Food from urban agriculture has carbon footprint 6 times larger than conventional produce, study shows
2024-01-22
Photos
A new University of Michigan-led international study finds that fruits and vegetables grown in urban farms and gardens have a carbon footprint that is, on average, six times greater than conventionally grown produce.
However, a few city-grown crops equaled or outperformed conventional agriculture under certain conditions. Tomatoes grown in the soil of open-air urban plots had a lower carbon intensity than tomatoes grown in conventional greenhouses, while the emissions difference between conventional and urban agriculture vanished for air-freighted crops like asparagus.
"The exceptions revealed by our ...
Scientists make COVID receptor protein in mouse cells
2024-01-22
UPTON, NY—A team of scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Columbia University has demonstrated a way to produce large quantities of the receptor that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, binds to on the surface of human cells. That binding between the now-infamous viral spike protein and the human “ACE2” receptor is the first step of infection by the virus. Making functional human ACE2 protein in mouse cells gives scientists a new way to study these receptors and potentially put them to use. In addition, as described in a paper just published in the journal Virology, the ...
Researchers unveil new way to counter mobile phone ‘account takeover’ attacks
2024-01-22
Computer science researchers have developed a new way to identify security weaknesses that leave people vulnerable to account takeover attacks, where a hacker gains unauthorized access to online accounts.
Most mobiles are now home to a complex ecosystem of interconnected operating software and Apps, and as the connections between online services has increased, so have the possibilities for hackers to exploit the security weaknesses, often with disastrous consequences for their owner.
Dr Luca Arnaboldi, from the University of Birmingham’s School of Computer Science, explains: “The ruse of looking over someone’s shoulder to find out their PIN is well known. ...
What factors affect patients’ decisions regarding active surveillance for low-risk prostate cancer?
2024-01-22
Because low-risk prostate cancer is unlikely to spread or impact survival, experts and guidelines recommend active surveillance, which involves regular monitoring and thus avoid or delay treatment like surgery or radiation therapy and their life-changing complications. A new study examined the rates of active surveillance use and evaluated the factors associated with selecting this management strategy over surgery or radiation, with a focus on underserved Black patients who have been underrepresented in prior studies. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, called the Treatment ...
New sustainable method for creating organic semiconductors
2024-01-22
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new, more environmentally friendly way to create conductive inks for use in organic electronics such as solar cells, artificial neurons, and soft sensors. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, pave the way for future sustainable technology.
Organic electronics are on the rise as a complement and, in some cases, a replacement to traditional silicon-based electronics. Thanks to simple manufacturing, high flexibility, and low weight combined with the electrical properties typically associated with traditional semiconductors, it can be useful for applications such as digital displays, energy storage, ...
Digital dice and youth: 1 in 6 parents say they probably wouldn’t know if teens were betting online
2024-01-22
As young people increasingly have access and exposure to online gambling, only one in four parents say they have talked to their teen about some aspect of virtual betting, a national poll suggests.
But over half of parents aren’t aware of their state’s legal age for online gambling and one in six admit they probably wouldn’t know if their child was betting online, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Teens and young adults may have a difficult time going ...
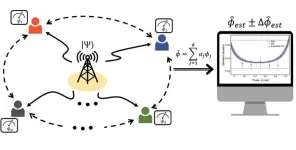
Enable distributed quantum sensors for simultaneous measurements in distant places
2024-01-22
We've all had the experience of trying to get the exact time of a highly competitive concert ticket or class beforehand. If the time in Seoul and Busan is off by even a fraction of an hour, one will be less successful than the other. Sharing the exact time between distant locations is becoming increasingly important in all areas of our lives, including finance, telecommunications, security, and other fields that require improved accuracy and precision in sending and receiving data.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that Dr. Hyang-Tag Lim and his team at the Center ...
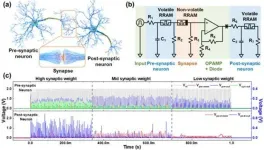
Implement artificial neural network hardware systems by stacking them like "neuron-synapse-neuron" structural blocks
2024-01-22
With the emergence of new industries such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and machine learning, the world's leading companies are focusing on developing next-generation artificial intelligence semiconductors that can process vast amounts of data while consuming energy efficiently. Neuromorphic computing, inspired by the human brain, is one of them. As a result, devices that mimic biological neurons and synapses are being developed one after another based on emerging materials and structures, but research on integrating individual devices into a system to verify and optimize them ...
The megalodon was less mega than previously believed
2024-01-22
A new study shows the Megalodon, a gigantic shark that went extinct 3.6 million years ago, was more slender than earlier studies suggested. This finding changes scientists’ understanding of Megalodon behavior, ancient ocean life, and why the sharks went extinct.
