High school students who report using alcohol, cannabis or nicotine at higher risk for suicidal thoughts and other mental health disorders
2024-01-29
BOSTON –High school students who reported using cannabis, alcohol, or nicotine were more likely to have thoughts about suicide, feel depressed or anxious, have unusual experiences, and exhibit inattention or hyperactivity, according to recent survey-based study conducted by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the University of Minnesota.
The study, which is published in JAMA Pediatrics, included 2022–2023 survey results from more than 15,000 high school students across Massachusetts.
“We sought to determine ...
New evidence informs risk factors, diagnosis and care of patients with CVT stroke
2024-01-29
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, Jan. 29, 2024
DALLAS, January 29, 2024 — A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association emphasizes the need to increase patients’ and physicians’ awareness of cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) to improve the recognition of this condition and initiate prompt medical treatment. The new statement, Diagnosis and Management of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis, published today in the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association’s peer-reviewed journal Stroke. ...
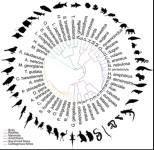
Researchers map genome for cats, dolphins, birds, and dozens of other animals
2024-01-29
Researchers mapped genetic blueprints for 51 species including cats, dolphins, kangaroos, penguins, sharks, and turtles, a discovery that deepens our understanding of evolution and the links between humans and animals.
“Being able to access that genetic information will have huge implications for understanding human health and evolution,” said lead author Michael Schatz, a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of computer science and biology at Johns Hopkins University. “A lot of work ...
Overcoming the stigma: study recommends steps to move past barriers of brain health conversation
2024-01-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- Approximately four of five primary care clinicians consider themselves on the front lines of brain health. In the U.S., clinicians are the first point of contact for patients worried about memory loss and are most likely the first to detect and evaluate patients experiencing mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease or related dementias.
In a new study focused on understanding the barriers of clinician-patient conversations about brain health and cognitive concerns, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine Research Scientist Malaz Boustani, M.D., MPH, found that early conversations about brain health between ...
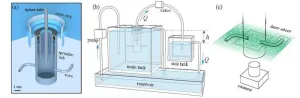
PolyU develops high-efficiency carbon dioxide electroreduction system for reducing carbon footprint and progressing carbon neutrality goals
2024-01-29
Global warming continues to pose a threat to human society and the ecological systems, and carbon dioxide accounts for the largest proportion of the greenhouse gases that dominate climate warming. To combat climate change and move towards the goal of carbon neutrality, researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) have developed a durable, highly selective and energy-efficient carbon dioxide (CO2) electroreduction system that can convert CO2 into ethylene for industrial purposes to provide an effective solution for ...
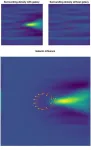
Lopsided galaxies shed light on the speed of dark matter
2024-01-29
So how can the speed of dark matter be measured? The prerequisite is to find a galaxy in the universe that moves relative to dark matter. Since everything in the universe is in motion and there is a great deal of dark matter, it is not difficult to find such galaxies.
Heavy objects, like galaxies, attract all types of matter, whether it is dark matter or visible matter that we encounter on a daily basis. As dark matter moves past a galaxy, the galaxy begins to pull the dark matter particles towards it. However, the change of speed direction of the particles takes time. Before ...
Breast cancer test may make bad chemotherapy recommendations for Black patients
2024-01-29
A common test used to decide whether breast cancer patients should get chemotherapy may be making bad recommendations for some Black women, leading them to forgo chemotherapy when it might have helped, according to new research from the University of Illinois Chicago.
The test, known as the 21-gene breast recurrence score, is the most commonly ordered biomarker test used to guide doctor’s recommendations for patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer — the most common ...
First-ever sighting of a live newborn great white
2024-01-29
Great whites, the largest predatory sharks in the world with the most fatal attacks on humans, are tough to imagine as newborn babies. That is partially because no one has seen one in the wild, it seems, until now.
Wildlife filmmaker Carlos Gauna and UC Riverside biology doctoral student Phillip Sternes were scanning the waters for sharks on July 9, 2023, near Santa Barbara on California’s central coast. That day, something exciting appeared on the viewfinder of Gauna’s drone camera. It was a shark ...
Back from the dead: Tropical tree fern repurposes its dead leaves
2024-01-29
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Plant biologists report that a species of tree fern found only in Panama reanimates its own dead leaf fronds, converting them into root structures that feed the mother plant. The fern, Cyathea rojasiana, reconfigures these “zombie leaves,” reversing the flow of water to draw nutrients back into the plant.
