis that marine biologist Jeroen Hoekendijk will defend on January 26 in Wageningen. "To better understand if and how marine mammals like seals are affected by climate change and the disappearance of sea ice, this help from artificial intelligence (AI) in observations is crucial," Hoekendijk said. Hoekendijk carried out his research at the Royal Netherlands Institute ...
Estuarine Management and Technologies: A brand new journal streamlines innovation in the conservation of estuarine ecosystems
2024-01-26
Where freshwater rivers meet seas and oceans lies a scientifically intriguing and ecologically important type of ecosystem. As estuarine ecosystems provide various and diverse services to humanity and the planet at large, including food security and natural buffers and filters in the events of storms and water pollution, there has been an increasing need to facilitate and support the exchange of research findings and ideas related to their conservation and sustainable management by means of new-age technology and novel approaches.
This is how a team of renowned and passionate ...
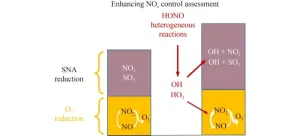
The missing link: Recent study explores the connection between NOx control and SNA, O3 reduction
2024-01-26
Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium (SNA) and other atmospheric aerosols play a significant role in influencing both atmospheric and environmental conditions. These aerosols impact climate directly through scattering and absorbing solar radiation, thus influencing the Earth's radiative balance. The presence of high concentrations of aerosols can lead to the formation of haze and reduce air quality, affecting human health and transportation. Furthermore, the fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) within aerosols poses health risks ...
Cultural encounters of landscape architects Xiaoxiang Sun and Lawrence Halprin
2024-01-26
“From nature to nature” is the major goal of landscape design. The former is the idea of nature, i.e., landscape architects regard nature as the archetype of design; the latter is the experience of nature, i.e., landscape architects hope people can perceive the natural atmosphere through designed landscape. In this sense, the transformation from idea to experience of nature refers to the process of landscape design, which materializes landscape. According to this, this article focuses on the following topics: 1) what role does nature play as the origin of the landscape design theory; 2) how does nature as an idea promote ...
First demonstration of predictive control of fusion plasma by digital twin
2024-01-26
Fusion energy is being developed as a solution to global energy problems. In particular, the magnetic confinement method, in which ultra-high temperature plasma is confined by a magnetic field, is the most advanced and is considered to be the most promising method for fusion reactors. By this method, the plasma is confined in the reactor in a high-temperature, high-density state by a magnetic field, and the energy released by the fusion reaction in the plasma is converted into electricity. To realize this power generation method, it is essential to predict and control the complex behavior of fusion plasma. One possible control method is digital twin control, in which the fusion plasma ...
Single dose typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV) provides lasting efficacy in children
2024-01-26
A single dose of the typhoid conjugate vaccine, Typbar TCV®, provides lasting efficacy in preventing typhoid fever in children ages 9 months to 12 years old, according to a new study conducted by researchers at University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) and led by in-country partners at the Malawi-Liverpool Wellcome Trust (MLW) Clinical Research Programme.
Results from the phase 3 clinical study were published today in The Lancet.
The ...
'Old smokers' and 'squalling newborns' among hidden stars spotted for first time
2024-01-26
'Hidden' stars including a new type of elderly giant nicknamed an 'old smoker' have been spotted for the first time by astronomers.
The mystery objects exist at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy and can sit quietly for decades – fading almost to invisibility – before suddenly puffing out clouds of smoke, according to a new study published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
An international team of scientists led by Professor Philip Lucas, of the University of Hertfordshire, made their ground-breaking discovery after monitoring almost a billion stars in infrared light during a 10-year survey ...
In search of muons: Why they switch sites in antiferromagnetic oxides
2024-01-26
Muon spectroscopy is an important experimental technique that scientists use to study the magnetic properties of materials. It is based on “implanting” a spin-polarized muon in the crystal and measuring how its behavior is affected by the surroundings. The technique relies on the idea that the muon will occupy a well-identified site that is mainly determined by electrostatic forces, and that can be found by calculating the material’s electronic structure.
