Columbia chemists create the first 2D heavy fermion
2024-01-17
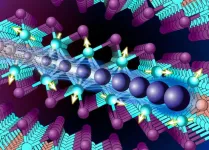
Researchers at Columbia University have successfully synthesized the first 2D heavy fermion material. They introduce the new material, a layered intermetallic crystal composed of cerium, silicon, and iodine (CeSiI), in a research article published today in Nature.
Heavy fermion compounds are a class of materials with electrons that are up to 1000x heavier than usual. In these materials, electrons get tangled up with magnetic spins that slow them down and increase their effective mass. Such interactions are ...
Therapy versus medication: comparing treatments for depression in heart disease
2024-01-17
New research by investigators from the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences at Cedars-Sinai shows that behavioral activation therapy is as effective as antidepressant medications in treating symptoms of depression in patients with heart failure.
Heart failure affects nearly 6 million adults in the United States, and approximately 50% of heart failure patients experience symptoms of depression along with their condition. Past studies show patients with heart failure and depression have lower cardiac function, more emergency department ...
Active membranes: The future of fresh water is bright
2024-01-17
The growth of Los Angeles as a startup hub is highlighted by a robust and diverse entrepreneurial ecosystem within UCLA. The Magnify Incubator at CNSI is no exception to showcasing the range of early-stage businesses.
One such company within the Magnify incubator, Active Membranes, is innovating the future of fresh water through membrane desalination. As freshwater is becoming increasingly scarce around the globe, resources such as seawater and industrial wastewater are costly to procure and operate. The company’s patented technology is electrically conducting ...
What’s stopping US climate policies from working effectively
2024-01-17
In an effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and curb global warming, the U.S. has enacted several ambitious federal laws, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) passed in 2022 and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) of 2021.
These provide significant investments in clean energy projects and encourage technological innovations. Some analyses suggest they could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by more than 40% below 2005 levels by 2030.
However, in a paper published Jan. 16 in the journal Nature Climate Change, researchers at the University ...
Chromatin modifier-centered pathway points to higher crop yield
2024-01-17
Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins that makes up the genetic material in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A chromatin modifier is a protein or complex of proteins that chemically modifies the structure of chromatin. Chromatin modifiers play a crucial role in regulating the expression of genes, which are segments of DNA strands, as well as in other chromatin-related processes. These modifiers mainly work by adding or subtracting chemical groups to histones, a type of protein within the chromatin, or to the DNA itself.
In the scientific effort to manipulate the expression of plant genes, such as for grain size or drought-resistance, etc., understanding the influence ...
U.S. voters’ climate change opinions swing elections
2024-01-17
When voters cast their ballots in the 2016 and 2020 presidential elections, many were driven by their concern for climate change, according to new research out of CU Boulder’s Center for Environmental Futures (C-SEF). The new report determined that views on climate change played a significant role in whom people voted for, concluding that the climate issue very likely cost Republicans the 2020 election, all else equal.
“This is obviously information that politicians and advocates across the political spectrum will want to know, heading into the 2024 election cycle,” said Matthew Burgess, CIRES Fellow and C-SEF director. “How ...
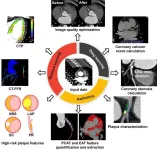
Artificial intelligence helps coronary CT angiography and accelerates the development of precision medicine
2024-01-17
This review was jointly published by Prof. Long-Jiang Zhang (Department of Radiology, Jinling Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University) and Prof. Christian Tesche (Division of Cardiovascular Imaging, Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Medical University of South Carolina and Department of Cardiology, Munich University Clinic, Ludwig-Maximilian-University).
With the continuous progress of science and technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an important driving force for a new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial change. It aims to mimic human consciousness and thought processes, continuously ...
New research finds half-cardio, half-strength training reduces cardiovascular disease risks
2024-01-17
AMES, Iowa — Approximately one in three deaths in the U.S. is caused by cardiovascular disease, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A robust body of evidence shows aerobic exercise can reduce risks, especially for people who are overweight or obese. But few studies have compared results with resistance exercise — also known as strength or weight training — or with workout regimens that are half aerobic and half resistance. Researchers at Iowa State University led one of the longest and largest supervised exercise trials to ...
