Protein discovery could help solve prostate cancer drug resistance
2024-01-22
SPOKANE, Wash. – Researchers have identified a receptor protein known as CHRM1 as a key player in prostate cancer cells’ resistance to docetaxel, a commonly used chemotherapy drug to treat advanced cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. The discovery opens the door to new treatment strategies that could overcome this resistance. This could ultimately help extend the lives of those with prostate cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer deaths among men.
Led by a team of scientists at Washington State University, ...
Improvement of social isolation and loneliness and excess mortality risk in people with obesity
2024-01-22
About The Study: The findings of this study of 398,000 UK Biobank participants support the improvement of social isolation and loneliness in people with obesity to decrease obesity-related excess risk of mortality.
Authors: Lu Qi, M.D., Ph.D., of the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine in New Orleans, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52824)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
In utero exposure to maternal COVID-19 vaccination and offspring neurodevelopment at 12 and 18 months
2024-01-22
About The Study: The results of this study including 2,261 and 1,940 infants ages 12 and 18 months, respectively, suggest that COVID-19 vaccination was safe during pregnancy from the perspective of infant neurodevelopment to 18 months of age. Additional longer-term research should be conducted to corroborate these findings and buttress clinical guidance with a strong evidence base.
Authors: Eleni G. Jaswa, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5743)
Editor’s ...
Scientists advance affordable, sustainable solution for flat-panel displays and wearable tech
2024-01-22
Key takeaways:
A new 3D-printable material called “supramolecular ink” replaces costly scarce metals with inexpensive, Earth-abundant materials.
The organic material requires far less energy to manufacture than conventional methods.
It could also enhance the sustainability of 3D-printable wearable devices, lighting technologies, and luminescent art and sculpture.
A research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has developed “supramolecular ink,” a new technology for use in OLED (organic light-emitting ...
Innovate UK, the Urban Future Lab, and Greentown Labs announce the Year 4 cohort for their Global Incubator Programme
2024-01-22
Commencing in January, the Urban Future Lab (UFL) at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, in collaboration with Greentown Labs, will serve as the supportive entry point in the U.S. for the fourth cohort of Innovate UK’s Global Incubator Programme: Clean Growth edition. This initiative is specifically designed to foster and assist the establishment of innovative climate technology companies demonstrating significant potential for international scalability into new markets.
The annual program extends the opportunity to eight U.K.-based businesses, enabling them to explore the U.S. market and gain access to esteemed mentors over a six-month period.
"We’re ...
KIER Accelerates Carbon-Neutral Technological Innovation through International Collaboration with Horizon Europe
2024-01-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) promotes active collaborations with prominent European institutions, including leading 'Research & Technology Organisations (RTO), prestigious universities, and small & medium-sized enterprises (SME). KIER has consistently stressed the importance of international collaborations in developing evolving and advanced green technologies. As a consequence, the consortium entitled "Scalable High-power Output and Low-Cost MAde-to-measure Tandem Solar Modules Enabling Specialized PV Applications (SOLMATES)", in which KIER participated and worked as a partner with 13 other ...
Groundbreaking discovery enables cost-effective and eco-friendly green hydrogen production
2024-01-22
A breakthrough technology has been developed that enables the production of green hydrogen in a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner, bringing us closer to a carbon-neutral society by replacing expensive precious metal catalysts.
Led by Professor Jungki Ryu in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST and Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, a joint research team has successfully developed a bifunctional water electrolysis catalyst for the high-efficiency and stable production of high-purity green hydrogen.
The newly-developed catalyst exhibits exceptional durability even in highly corrosive acidic environments. ...
Navigating the ‘big little leap’ to kindergarten
2024-01-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – No matter how well children are prepared for kindergarten, their transition to the classroom during the first few months plays a key role in their success, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that kids who made a more successful transition in the first 10-14 weeks of kindergarten scored higher than others on tests of academic and social-behavioral skills at the end of the school year.
Important parts of the transition – what the researchers called a “big little leap” – included making new friends, ...
Bad to the bone: UMass Amherst engineer aims to prevent fractures in cancer patients
2024-01-22
Bad to the Bone: UMass Amherst Engineer Aims to Prevent Fractures in Cancer Patients
National Cancer Institute funds research to assess if the treatment of cancer metastasis in patients is as damaging as the disease
AMHERST, Mass. – For some patients whose cancer has spread to their bones, the ensuing treatment can be more physically damaging than the original disease, leading to increased bone loss and fracture. Stacyann Bailey, assistant professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has received a two-year grant from the National Cancer Institute to study the complex relationship between drugs used to treat metastatic cancer ...
