$24 million grant to extend Study of Healthy Aging in African Americans (STAR)
2024-01-17
Researchers at UC Davis Health and Kaiser Permanente Division of Research have received a $24 million grant from the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to continue the Study of Healthy Aging in African Americans (STAR) for an additional five years.
STAR, which launched in 2017, follows a group of approximately 750 older adults to understand how behaviors and lifestyle may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias for Black and African Americans. The study ...
Metastatic breast cancer treatments have aided decline in deaths, Stanford Medicine-led study finds
2024-01-17
Deaths from breast cancer dropped 58% between 1975 and 2019 due to a combination of screening mammography and improvements in treatment, according to a new multicenter study led by Stanford Medicine clinicians and biomedical data scientists.
Nearly one-third of the decrease (29%) is due to advances in treating metastatic breast cancer —a form that has spread to other areas of in the body and is known as stage 4 breast cancer or recurrent cancer. Although these advanced cancers are not considered curable, women with metastatic disease are living longer than ever.
The analysis helps cancer researchers assess where to focus future efforts and resources.
“We’ve ...
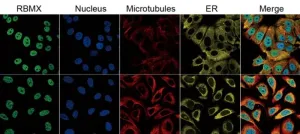
Aberrant RBMX expression relevant for cancer prognosis and immunotherapy response
2024-01-17
“In the future, targeting of RBMX may be a novel method in cancer therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “Aberrant RBMX expression is relevant for cancer prognosis and immunotherapy response.”
Cancer accounts for the highest rates of morbidity and mortality worldwide. RNA binding motif protein X-linked (RBMX) is a nuclear ...
Higher measurement accuracy opens new window to the quantum world
2024-01-17
A team at HZB has developed a new measurement method that, for the first time, accurately detects tiny temperature differences in the range of 100 microkelvin in the thermal Hall effect. Previously, these temperature differences could not be measured quantitatively due to thermal noise. Using the well-known terbium titanate as an example, the team demonstrated that the method delivers highly reliable results. The thermal Hall effect provides information about coherent multi-particle states in quantum materials, based on their interaction with lattice vibrations (phonons).
The laws of quantum physics apply to all materials. However, in so-called ...
National collaborative for health equity roundtable: a call for unity and the power of racial healing
2024-01-17
A new Roundtable discussion in the peer-reviewed journal Health Equity explores the results of a poll conducted by the National Collaborative for Health Equity (NCHE), called the “Heart of America Annual Survey.” The survey found that more than 80% of respondents want a national leader that unifies rather than divides us, suggesting that there is a readiness in the country to put polarization and division behind us so that we can solve our collective and common challenges and problems. Click here to read the Roundtable now.
Moderating ...
New project to improve modeling of climate change
2024-01-17
Jingrui He, professor of information sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has been awarded a two-year, $600,000 grant from the IBM-Illinois Discovery Accelerator Institute to improve modeling climate change and its impact across multiple application domains. He and a team of researchers from the University of Illinois and IBM will build Climate Runtime, a computational framework integrating cutting-edge capabilities from climate foundation models and multimodal fusion. This framework will allow for accurate prediction and quantification of weather and climate events and their impact in areas such as finance ...
Climate change isn’t producing expected increase in atmospheric moisture over dry regions
2024-01-17
Contacts:
David Hosansky, UCAR and NSF NCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
Audrey Merket, UCAR and NSF NCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
The laws of thermodynamics dictate that a warmer atmosphere can hold more water vapor, but new research has found that atmospheric moisture has not increased as expected over arid and semi-arid regions of the world as the climate has warmed.
The findings are particularly puzzling because climate models have been predicting ...
New research highlights unprecedented targeted approach to treating triple-negative breast cancer
2024-01-17
Cleveland Clinic researchers have successfully developed a therapeutic peptide that blocks aggressive cancer cells from multiplying rapidly. The results highlight a potential new strategy for developing targeted treatments for triple-negative breast cancer, which currently has no approved options.
Targeted drugs attack cancer cell functions directly, offering a more precise approach to complement broader treatments like chemotherapy. A research team led by Ofer Reizes, PhD, and Justin Lathia, PhD, designed a peptide therapeutic that disrupts the molecular processes behind aggressive cancer growth when delivered into cells.