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group melanoma research team led by Michael Atkins, MD, receives the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction from the Journal of Clinical Oncology
2024-01-17
A team of melanoma researchers with the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) is honored with the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction by the Journal of Clinical Oncology. The recognition is for the results of the DREAMseq randomized phase 3 clinical trial. DREAMseq (EA6134) showed an optimal treatment sequence for combination therapy in patients with advanced melanoma with a BRAFV600 tumor gene mutation. The treatment sequence beginning with immunotherapy (nivolumab and ipilimumab), followed by targeted therapy (dabrafenib and trametinib) if there was disease progression, resulted ...
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition launches new article series to educate physicians and other health care professionals on nutrition
2024-01-17
Rockville, MD (January 16, 2024) – To educate physicians and other health care professionals on the fundamentals of nutrition, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has launched a new article series titled Nutrition for the Clinician. The effort supports the White House National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health and its directives to expand nutrition knowledge of health care providers, an effort long supported by the American Society for Nutrition. Nancy Krebs, MD, MS, Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado ...
New research shows that most early galaxies looked like breadsticks rather than pizza pies or dough balls
2024-01-17
Columbia researchers analyzing images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found that galaxies in the early universe are often flat and elongated, like breadsticks—and are rarely round, like balls of pizza dough. “Roughly 50 to 80% of the galaxies we studied appear to be flattened in two dimensions,” explained Viraj Pandya, a NASA Hubble Fellow at Columbia University, and the lead author of a new paper slated to appear in The Astrophysical Journal that outlines the findings. “Galaxies that look like long, thin breadsticks seem to be very common in the early universe, which is surprising, since they are uncommon among galaxies ...
Podcasts and compulsory attendance improved student learning
2024-01-17
Consider a group of new sociology students who are about to dive into a completely new subject. Half of them are fresh out of upper secondary school.
They need to settle into student life and get to know other students. They are about to embark on studies in a new field and must learn new ways of acquiring knowledge, regardless of their discipline.
They also need to come to grips with concepts such as legitimation, linguistic objectification, internalization and externalization. What on Earth do ...
Brush biopsy enables early detection of oral cancer without surgery
2024-01-17
A new test invented by University of Illinois Chicago researchers allows dentists to screen for the most common form of oral cancer with a simple and familiar tool: the brush.
The diagnostic kit, created and patented by Guy Adami and Dr. Joel Schwartz of the UIC College of Dentistry, uses a small brush to collect cells from potentially cancerous lesions inside the mouth. The sample is then analyzed for genetic signals of oral squamous cell carcinoma, the ninth most prevalent cancer globally.
This new screening method, which is currently seeking commercialization ...
Diets rich in plant protein may help women stay healthy as they age
2024-01-17
Women who consume higher amounts of protein, especially protein from plant-based sources, develop fewer chronic diseases and are more likely to be healthier overall as they age, according to a study led by researchers at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University and published Jan. 17 in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Analyzing self-reported data from more than 48,000 women, the researchers saw notably less heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, and cognitive and mental health decline, in those who included more protein in their diets from sources such as fruits, ...
Study uncovers mechanics of machete-like ‘tail-whipping’ in thresher sharks
2024-01-17
Like Indiana Jones, thresher sharks (Alopias spp.) have mastered the art of the whip using their tails. With incredible speed, their long, machete-like tails can slap and stun their prey, allowing them to swallow multiple fish in one fell swoop. Their exceptionally elongated tail, which can often be as long as their entire body, not only makes this particular shark unique, but also a formidable hunter.
Thresher shark “tail-whipping” consists of four phases: preparation, strike, wind-down recovery, and prey collection. Overhead tail slaps begin in the preparation phase by lunging ...
Glowing COVID-19 diagnostic test prototype produces results in one minute
2024-01-17
Cold, flu and COVID-19 season brings that now-familiar ritual: swab, wait, look at the result. But what if, instead of taking 15 minutes or more, a test could quickly determine whether you have COVID-19 with a glowing chemical? Now, in ACS Central Science, researchers describe a potential COVID-19 test inspired by bioluminescence. Using a molecule found in crustaceans, they have developed a rapid approach that detects SARS-CoV-2 protein comparably to one used in vaccine research.
From fireflies ...
