Mass General Cancer Center announces first recipients of Krantz Awards for Cancer Research
2024-01-24
The Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at the Mass General Cancer Center today announced the selection of 17 scientists who have been awarded a combined $6 million in funding. These competitive awards, which will be granted annually, were established to recognize the trailblazing efforts of Krantz Center scientists and accelerate ideas, projects and initiatives with the potential to fundamentally change how cancer is diagnosed and treated.
Philanthropists Jason and Keely Krantz, who ...
A large percentage of European plastic sent to Vietnam ends up in nature
2024-01-24
Despite strict EU regulations on plastic recycling, there is little oversight on plastic waste shipped from the EU to Vietnam. A large percentage of the exported European plastic cannot be recycled and gets dumped in nature. That is what new research led by Utrecht University’s Kaustubh Thapa has found.
Following the recycling path
About half of Europe’s plastic waste is exported to a number of countries in the Global South, including Vietnam. A Dutch and Vietnamese research team ventured to Minh Khai Craft Village, the largest recycling hub ...
A year of breakthroughs from Cincinnati Children’s
2024-01-24
Cincinnati Children’s continues to be a cradle for great discoveries.
Our latest Research Annual Report, online now, recounts a remarkable year of scientific advancement supported by a record-high level of research funding from federal, state, industry and philanthropic sources.
Among the many accomplishments from more than 1,000 faculty working in 50 research areas:
Promising results from the world’s first clinical trial of FLASH proton therapy for cancer treatment
Developing the first intestine organoids with functional immune cells, a major step closer to testing potential treatments using these amazing lab-grown tissues
Completing ...
AMS Science Preview: The “Black Swan” heatwave; volcanic chillers; tornadogenesis
2024-01-24
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. To view full article text, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
Searching for the Most Extreme Temperature Events in Recent History
Bulletin ...
Ultrasounds can help predict the risk of preterm births, new research shows
2024-01-24
Researchers have developed a way to use ultrasound to predict whether a pregnant person is at risk of delivering a baby prematurely, which occurs in upward of 10% of pregnancies in the U.S.
The new method — the result of more than 20 years of collaboration between researchers in nursing and engineering at University of Illinois Chicago and University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign — measures microstructural changes in a woman’s cervix using quantitative ultrasound. The ultrasound method works as early as 23 weeks into a pregnancy, according to the research, which is published in ...
Exposure to flame retardants linked to premature birth, higher birth weight
2024-01-24
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — In the largest study of its kind, researchers at UC Davis Health found that exposure to organophosphate ester flame retardants during pregnancy was associated with preterm birth, especially among females. The chemicals were also linked to higher birth weight, a concern for increased obesity risk. The major new research study was published in Environmental Health Perspectives.
“The importance of this study lies in unraveling the potential impact of exposure to environmental chemicals during pregnancy on fetal development. Our findings guide our understanding of how these chemicals may be silently seeding lasting challenges ...
How a protein fights off bacteria
2024-01-24
The human immune system is constantly fending off a wide range of invaders – a feat that requires a diverse array of cellular troops and molecular weaponry. Although a great deal is already known about immune defense cells and the strategies they employ, many molecular details have remained elusive. Now a research team led by Professor Oliver Daumke, a lab head at the Max Delbrück Center, has managed to unravel the main activation mechanism of GBP1, a protein that plays a pivotal role in combating certain bacteria. They report in “The EMBO ...
Breakthrough technology offers promising treatment for ischemic retinopathy
2024-01-24
A groundbreaking technology with immense potential in treating ischemic retinopathy in premature infants and diabetic patients has been developed by Professor Byoung Heon Kang and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Dong Ho Park’s team at Kyungpook National University Hospital. Ischemic retinopathy, characterized by the breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier and abnormal blood vessel growth, often leads to vision impairment and loss. The researchers have identified the critical role of a mitochondrial ...
Death rate higher than expected for patients with functional, nonepileptic seizures
2024-01-24
The death rate for patients with functional, nonepileptic seizures is higher than expected, with a rate comparable to epilepsy and severe mental illness, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.
A team of researchers reviewed data from 700 patients who were diagnosed with functional seizures, also called psychogenic or nonepileptic seizures, between 2014 and mid-2023 and followed for a median of 15 months.