Breakthrough research enhances stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells
2024-01-22
A team of researchers from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, jointly led by Professors Sung-Yeon Jang, Jungki Ryu, and Ji-Wook Jang, in collaboration with Professor Sang Kyu Kwak from Korea University, have achieved remarkable advancements in the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells. Their groundbreaking work not only paves the way for the commercialization of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), but also offers significant potential in green hydrogen production technology, ensuring long-term operation with high efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered attention due to their reduced toxicity and broad light absorption ...
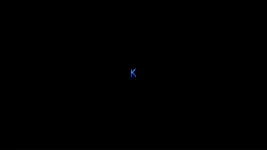
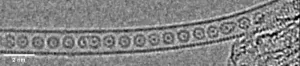
Scientists trap krypton atoms to form one-dimensional gas
2024-01-22
For the first time, scientists have successfully trapped atoms of krypton (Kr), a noble gas, inside a carbon nanotube to form a one-dimensional gas.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used advanced transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods to capture the moment when Kr atoms joined together, one by one, inside a “nano test tube” container with diameter half a million times smaller than the width of a human hair. The research has been published in the journal of the American Chemical Society.
The behaviour of atoms has been studied by scientists ever since it was hypothesized that ...
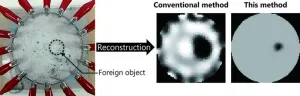
Hybrid machine learning method boosts resolution of electrical impedance tomography for structural imaging
2024-01-22
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-destructive imaging technique used to visualize the interior of materials. In this method, an electric current is injected between two electrodes, creating an electric field, and other electrodes measure distortions caused by the presence of foreign objects inside the material. Compared to other imaging methods, such as X-ray imaging, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, EIT has the advantages of being low cost and less cumbersome as it does not require large magnets or radiation. Therefore, it holds great potential as a non-destructive structural health monitoring ...
New study finds liquid laundry detergent packet exposure burden among young children remains; increase in exposures among older children, teens, and adults
2024-01-22
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – A new study conducted by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy of the Abigail Wexner Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital and the Central Ohio Poison Center investigated trends in calls to poison centers across the country for exposures to liquid laundry detergent packets. The study investigators identified declines in the number, rate and severity of liquid laundry detergent packet exposures among children younger than 6 years. However, the exposure burden remained high. Additionally, exposures have increased among older children, teens and adults.
The study, published in Clinical Toxicology, found that in the most recent ...
Food from urban agriculture has carbon footprint 6 times larger than conventional produce, study shows
2024-01-22
Photos
A new University of Michigan-led international study finds that fruits and vegetables grown in urban farms and gardens have a carbon footprint that is, on average, six times greater than conventionally grown produce.
However, a few city-grown crops equaled or outperformed conventional agriculture under certain conditions. Tomatoes grown in the soil of open-air urban plots had a lower carbon intensity than tomatoes grown in conventional greenhouses, while the emissions difference between conventional and urban agriculture vanished for air-freighted crops like asparagus.
"The exceptions revealed by our ...
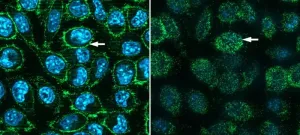
Scientists make COVID receptor protein in mouse cells
2024-01-22
UPTON, NY—A team of scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Columbia University has demonstrated a way to produce large quantities of the receptor that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, binds to on the surface of human cells. That binding between the now-infamous viral spike protein and the human “ACE2” receptor is the first step of infection by the virus. Making functional human ACE2 protein in mouse cells gives scientists a new way to study these receptors and potentially put them to use. In addition, as described in a paper just published in the journal Virology, the ...
Researchers unveil new way to counter mobile phone ‘account takeover’ attacks
2024-01-22
Computer science researchers have developed a new way to identify security weaknesses that leave people vulnerable to account takeover attacks, where a hacker gains unauthorized access to online accounts.
Most mobiles are now home to a complex ecosystem of interconnected operating software and Apps, and as the connections between online services has increased, so have the possibilities for hackers to exploit the security weaknesses, often with disastrous consequences for their owner.
Dr Luca Arnaboldi, from the University of Birmingham’s School of Computer Science, explains: “The ruse of looking over someone’s shoulder to find out their PIN is well known. ...
What factors affect patients’ decisions regarding active surveillance for low-risk prostate cancer?
2024-01-22
Because low-risk prostate cancer is unlikely to spread or impact survival, experts and guidelines recommend active surveillance, which involves regular monitoring and thus avoid or delay treatment like surgery or radiation therapy and their life-changing complications. A new study examined the rates of active surveillance use and evaluated the factors associated with selecting this management strategy over surgery or radiation, with a focus on underserved Black patients who have been underrepresented in prior studies. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, called the Treatment ...