The Megalodon or megatooth shark is typically portrayed as a super-sized monster in popular culture, with recent examples in the sci-fi films “The Meg” (2018) and “Meg 2: The Trench” (2023). Previous studies assume that the shark likely reached lengths of at least 50 feet and possibly as much as 65 feet.
However, the Megalodon is largely known only from its teeth and vertebrae in the ...
Slender shark: Study finds Megalodon was not like a gigantic great white shark
2024-01-22
CHICAGO — A new scientific study shows that the prehistoric gigantic shark, Megalodon or megatooth shark, which lived roughly 15-3.6 million years ago nearly worldwide, was a more slender shark than previous studies have suggested.
Formally called Otodus megalodon, it is typically portrayed as a super-sized, monstrous shark in novels and sci-fi films, including “The Meg.” Previous studies suggest the shark likely reached lengths of at least 50 to 65 feet (15 to 20 meters). However, ...
New criteria for sepsis in children based on organ dysfunction
2024-01-21
Clinician-scientists from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago were among a diverse, international group of experts tasked by the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) with developing and validating new data-based criteria for sepsis in children. Sepsis is a major public heath burden, claiming the lives of over 3.3 million children worldwide every year. The new pediatric sepsis criteria – called the Phoenix criteria – follow the paradigm shift in the recent adult criteria that define sepsis as severe ...
Development and validation of the Phoenix criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock
2024-01-21
About The Study: In this international, multicenter, retrospective cohort study including more than 3.6 million pediatric encounters, a novel score, the Phoenix Sepsis Score, was derived and validated to predict mortality in children with suspected or confirmed infection. The new criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock based on the score performed better than existing organ dysfunction scores and the International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria.
Authors: Tellen D. Bennett, M.D., M.S., of the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
International consensus criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock
2024-01-21
About The Study: The Phoenix sepsis criteria for sepsis and septic shock in children were derived and validated by the international Society of Critical Care Medicine Pediatric Sepsis Definition Task Force using a large international database and survey, systematic review and meta-analysis, and modified Delphi consensus approach. A Phoenix Sepsis Score of at least 2 identified potentially life-threatening organ dysfunction in children younger than 18 years with infection, and its use has the potential to improve clinical care, epidemiological assessment, and research in pediatric sepsis and septic shock around the world.
Authors: R. Scott ...
CU researchers unveil modernized criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock
2024-01-21
An international research team led by Tell Bennett, MD, MS, professor of biomedical informatics and pediatric critical care at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, released new diagnostic criteria for sepsis in children this week, marking the first update to the pediatric sepsis definition in nearly two decades.
The updated criteria, presented at the 2024 Critical Care Congress of the Society for Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), will be utilized ...
A computerized decision support system significantly reduces high-risk drug combinations in Intensive Care patients
2024-01-21
A recent multicentre study led by Amsterdam UMC and conducted in nine Dutch Intensive Care Units (ICUs) has shown that tailoring a computerised decision support system (CDSS) to the ICU environment significantly reduced the number of high-risk drug combinations administered to ICU patients. It also improved monitoring ICU patients when avoiding such combinations was not possible, and reduced the length of patients’ stay in the ICU. This study is published today in The Lancet.
"Not more, but fewer and more relevant alerts by a CDSS make such a system more valuable for healthcare providers and patients," says Amsterdam ...
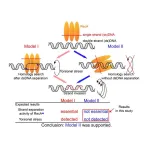
Scientists unravel key steps in the road to DNA repair
2024-01-20
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have been studying DNA repair by homologous recombination, where the RecA protein repairs breaks in double-stranded DNA by incorporating a dangling single-strand end into intact double strands, and repairing the break based on the undamaged sequence. They discovered that RecA finds where to put the single strand into the double helix without unwinding it by even a single turn. Their findings promise new directions in cancer research.
Homologous recombination (HR) is a ubiquitous biochemical process shared across all living things, including animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. As we go about our daily ...
Study identifies new PD-1 immune checkpoint mechanism promoting merkel cell carcinoma growth
2024-01-19
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) is an important target for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies that block its signaling and boost T-cell activity. PD-1 inhibitors have been approved for treating various types of cancer.
But PD-1 functions can vary between different cell and cancer types, either promoting or suppressing disease progression. Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC), a rare and aggressive form of skin cancer, responds well to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. However, it was previously unknown if MCC cells express PD-1 themselves, and unclear how exactly cancer cell-intrinsic ...