Microplastics from natural fertilizers are blowing in the wind more often than once thought
2024-01-17
Though natural fertilizers made from treated sewage sludge are used to reintroduce nutrients onto agricultural fields, they bring along microplastic pollutants too. And according to a small-scale study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters, more plastic particles get picked up by the wind than once thought. Researchers have discovered that the microplastics are released from fields more easily than similarly sized dust particles, becoming airborne from even a slight breeze.
Microplastics, or small bits of plastic less than 5 millimeters long, have appeared everywhere from clouds to heart tissues. And with these plastics’ increasing prevalence in ...
New AI makes better permafrost maps
2024-01-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Jan. 17, 2024 — New insights from artificial intelligence about permafrost coverage in the Arctic may soon give policy makers and land managers the high-resolution view they need to predict climate-change-driven threats to infrastructure such as oil pipelines, roads and national security facilities.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the globe, and permafrost is a component of the Arctic that’s changing really rapidly,” said Evan Thaler, a Chick Keller Postdoctoral Fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Thaler is corresponding ...
New study unveils emotional hubs that exist across languages
2024-01-17
Emotions exert a profound influence on human behavior, prompting extensive explorations in the realms of psychology and linguistics. Understanding central emotions also has practical utility since it can help organizations create messages that resonate better with people. For instance, businesses can enhance their connection with their customers, and non-profits can prompt quicker action by skillfully leveraging the salient emotions in humans.
Colexification is a phenomenon in which the occurrence of a single word is associated with multiple concepts that share semantic relationships. The analysis of colexification is an innovative linguistic method for ...
Childhood stress linked to higher risk of high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes in adults
2024-01-17
Research Highlights:
Consistently high scores of perceived stress during adolescence through adulthood may contribute to worse cardiometabolic health including obesity in young adults..
Researchers suggest the adoption of healthy coping strategies for stress management early in life may help prevent cardiometabolic diseases, from heart disease to Type 2 diabetes.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 17, 2024
DALLAS, January 17, 2024 — Young adults who reported higher stress during their teenage years to adulthood were more likely to ...
US air pollution rates on the decline but pockets of inequities remain
2024-01-17
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission ...
Fly brain, mouse brain, worm brain: They all network the same
2024-01-17
New York, January 17, 2024 — In all species, brain function relies on an intricate network of connections that allows neurons to send information back and forth between one another, commanding thought and physical activity. But within those networks a small number of neurons share much stronger connections to one another than all the others. These abnormally strong connections—known as “heavy tailed” based on the shape of their distribution—are thought to play an outsized role in brain function.
Researchers ...
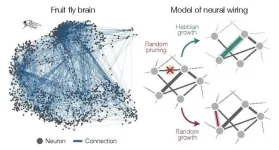
Surprisingly simple model explains how brain cells organize and connect
2024-01-17
A new study by physicists and neuroscientists from the University of Chicago, Harvard and Yale describes how connectivity among neurons comes about through general principles of networking and self-organization, rather than the biological features of an individual organism.
The research, published on January 17, 2024 in Nature Physics, accurately describes neuronal connectivity in a variety of model organisms and could apply to non-biological networks like social interactions as well.
“When you’re building simple models to ...
Transforming clinical recording of deep brain activity with a new take on sensor manufacturing
2024-01-17
Sensors built with a new manufacturing approach are capable of recording activity deep within the brain from large populations of individual neurons–with a resolution of as few as one or two neurons–in humans as well as a range of animal models, according to a study published in the Jan. 17, 2024 issue of the journal Nature Communications. The research team is led by the Integrated Electronics and Biointerfaces Laboratory (IEBL) at the University of California San Diego.
The approach is unique in several ways. It relies on ultra-thin, flexible and customizable probes, made of clinical-grade materials, and equipped with sensors that can record extremely localized ...
Role of inherited genetic variants in rare blood cancer uncovered
2024-01-17
Large-scale genetic analysis has helped researchers uncover the interplay between cancer-driving genetic mutations and inherited genetic variants in a rare type of blood cancer.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, and collaborators, combined various comprehensive data sets to understand the impact of both cancer-driving spontaneous mutations and inherited genetic variation on the risk of developing myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN).
The study, published today (17 January) in Nature Genetics, describes how inherited genetic variants can influence whether a spontaneous mutation in a particular ...
[1] ... [1431]
[1432]
[1433]
[1434]
[1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
1439
[1440]
[1441]
[1442]
[1443]
[1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.