Watch a video about the findings.
This weird phenomenon occurs only after the leaves die and droop to the ground, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign plant biology professor James Dalling, ...
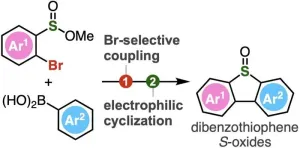
New horizons in chemical biology: A novel approach to synthesize dibenzothiophene s-oxides
2024-01-29
Organic compounds in the field of chemistry range from simple hydrocarbons to complex molecules, with diverse functional groups added to the main carbon backbone. These functional groups impart the compounds distinct chemical properties as well as participate in various chemical transformations, making them important precursors for the synthesis of diverse compounds. Scientists have, therefore, actively engaged in creating molecules that feature novel and highly reactive functional groups.
One such class of compounds are dibenzothiophenes and their derivatives containing ...
Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination
2024-01-29
A sequence variant that increases risk of pregnancy loss
Scientists at deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen and their collaborators from Iceland, Denmark and USA published a study today in Nature Structural and Molecular Biology titled “Variant in the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE2 associates with pregnancy loss through effects on recombination”.
While it is well established that chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of miscarriages the biology behind pregnancy losses with or without chromosomal errors is not well understood. Over 114 thousand women from Iceland, Denmark, UK, USA and Finland who have ...
How obesity dismantles our mitochondria
2024-01-29
The number of people with obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, resulting in a worldwide epidemic. While lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a role in the development and progression of obesity, scientists have come to understand that obesity is also associated with intrinsic metabolic abnormalities. Now, researchers from University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on how obesity affects our mitochondria, the all-important energy-producing structures of our cells.
In a study published January ...
Cancer treatment two and a half times more effective when tumours have defective "energy factories"
2024-01-29
Cancer Research UK-funded scientists have made an unusual discovery that could help to identify patients who are up to two and a half times more likely to respond to currently available cancer drugs.
Scientists at the Cancer Research UK Scotland Institute and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre in the USA have “rewired” the DNA of mitochondria – energy factories found in every living cell. They found that creating mutations in parts of this DNA determines how well cancer will respond to immunotherapy – treatments which harness the body’s natural defences ...
How does a “reverse sprinkler” work? Researchers solve decades-old physics puzzle
2024-01-29
For decades scientists have been trying to solve Feynman’s Sprinkler Problem: How does a sprinkler running in reverse—in which the water flows into the device rather than out of it—work? Through a series of experiments, a team of mathematicians has figured out how flowing fluids exert forces and move structures, thereby revealing the answer to this long-standing mystery.
“Our study solves the problem by combining precision lab experiments with mathematical modeling that explains how a reverse sprinkler operates,” explains Leif Ristroph, an associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author ...
Neuroblastoma: Liquid biopsies to detect relapse of childhood cancer early
2024-01-29
(Utrecht/Vienna, 29.1.2024) Neuroblastoma mainly affects toddlers and young children - in the EU region there are 1500 new cases per year. Neuroblastoma is a malignant tumor of the peripheral nervous system and around 50% of patients are high-risk cases. Recurrences occur frequently, and conventional therapies are no longer effective for these children. With liquid biopsies it is possible to monitor therapy success and to predict the recurrence of the tumor in time to take medical countermeasures. Scientists from leading European ...
Speaking in a local accent might make social robots seem more trustworthy and competent
2024-01-29
Social robots can help us with many things: teaching, learning, caring. Because they’re designed to interact with humans, they’re designed to make us comfortable — and that includes the way they talk. But how should they talk? Some research suggests that people like robots to use a familiar accent or dialect, while other research suggests the opposite.
“Surprisingly, people have mixed feelings about robots speaking in a dialect — some like it, while others prefer standard language,” said Katharina Kühne of the University of Potsdam, lead author ...
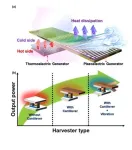
Hybrid energy harvesters that harness heat and vibration simultaneously
2024-01-29
Harvesting energy sources such as heat, vibration, light, and electromagnetic waves from everyday environments such as industrial sites and automobiles and converting them into electrical energy is known as energy harvesting. Energy harvesting makes it easier to power today's popular IoT sensors and wireless devices that are located in environments where battery replacement is difficult.