It is the largest study of its kind in the United States, matching international studies in Australia, Denmark, Sweden and the United Kingdom, all of which have nationalized health care systems.
Of the 700 patients with functional ...
National Science Foundation and The Kavli Foundation partner on call for research proposals in neurobiology and changing ecosystems
2024-01-24
The Kavli Foundation and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Directorate for Biological Sciences' Division for Integrative Organismal Systems have joined forces to launch a grant program in neurobiology and changing ecosystems. Research in this emerging field has great potential to reveal novel scientific insights that will accelerate understanding of basic biology in neural adaptation and resilience at the molecular, biophysical, cellular, and circuit levels.
“NSF’s partnership with The Kavli Foundation will enable the U.S. to advance research in this emerging and understudied field,” remarked Denise Dearing, Division ...
Facial recognition app for dogs developed to help in fight against rabies
2024-01-24
A new mobile phone-based facial recognition application for dogs has the potential to significantly improve rabies vaccination efforts in endemic areas like Africa and Asia, according to a study on the research published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Led by researchers at Washington State University, a team used the app to test its effectiveness at a rabies vaccination clinic in rural Tanzania where they microchipped, vaccinated and registered dogs. The technology proved remarkably accurate during a subsequent visit to surrounding villages once poor images and improperly recorded ...
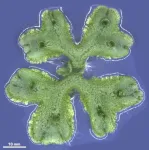
New study unveils how plants control the production of reactive oxygen species
2024-01-24
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive molecules containing oxygen. These compounds, which are normal byproducts of biological processes in all living organisms such as aerobic respiration as well as photosynthesis, are highly toxic. In most cases, ROS damage cellular machinery and can trigger a harmful stress response if their levels are not kept in tight check; this is why antioxidants are an important part of our diet.
However, over the past few decades, scientists have discovered that ROS are often intentionally ...
Rice study unlocks breakthrough for breast cancer bone metastases
2024-01-24
HOUSTON – (Jan. 24, 2023) – Rice University researchers in the lab of chemist Han Xiao have identified a promising new immunological pathway to treat stubborn bone tumors, one of most prevalent forms of metastases in breast cancer patients.
“More than 70% of people with metastatic breast cancer will see the cancer cells move to bone, which can lead to skeletal-related events like bone pain, fractures, and hypercalcemia,” said Yixian Wang, a Rice graduate student in the Han lab who is a lead author on a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. ...
The fountain of youth is … a T cell?
2024-01-24
The fountain of youth has eluded explorers for ages. It turns out the magic anti-aging elixir might have been inside us all along.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Corina Amor Vegas and colleagues have discovered that T cells can be reprogrammed to fight aging, so to speak. Given the right set of genetic modifications, these white blood cells can attack another group of cells known as senescent cells. These cells are thought to be responsible for many of the diseases we grapple with later in life.
Senescent cells are those that stop replicating. As we age, they build up in our bodies, ...
Infants born to COVID-infected mothers have triple the risk of developing respiratory distress
2024-01-24
New UCLA-led research finds that infants born full term to mothers who were infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy had three times the risk of having respiratory distress compared with unexposed infants, even though they themselves were not infected with the virus. The risk was significantly lower when the mothers infected during pregnancy were previously vaccinated.
The researchers found that in-utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2 sparked an “inflammatory cascade” in the infants, increasing the risk of a breathing disorder that most often ...
More than half of US adults don’t know heart disease is leading cause of death, despite 100-year reign
2024-01-24
Highlights:
More than half (51%) of respondents in a 2023 Harris Poll survey conducted on behalf of the American Heart Association did not identify heart disease as the leading cause of death in the U.S.
According to the 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of U.S. and Global Data From the American Heart Association, heart disease has been the leading cause of death in the U.S. for 100 years.
Heart disease along with stroke, which is the fifth leading cause of death, claimed more lives ...
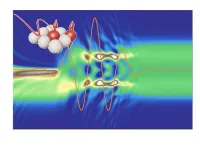
Ultrafast excitations in correlated systems
2024-01-24
An international team of researchers from the European XFEL together with colleagues from the Max Born Institute in Berlin, Universities of Berlin and Hamburg, The University of Tokyo, the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), the Dutch Radboud University, Imperial College London, and Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging, have presented new ideas for ultrafast multi-dimensional spectroscopy of strongly correlated solids. This work has now been published in Nature Photonics.
