Diabetes and liver cancer — Stanford Medicine study suggests new screening guidelines
2024-02-01
For centuries, doctors have used their hands as essential diagnostic tools — exploring joints and palpating abdomens to assess a patient’s health. Often a cancer will reveal itself as a lump or unusual stiffness in a normally bouncy tissue or organ.
More recently, the relationship between stiffness and cancer has been documented through biophysical studies and clinical trials, particularly in liver and breast cancer. For example, stiffness is a primary hallmark of liver cirrhosis, which can progress to liver cancer.
Now researchers ...
Researchers take new ‘mixed reality’ headsets for a spin
2024-02-01
Among the buzziest consumer technologies right now are “mixed reality” or “spatial computing” headsets that convincingly blend views of the real world with digital content.
A key enabling technology behind these gizmos is passthrough video, which involves blocking out all light so users must rely on cameras on the headsets to see the external world around them via real-time video playing on tiny screens. The arrangement allows users to physically interact with their environments and go about daily activities but with added digital content displayed, ranging from familiar device apps to innovative gaming scenarios. ...
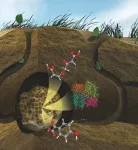
How leafcutter ants cultivate a fungal garden to degrade plants and provide insights into future biofuels
2024-02-01
By Maegan Murray
Scientists have spent decades finding ways to efficiently and affordably degrade plant materials so that they can be converted into useful bioproducts that benefit everyday life.
Bio-based fuels, detergents, nutritional supplements, and even plastics are the result of this work. And while scientists have found ways to degrade plants to the extent needed to produce a range of products, certain polymers such as lignin, which is a primary ingredient in the cell wall of plants, remain incredibly difficult to affordably break down without adding pollutants back into the environment. These polymers can be left behind as waste products with ...
UC Davis establishes bird flight research center
2024-02-01
Researching how bird flight can inform aircraft design is the goal of a new center to be established at the University of California, Davis.
Christina Harvey, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at UC Davis, and Michelle Hawkins, a professor in the School of Veterinary Medicine and director of the California Raptor Center, are launching the bird flight research center with a nearly $3 million grant from the Department of Defense. The new center will utilize motion capture and photogrammetry ...
ADA releases updated recommendations to enhance radiography safety in dentistry
2024-02-01
CHICAGO, Feb. 1, 2024 – The use of lead abdominal aprons or thyroid collars on patients when conducting dental X-rays is no longer recommended, according to an expert panel established by the American Dental Association (ADA) Council on Scientific Affairs. Additionally, dentists should take into consideration the diagnostic information needed from X-rays to benefit patient care or substantially improve clinical outcomes.
The Journal of the American Dental Association published the new recommendations today, which aim to improve radiation ...
Cheating death: How cancer cells escape
2024-02-01
Cell death is fundamental to life and, thus, healthy aging. In the realm of cellular biology, ferroptosis (a form of programmed cell death) has emerged not only as a focal point of research for its potential in eliminating cancer cells, but also its role in a plethora of other diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, eye diseases such as Retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, as well as ischemia, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, acute kidney injury and inflammation.
While studies of other forms of cell death such as apoptosis focus largely on ...
JMIR Medical Informatics invites submissions on AI language models in health care
2024-02-01
JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new section titled, “AI Language Models in Health Care” in JMIR Medical Informatics. This leading peer-reviewed journal is indexed in PubMed and has a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes. This section will have a broad focus and encompass topics about the successful implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) language models in diverse health care settings. The topics will include details about the process, use, outcomes, and ...
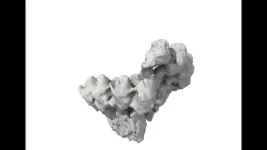
Human cells building ‘molecular highways’ captured for first time
2024-02-01
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona and the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) in Madrid have captured the world’s first high-resolution images of the earliest moments of microtubule formation inside human cells. The findings, published today in the journal Science, lay the foundations for potential breakthroughs in treating many different types of diseases ranging from cancer to neurodevelopmental disorders.
“Microtubules are critical components of cells, but all the images we see in textbooks describing the first moments of their creation are models or cartoons based ...
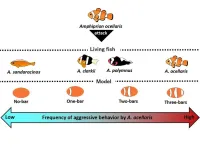
Clown anemonefish seem to be counting bars and laying down the law
2024-02-01
We often think of fish as carefree swimmers in the ocean, reacting to the world around them without much forethought. However, new research from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) suggests that our marine cousins may be more cognizant than we credit them for.