Vanderbilt chemist Ben Brown awarded $2.375M to develop nonaddictive painkillers with AI
2024-01-19
When Ben Brown, research assistant professor of chemistry, thinks about the opioid epidemic, he views the problem on a molecular level. Painkillers used legitimately in medicine, such as oxycodone, are highly addictive, but better understanding of how their molecules interact with proteins in the body could lead to the formulation of nonaddictive alternatives, he said.
In May, the National Institute on Drug Abuse awarded Brown $1.5 million over five years to further his work in this area. Brown, faculty affiliate of the Vanderbilt Center for Addiction Research and the Center for Applied Artificial Intelligence in Protein Dynamics, is developing artificial intelligence that ...
National champion tree program finds new home
2024-01-19
The National Champion Tree Program started 83 years ago at American Forests to discover the largest, living trees in the United States. Now, the program is moving from the organization’s headquarters to a new home in the School of Natural Resources at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture (UTIA).
American Forests launched the Champion Tree Program in 1940. Its vision included establishing a nationwide laboratory for the study of forestry and trees. Being housed at Tennessee’s 1862 public land-grant university will advance the program’s understanding of big trees. “The National Champion Tree Program moving to UTIA means it can continue protecting ...
New AEM study evaluates potential disparities in restraint use in the emergency department at a minority-serving safety-net hospital
2024-01-19
Des Plaines, IL — A new study that contributes additional data to a growing body of evidence demonstrating disparities in restraint use in the emergency department (ED) has been published in the January issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), the peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM). The study, titled Disparities in use of physical restraints at an urban, minority-serving hospital emergency department evaluates the association between race/ethnicity and the use of restraints in an ED population ...
CRISPR off-switches: A path towards safer genome engineering?
2024-01-19
Using CRISPR, an immune system bacteria use to protect themselves from viruses, scientists have harnessed the power to edit genetic information within cells. In fact, the first CRISPR-based therapeutic was recently approved by the FDA to treat sickle cell disease in December 2023. That therapy is based on a highly studied system known as the CRISPR-Cas9 genetic scissor.
However, a newer and unique platform with the potential to make large-sized DNA removals, called Type I CRISPR or CRISPR-Cas3, waits in the wings for potential therapeutic use.
A new study from Yan Zhang, ...
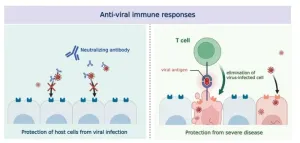
Evolution of the human immune system in the post-Omicron era
2024-01-19
It has been 4 years since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be eradicated and new variants are continuously emerging. Despite the extensive immunization programs, breakthrough infections (infection after vaccination) by new variants are common. New research suggests that human immune responses are also changing in order to combat the never-ending emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants. Specifically, it has been discovered the immune system that encountered breakthrough infection by the Omicron variant acquires enhanced immunity against future versions of the Omicron.
A team of South Korean scientists ...
First therapeutic target for preserving heart function in patients with pulmonary hypertension
2024-01-19
A team led by Dr. Guadalupe Sabio at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) in Madrid has discovered a possible therapeutic target for pulmonary hypertension.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, identifies the first therapeutic target that can be modulated to preserve cardiac function in pulmonary hypertension, providing hope in the fight against this rare but fatal disease for which there is currently no cure.
Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of elevated blood pressure in the arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. This increased pulmonary blood pressure puts the heart under continuous strain ...
Endless biotechnological innovation requires a creative approach
2024-01-19
Scientists working on biological design should focus on the idiosyncrasies of biological systems over optimisation, according to new research.
In a study, published today in Science Advances, researchers from the Universities of Bristol and Ghent have shown how exploring the unknown may be the crucial step needed to realise the continual innovation needed for the biotechnologies of the future.
Recognising the role of open-endedness in achieving this goal and its growing importance in fields like computer science and evolutionary biology, the team mapped out how open-endedness is linked to bioengineering practice today and what would be required to achieve it in ...
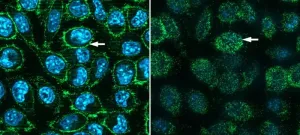
The secret life of CD4+ T cells: from helpers to melanoma fighters
2024-01-19
In the study led by the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) and published in Science Immunology, the researchers found that CD4+ T cells, traditionally called ‘helper T cells’ for their role in aiding the activation of other immune cells, are remarkably effective in controlling melanoma.
University of Melbourne’s Dr Emma Bawden, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Doherty Institute and lead author of the study, said this discovery challenges the conventional understanding of the role of CD4+ T cells in cancer immunity.
“Our ...
[1] ... [1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
[1429]
[1430]
1431
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
[1439]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.