The ...
ASBMB names Mona V. Miller as next executive officer
2024-01-17
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology today named Mona V. Miller its next chief executive officer, effective April 1.
Miller is an experienced association leader with significant experience in strategic planning, advocacy and fundraising. Most recently, she was CEO of the American Society of Human Genetics. Before that she held multiple high-level positions at the Society for Neuroscience.
Miller said she was drawn to the ASBMB because “scientifically, biochemistry and molecular biology is at the forefront of knowledge that is transforming health and society.”
She said she looks forward to “focusing on the pivotal ...
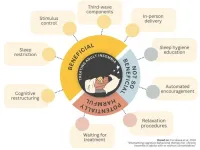
Streamlining cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic insomnia
2024-01-17
A combination of cognitive and behavioral strategies, ideally delivered in person by a therapist, maximizes the benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), according to new research. CBT-I is a form of talk therapy, which can be delivered in person or through self-help guides. By analyzing 241 studies, involving over 30,000 adults, researchers identified the most beneficial components of CBT-I. These included: cognitive restructuring, third-wave components, sleep restriction, stimulus control and in-person delivery. Self-help with human encouragement could also be beneficial, while waiting for active treatment and enforcing ...
Prenatal opioid exposure and immune-related conditions in children
2024-01-17
About The Study: Prenatal opioid exposure was associated with an increased risk of infection, eczema and dermatitis, and asthma, but not allergies and anaphylaxis or autoimmune conditions in this study of 401,000 neonates. These findings highlight the importance of further study of opioid-induced immune changes during pregnancy, the potential impact on long-term health in exposed children, and the mechanisms of opioid-induced immune dysregulation.
Authors: Erin Kelty, Ph.D., of the University of Western Australia in Crawley, Western Australia, ...
Comparative effectiveness of psychotherapy vs antidepressants for depression in heart failure
2024-01-17
About The Study: In this comparative effectiveness trial of behavioral activation psychotherapy (BA) and antidepressant medication management (MEDS) in 416 patients with heart failure experiencing depression, both treatments significantly reduced depressive symptoms by nearly 50% with no statistically significant differences between treatments. BA recipients experienced better physical health-related quality of life, fewer emergency department visits, and fewer days hospitalized. The study findings suggest that patients with heart failure could be given the choice between BA or MEDS to ameliorate depression.
Authors: Waguih ...
Origin of intense light in supermassive black holes and tidal disruption events revealed
2024-01-17
A new study by Hebrew University is a significant breakthrough in understanding Tidal Disruption Events (TDEs) involving supermassive black holes. The new simulations, for the first time ever, accurately replicate the entire sequence of a TDE from stellar disruption to the peak luminosity of the resulting flare. This study has unveiled a previously unknown type of shockwave within TDEs, settling a longstanding debate about the energy source of the brightest phases in these events. It confirms that shock dissipation powers the brightest weeks ...
Astronomers detect oldest black hole ever observed
2024-01-17
Researchers have discovered the oldest black hole ever observed, dating from the dawn of the universe, and found that it is ‘eating’ its host galaxy to death.
The international team, led by the University of Cambridge, used the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to detect the black hole, which dates from 400 million years after the big bang, more than 13 billion years ago. The results, which lead author Professor Roberto Maiolino says are “a giant leap forward”, are reported ...
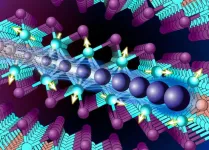
Columbia chemists create the first 2D heavy fermion
2024-01-17
Researchers at Columbia University have successfully synthesized the first 2D heavy fermion material. They introduce the new material, a layered intermetallic crystal composed of cerium, silicon, and iodine (CeSiI), in a research article published today in Nature.
Heavy fermion compounds are a class of materials with electrons that are up to 1000x heavier than usual. In these materials, electrons get tangled up with magnetic spins that slow them down and increase their effective mass. Such interactions are ...
Therapy versus medication: comparing treatments for depression in heart disease
2024-01-17
New research by investigators from the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences at Cedars-Sinai shows that behavioral activation therapy is as effective as antidepressant medications in treating symptoms of depression in patients with heart failure.