By observing how a colony of clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris) – the species of the titular character in Finding Nemo – reacts to intruders in their sea anemone home, OIST researchers have found that ...
New research shows that the arrangement of bacteria in biofilms affects their sensitivity to antibiotics
2024-02-01
Bacteria are traditionally imagined as single-cell organisms, spread out sparsely over surfaces or suspended in liquids, but in many environments the true bacterial mode of growth is in sticky clusters called biofilms. Biofilm formation can be useful to humans—it is integral, for example, to the production of kombucha tea. But it is more often problematic, because it makes it more difficult to control bacterial growth: When bacterial cells produce a biofilm, it acts as a shield against outside invaders, making the bacteria more ...
First atomic-scale 'movie' of microtubules under construction, a key process for cell division
2024-02-01
· Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) , the Spanish National Cancer Research Center (CNIO) and the IBMB-CSIC solve a key problem in biology: how human cells build their microtubules
· During cell division, microtubules function as nanometer-thick long ‘ropes' inside cells that pull chromosomes apart so that each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material
· The work published in Science lays the groundwork for future breakthroughs in the treatment of diseases ranging from cancer to neurodevelopmental disorders
Cells in the human body are constantly dividing. With each division the genetic information contained in the ...
Mapping the structure and organization of hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain
2024-02-01
Single-cell projectome analysis has revealed previously unknown spatial organization principles of the brain-wide structure and connectivity of more than 10,000 individual hippocampal neurons in the mouse brain, according to a new study. Specialized projections called axons allow neurons to transmit signals to other neurons across the brain. The hippocampus (HIP) – one of the most extensively studied brain regions – plays a crucial role in many crucial brain functions, including learning, memory, ...
Large herbivores’ effects on ecosystems depend more on size and diet than on herbivore origin
2024-02-01
The effect of large herbivores on plant abundance and diversity depends more on their size and diet than whether they are native or introduced into their host ecosystems, according to a meta-analysis of more than 200 studies worldwide. The findings counter the widely held notion that the impacts of introduced megafauna are distinct and more harmful than those of native megafauna and suggest that trait-based ecology provides better insight into megaherbivore-plant interactions than concepts of species origin. Large mammal herbivores play a key role in shaping ecosystems and biodiversity by consuming vegetation, dispersing seeds and nutrients, and creating ...
The evolution of sign languages globally revealed through computational analyses
2024-02-01
A computational analysis has highlighted the poorly understood relationships and elusive histories of modern sign languages worldwide, revealing two major sign language families shaped by geopolitical forces and relevant signing communities. The findings show that the computational methods applied – which have been useful in understanding spoken languages – can be extended to the study of sign languages; as such, they offer promise for addressing the disparities in our understanding of other marginalized and diverse ...
AI system reveals new insights into early language acquisition through the experience of a single child
2024-02-01
A new machine learning model – trained on video and audio recorded from the first-person perspective of one young child for over a year – has provided new insights into early language acquisition. Not only do the findings offer a valuable framework to understand how children learn words and concepts, but they could be critical in developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can learn language in more human-like ways. Beginning around 6 to 9 months of age, children begin acquiring their ...
Targeting treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2024-02-01
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL FEB. 1, 2024, AT 2 P.M. ET) – New research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations has identified a next-generation BTK degrader that could help overcome treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and related blood cancers.
Their findings, published Feb. 2 in the journal Science, could offer a therapeutic option for CLL patients whose tumors become drug-resistant or are unresponsive to frontline treatment.
“This new compound not only inhibits the cellular molecule BTK, but goes further by taking aim at the target ...
Sustainable carbon removals limits identified, huge climate mitigation challenge revealed
2024-02-01
*Embargoed until 14:00 US Eastern / 19:00 UK GMT / 20:00 Europe CET – Thursday 1 February*
Governments and businesses are relying on dangerous amounts of future removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, instead of more rapidly reducing emissions and phasing out fossil fuels. This problem is partly due to an incomplete picture1 of the damaging consequences of carbon dioxide removal for people, food security and natural ecosystems, according to new research published in Science.
The paper finds that the carbon dioxide removal potential currently reported by the UN ...
Whole-brain projection patterns of single neurons in mouse hippocampus unveiled
2024-02-01
A study published in Science on Feb. 1 reported a comprehensive database of single-neuron projectomes consisting of over 10,000 mouse hippocampal neurons, thus revealing the spatial connectivity patterns of mouse hippocampal neurons at the mesoscopic level.