"Strongly correlated solids are complex and fascinating quantum systems in which new electronic states often ...
Chemotherapy becomes more efficient when senescent cells are eliminated by immunotherapy
2024-01-24
Barcelona, 24 January 2024 – Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, in addition to killing a large number of tumour cells, also result in the generation of senescent tumour cells (also called “zombi cells”). While senescent cells do not reproduce, they do, unfortunately, generate a favourable environment for the expansion of tumour cells that may have escaped the effects of the chemotherapy and eventually result in tumour regrowth.
An international team of researchers led by Dr. Manuel Serrano at IRB Barcelona have described how cancer cells that have become senescent after ...
TRAILS AI Institute announces first round of Seed Funding
2024-01-24
The Institute for Trustworthy AI in Law & Society (TRAILS) has unveiled an inaugural round of seed grants designed to integrate a greater diversity of stakeholders into the artificial intelligence (AI) development and governance lifecycle, ultimately creating positive feedback loops to improve trustworthiness, accessibility and efficacy in AI-infused systems.
The eight grants announced on January 24, 2024—ranging from $100K to $150K apiece and totaling just over $1.5 million—were awarded to interdisciplinary ...
Cognitive behavioral therapy alters brain activity in children with anxiety
2024-01-24
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found overactivation in many brain regions, including the frontal and parietal lobes and the amygdala, in unmedicated children with anxiety disorders. They also showed that treatment with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) led to improvements in clinical symptoms and brain functioning. The findings illuminate the brain mechanisms underlying the acute effects of CBT to treat one of the most common mental disorders. The study, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, was led by researchers at NIH’s ...
Do different plant-based diets affect pregnancy and birth outcomes?
2024-01-24
Women who follow vegan diets during pregnancy may face higher risks of developing preeclampsia and of giving birth to newborns with lower birth weight, suggests a recent study published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.
For the study, 65,872 women identified themselves as omnivorous, 666 as fish/poultry vegetarians, 183 as lacto/ovo vegetarians, and 18 as vegans. Based on a questionnaire completed mid-pregnancy, investigators found that protein intake was lower among lacto/ovo vegetarians (13.3%) and vegans (10.4%) compared with omnivorous participants (15.4%). Micronutrient intake was also ...
Do couples’ wages differ based on interracial versus intraracial marriage?
2024-01-24
In a study published in Economic Inquiry, investigators compared wages of Black and white interracially married individuals with those of intraracially married individuals in the United States.
After controlling for other factors that influence wages, the researchers found a wage penalty for white males in interracial marriages and a wage premium for Black males in interracial marriages, compared with their same sex and race counterparts in intraracial marriages. There were no wage penalties or premiums for white or Black females in interracial marriages.
The study also ...
How does climate change affect eczema?
2024-01-24
In an analysis of all relevant published studies that assessed atopic dermatitis (also known as eczema) associated with trends in climate-related hazards due to greenhouse gas emissions, investigators found that impacts include direct effects on eczema, like particulate matter-induced inflammation from wildfires, and indirect effects, such as stress resulting from drought-induced food insecurity.
In their research published in Allergy, the scientists created maps showing the past, ...
Can genetics affect the need for surgery in patients with thumb osteoarthritis?
2024-01-24
Rhizarthrosis, also known as trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis, is a type of osteoarthritis that affects the thumb, and treatments range from splints to surgery. Investigators have uncovered various genetic differences between individuals with rhizarthrosis who undergo surgery for their condition versus those who opt for nonsurgical treatments.
The study, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, included 1,083 surgical patients and 1,888 nonsurgical patients with rhizarthrosis, as well as 205,371 controls ...
AA attendance lower among African American, Hispanic and young populations
2024-01-24
By Amy Norton
Alcoholics Anonymous has long been a cornerstone of treating alcohol use disorders in the United States. But even today, Americans are not accessing it equally, according to a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Alcoholics Anonymous, or AA, got its start nearly 90 years ago and is famous for spurring the "12-step" approach to recovery -- which includes acknowledging powerlessness over alcohol and giving your life over to a "higher power."
Over the years, AA and similar "mutual-help groups" ...
[1] ... [1416]
[1417]
[1418]
[1419]
[1420]
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
1424
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
[1429]
[1430]
[1431]
[1432]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.