New sustainable method for creating organic semiconductors
2024-01-22
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a new, more environmentally friendly way to create conductive inks for use in organic electronics such as solar cells, artificial neurons, and soft sensors. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, pave the way for future sustainable technology.
Organic electronics are on the rise as a complement and, in some cases, a replacement to traditional silicon-based electronics. Thanks to simple manufacturing, high flexibility, and low weight combined with the electrical properties typically associated with traditional semiconductors, it can be useful for applications such as digital displays, energy storage, ...
Digital dice and youth: 1 in 6 parents say they probably wouldn’t know if teens were betting online
2024-01-22
As young people increasingly have access and exposure to online gambling, only one in four parents say they have talked to their teen about some aspect of virtual betting, a national poll suggests.
But over half of parents aren’t aware of their state’s legal age for online gambling and one in six admit they probably wouldn’t know if their child was betting online, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
“Teens and young adults may have a difficult time going ...
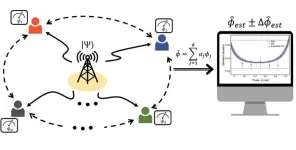
Enable distributed quantum sensors for simultaneous measurements in distant places
2024-01-22
We've all had the experience of trying to get the exact time of a highly competitive concert ticket or class beforehand. If the time in Seoul and Busan is off by even a fraction of an hour, one will be less successful than the other. Sharing the exact time between distant locations is becoming increasingly important in all areas of our lives, including finance, telecommunications, security, and other fields that require improved accuracy and precision in sending and receiving data.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that Dr. Hyang-Tag Lim and his team at the Center ...
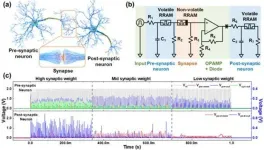
Implement artificial neural network hardware systems by stacking them like "neuron-synapse-neuron" structural blocks
2024-01-22
With the emergence of new industries such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and machine learning, the world's leading companies are focusing on developing next-generation artificial intelligence semiconductors that can process vast amounts of data while consuming energy efficiently. Neuromorphic computing, inspired by the human brain, is one of them. As a result, devices that mimic biological neurons and synapses are being developed one after another based on emerging materials and structures, but research on integrating individual devices into a system to verify and optimize them ...
The megalodon was less mega than previously believed
2024-01-22
A new study shows the Megalodon, a gigantic shark that went extinct 3.6 million years ago, was more slender than earlier studies suggested. This finding changes scientists’ understanding of Megalodon behavior, ancient ocean life, and why the sharks went extinct.
The Megalodon or megatooth shark is typically portrayed as a super-sized monster in popular culture, with recent examples in the sci-fi films “The Meg” (2018) and “Meg 2: The Trench” (2023). Previous studies assume that the shark likely reached lengths of at least 50 feet and possibly as much as 65 feet.
However, the Megalodon is largely known only from its teeth and vertebrae in the ...
Slender shark: Study finds Megalodon was not like a gigantic great white shark
2024-01-22
CHICAGO — A new scientific study shows that the prehistoric gigantic shark, Megalodon or megatooth shark, which lived roughly 15-3.6 million years ago nearly worldwide, was a more slender shark than previous studies have suggested.
Formally called Otodus megalodon, it is typically portrayed as a super-sized, monstrous shark in novels and sci-fi films, including “The Meg.” Previous studies suggest the shark likely reached lengths of at least 50 to 65 feet (15 to 20 meters). However, ...
New criteria for sepsis in children based on organ dysfunction
2024-01-21
Clinician-scientists from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago were among a diverse, international group of experts tasked by the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) with developing and validating new data-based criteria for sepsis in children. Sepsis is a major public heath burden, claiming the lives of over 3.3 million children worldwide every year. The new pediatric sepsis criteria – called the Phoenix criteria – follow the paradigm shift in the recent adult criteria that define sepsis as severe ...
Development and validation of the Phoenix criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock
2024-01-21
About The Study: In this international, multicenter, retrospective cohort study including more than 3.6 million pediatric encounters, a novel score, the Phoenix Sepsis Score, was derived and validated to predict mortality in children with suspected or confirmed infection. The new criteria for pediatric sepsis and septic shock based on the score performed better than existing organ dysfunction scores and the International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria.
Authors: Tellen D. Bennett, M.D., M.S., of the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
[1] ... [1435]
[1436]
[1437]
[1438]
[1439]
[1440]
[1441]
[1442]
1443
[1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
[1451]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.