The study was conducted by teams from the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT), the Institute of Neuroscience of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the HUST-Suzhou Institute for Brainsmatics, Hainan University, the Kunming Institute of Zoology of CAS, Lingang Laboratory, and the Shanghai Center for ...
New study suggests culling animals who ‘don’t belong’ can be a flawed nature conservation practice
2024-02-01
New research published today in the journal Science has concluded that eradicating animals on the basis that they are not native in order to protect plant species, can be a flawed practice costing millions of dollars, and resulting in the slaughter of millions of healthy wild animals.
Introduced large herbivores, or megafauna, are claimed to have distinct and harmful ecological impacts, including damaging sensitive plants and habitats, reducing native plant diversity, and facilitating introduced plants. However, up to now these impacts have been studied without comparison to a proper ...
IU surgeon-scientist studying physiological effect of microorganisms in sinuses of chronic rhinosinusitis patients
2024-02-01
INDIANAPOLIS—An Indiana University School of Medicine surgeon-scientist is leading a multi-institutional grant investigating the role of the sinus microbiome in chronic rhinosinusitis, an inflammatory disease that causes the lining of the sinuses to swell. The research team will study biospecimens from human sinus surgery patients in the lab and examine how bacteria in the microbiome shape the disease process and might offer novel therapeutic strategies.
Vijay Ramakrishnan, MD, professor of otolaryngology—head ...
Stand Up to Cancer announces changes to scientific advisory committee
2024-02-01
LOS ANGELES – February 1, 2024 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced changes to its Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC), which oversees SU2C’s scientific research.
Composed of cancer research leaders from academic, government, industry, and advocacy fields, SU2C’s SAC sets direction for research initiatives, reviews proposals for new grant awards, and conducts rigorous oversight of all active grants in the SU2C research portfolio in collaboration with SU2C’s president and CEO Julian Adams, Ph.D.
World renowned cancer researcher and Nobel laureate Phillip A. Sharp, Ph.D., who has chaired the SAC since SU2C launched in ...
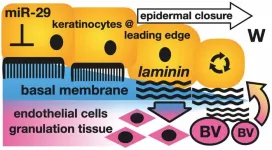
Small RNAs take on the big task of helping skin wounds heal better and faster with minimal scarring
2024-02-01
Philadelphia, February 1, 2024 – New findings in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, report that a class of small RNAs (microRNAs), microRNA-29, can restore normal skin structure rather than producing a wound closure by a connective tissue (scar). Any improvement of normal skin repair would benefit many patients affected by large-area or deep wounds prone to dysfunctional scarring.
Because the burden of non-healing wounds is so significant, it is sometimes called a “silent pandemic.” Worldwide, costs associated with wound care are expected to ...
Rural placements for medical students feed ‘pipeline’ for new family docs
2024-02-01
EDMONTON — New research shows an innovative education program is helping to address Alberta’s rural doctor shortage by making it more likely medical students will set up a rural family practice after graduation.
The University of Alberta was one of the first medical schools in Canada to set up its Rural Integrated Community Clerkship program back in 2007. It sends up to 25 third-year students for 10-month intensive work experiences with a single or small number of teaching physicians.
Instead of rotating to a new specialty placement every four to six weeks as in an urban ...
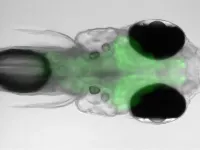
Zebrafish navigate to find their comfortable temperature
2024-02-01
All animals need to regulate their body temperature and cannot survive for long if it gets too high or too low. Warm-blooded organisms like humans have various ways to do this. They release heat by sweating or expanding the blood vessels in their skin, while shivering or burning fat in their brown adipose tissue has the opposite effect.
Cold-blooded animals such as the zebrafish, by contrast, cannot do any of these, so they have a different strategy. They look for places nearby that are at their “comfortable temperature,” just like how we might go out into the sun when we feel chilly or seek out some shade once it gets too ...
Buck scientists discover a potential way to repair synapses damaged in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-02-01
While newly approved drugs for Alzheimer’s show some promise for slowing the memory-robbing disease, the current treatments fall far short of being effective at regaining memory. What is needed are more treatment options targeted to restore memory, said Buck Assistant Professor Tara Tracy, PhD, the senior author of a study that proposes an alternate strategy for reversing the memory problems that accompany Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.
Since most current research on potential treatments for Alzheimer’s focuses on reducing the toxic proteins, such as tau and amyloid beta, that accumulate in ...
[1] ... [1409]
[1410]
[1411]
[1412]
[1413]
[1414]
[1415]
[1416]
1417
[1418]
[1419]
[1420]
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.