But a new study led by scientists in Italy, Switzerland, UK and Germany has found that, at least for some materials, that is not the end of the story: the muon site ...
Locked-in syndrome is predominant outcome when children survive drowning, larger study confirms
2024-01-26
SAN ANTONIO, Jan. 25, 2024 — It is a far cry from the traditionally thought-of “vegetative state” in which the mind is absent while the body lives on. Indeed, it is the opposite. Children with “locked-in syndrome,” unable to move or speak, are awake and fully aware of their surroundings.
Researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) were the first to report in peer-reviewed medical literature that, after non-fatal drownings, children would be locked in. The team, directed by Peter T. Fox, MD, professor of radiology and neurology and director of UT ...
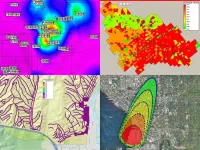
Achieving sustainable urban growth on a global scale
2024-01-25
From the impacts on the environment and climate to transforming land cover and habitats, urban growth is driving global change. Urban areas contribute up to 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions. By 2050, urban areas globally will either double or triple, and the raw materials needed to build future cities is more than the world can sustainably provide.
Yet, the impacts of cities on Earth systems are not factored into policy and planning among international agencies and that needs to change, says Karen Seto, Frederick ...
Illinois Tech professor Chun Liu honored as 2024 Fellow by American Mathematical Society
2024-01-25
CHICAGO—January 25, 2024—Illinois Institute of Technology (Illinois Tech) Professor Chun Liu has been elected a 2024 fellow of the American Mathematical Society (AMS)—one of just 40 mathematical scientists to be honored this year for his contribution to mathematics.
“It’s nice to be recognized by my colleagues, but this also gives visibility for the whole department and Illinois Tech,” says Liu, chair of the Department of Applied Mathematics. “It’s great recognition for the mathematics research that’s going on here at Illinois Tech.”
Liu’s research includes partial differential ...
Chats with AI shift attitudes on climate change, Black Lives Matter
2024-01-25
MADISON — People who were more skeptical of human-caused climate change or the Black Lives Matter movement who took part in conversation with a popular AI chatbot were disappointed with the experience but left the conversation more supportive of the scientific consensus on climate change or BLM. This is according to researchers studying how these chatbots handle interactions from people with different cultural backgrounds.
Savvy humans can adjust to their conversation partners’ political leanings and cultural expectations to make sure they’re understood, but more and more often, humans find themselves in ...
PNNL Software Technology wins FLC Award
2024-01-25
RICHLAND, Wash.—Visual Sample Plan (VSP), a free software tool developed at the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) that boosts statistics-based planning, has been recognized with a 2024 Federal Laboratory Consortium (FLC) Award.
The FLC represents over 300 federal laboratories, agencies, and research centers. The annual FLC awards program recognizes agencies for their contributions to technology transfer, which turns innovative research into impactful products and services.
Judges bestowed ...
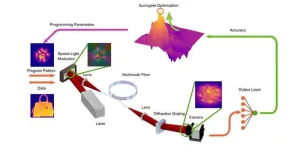
Programming light propagation creates highly efficient neural networks
2024-01-25
Current artificial intelligence models utilize billions of trainable parameters to achieve challenging tasks. However, this large number of parameters comes with a hefty cost. Training and deploying these huge models require immense memory space and computing capability that can only be provided by hangar-sized data centers in processes that consume energy equivalent to the electricity needs of midsized cities. The research community is presently making efforts to rethink both the related computing hardware and the machine learning algorithms to sustainably keep the development of artificial intelligence at its current pace.
Optical implementation ...
[1] ... [1410]
[1411]
[1412]
[1413]
[1414]
[1415]
[1416]
[1417]
1418
[1419]
[1420]
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.