Dr. Hyun-Cheol Song and Dr. Sunghoon Hur of Electronic Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have developed a hybrid energy harvesting ...
Organ donations after MAiD made up 14% of deceased donations in Quebec
2024-01-29
Organ donation after medical assistance in dying (MAiD) represented 14% of Quebec's total deceased donations in 2022, according to a new study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230883.
To understand the impact of organ donation after MAiD, Quebec researchers analyzed data on all patients referred to Transplant Québec for possible organ donation after MAiD from January 2018 to December 2022. This represented the first 5 full years when organ donation after MAiD was allowed in the province. Over the 5-year period, Transplant Québec received 245 referrals for donation after MAiD, ...
Polycystic ovarian syndrome: new review to help diagnose and manage
2024-01-29
A new review in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) is aimed at helping clinicians diagnose and manage polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), an endocrine disorder that affects about 10% of femaleshttps://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231251.
This disorder affects females of reproductive age and is associated with infertility, miscarriage and pregnancy complications. Its long-term health consequences include hypertension, cancer risks, and metabolic and psychological impacts. Patients usually present to health care between ages 18 and 39 years complaining of menstrual cycle irregularities, ...
Robot trained to read braille at twice the speed of humans
2024-01-29
Researchers have developed a robotic sensor that incorporates artificial intelligence techniques to read braille at speeds roughly double that of most human readers.
The research team, from the University of Cambridge, used machine learning algorithms to teach a robotic sensor to quickly slide over lines of braille text. The robot was able to read the braille at 315 words per minute at close to 90% accuracy.
Although the robot braille reader was not developed as an assistive technology, the researchers say the high sensitivity required to read braille makes it an ideal test in the development of robot ...
Obesity and alcohol are contributing to increases in bowel cancer rates among young adults
2024-01-29
Overweight and obesity are contributing to rising death rates from bowel cancer among people aged 25-49 years in the European Union (EU) and the UK, although death rates from this type of cancer are decreasing overall across Europe.
These findings are from a new study published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday), which predicts death rates from cancer in the EU and UK for 2024. It is the first time that an increase in bowel cancer death rates among young adults has been predicted for the EU, and it confirms a trend in the UK that the researchers first noted in 2021.
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), ...
Playing an instrument linked to better brain health in older adults
2024-01-29
Engaging in music throughout your life is associated with better brain health in older age, according to a new study published by experts at the University of Exeter.
Scientists working on PROTECT, an online study open to people aged 40 and over, reviewed data from more than a thousand adults over the age of 40 to see the effect of playing a musical instrument – or singing in a choir - on brain health. Over 25000 people have signed up for the PROTECT study, which has been running for 10 years.
The team reviewed participants’ musical experience and lifetime exposure ...
New research finds volume alone does not predict quality outcomes in pediatric cardiac surgery
2024-01-28
A study of pediatric heart surgery centers across the United States has demonstrated that, when it comes to successful surgery, it’s not just the size of the program that matters in determining quality outcomes.
Historically, hospitals with a “low volume” of pediatric heart operations—in this case, those that perform 103 surgeries or fewer a year—have been associated with worse outcomes for patients. However, a team led by D. Chauhan, MD, from WVU Medicine Children’s ...
Almost 50% of patients under 60 years choose TAVR over surgical aortic valve replacement with worse outcomes
2024-01-28
Despite national guidelines recommending surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) for patients under age 65 with severe aortic stenosis, many hospitals are still opting for a nonsurgical approach in patients under 60—possibly with poorer survival rates.
In a study presented at The Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ 2024 Annual Meeting in San Antonio, Texas, researchers from the department of cardiac surgery in the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles and the department of population health science and policy at Mount Sinai New York compared ...
New study reveals the profound impact of forced separation between humans and their pets
2024-01-28
Pet owners forced to be separated from their animals in crisis situations, including those who are victims of domestic violence, are suffering from a lack of support services needed to protect them.
These are the findings of a new review of 27 years of international research, published in the peer-reviewed journal Anthrozoös, which unveils the increased risks to both safety and psychological well-being when people are faced with the threat of forced separation from their pets.
The results provide important insights towards addressing the challenges arising from domestic violence, homelessness or natural disasters that can threaten the bond between humans and ...
[1] ... [1420]
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
1428
[1429]
[1430]
[1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.