Heart failure affects nearly 6 million adults in the United States, and approximately 50% of heart failure patients experience symptoms of depression along with their condition. Past studies show patients with heart failure and depression have lower cardiac function, more emergency department ...
Active membranes: The future of fresh water is bright
2024-01-17
The growth of Los Angeles as a startup hub is highlighted by a robust and diverse entrepreneurial ecosystem within UCLA. The Magnify Incubator at CNSI is no exception to showcasing the range of early-stage businesses.
One such company within the Magnify incubator, Active Membranes, is innovating the future of fresh water through membrane desalination. As freshwater is becoming increasingly scarce around the globe, resources such as seawater and industrial wastewater are costly to procure and operate. The company’s patented technology is electrically conducting ...
What’s stopping US climate policies from working effectively
2024-01-17
In an effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and curb global warming, the U.S. has enacted several ambitious federal laws, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) passed in 2022 and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) of 2021.
These provide significant investments in clean energy projects and encourage technological innovations. Some analyses suggest they could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by more than 40% below 2005 levels by 2030.
However, in a paper published Jan. 16 in the journal Nature Climate Change, researchers at the University ...
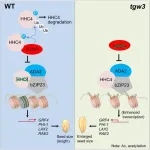
Chromatin modifier-centered pathway points to higher crop yield
2024-01-17
Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins that makes up the genetic material in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A chromatin modifier is a protein or complex of proteins that chemically modifies the structure of chromatin. Chromatin modifiers play a crucial role in regulating the expression of genes, which are segments of DNA strands, as well as in other chromatin-related processes. These modifiers mainly work by adding or subtracting chemical groups to histones, a type of protein within the chromatin, or to the DNA itself.
In the scientific effort to manipulate the expression of plant genes, such as for grain size or drought-resistance, etc., understanding the influence ...
U.S. voters’ climate change opinions swing elections
2024-01-17
When voters cast their ballots in the 2016 and 2020 presidential elections, many were driven by their concern for climate change, according to new research out of CU Boulder’s Center for Environmental Futures (C-SEF). The new report determined that views on climate change played a significant role in whom people voted for, concluding that the climate issue very likely cost Republicans the 2020 election, all else equal.
“This is obviously information that politicians and advocates across the political spectrum will want to know, heading into the 2024 election cycle,” said Matthew Burgess, CIRES Fellow and C-SEF director. “How ...
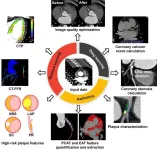
Artificial intelligence helps coronary CT angiography and accelerates the development of precision medicine
2024-01-17
This review was jointly published by Prof. Long-Jiang Zhang (Department of Radiology, Jinling Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University) and Prof. Christian Tesche (Division of Cardiovascular Imaging, Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Medical University of South Carolina and Department of Cardiology, Munich University Clinic, Ludwig-Maximilian-University).
With the continuous progress of science and technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an important driving force for a new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial change. It aims to mimic human consciousness and thought processes, continuously ...
New research finds half-cardio, half-strength training reduces cardiovascular disease risks
2024-01-17
AMES, Iowa — Approximately one in three deaths in the U.S. is caused by cardiovascular disease, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A robust body of evidence shows aerobic exercise can reduce risks, especially for people who are overweight or obese. But few studies have compared results with resistance exercise — also known as strength or weight training — or with workout regimens that are half aerobic and half resistance. Researchers at Iowa State University led one of the longest and largest supervised exercise trials to ...
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group melanoma research team led by Michael Atkins, MD, receives the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction from the Journal of Clinical Oncology
2024-01-17
A team of melanoma researchers with the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) is honored with the 2023 Paper of the Year distinction by the Journal of Clinical Oncology. The recognition is for the results of the DREAMseq randomized phase 3 clinical trial. DREAMseq (EA6134) showed an optimal treatment sequence for combination therapy in patients with advanced melanoma with a BRAFV600 tumor gene mutation. The treatment sequence beginning with immunotherapy (nivolumab and ipilimumab), followed by targeted therapy (dabrafenib and trametinib) if there was disease progression, resulted ...
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition launches new article series to educate physicians and other health care professionals on nutrition
2024-01-17
Rockville, MD (January 16, 2024) – To educate physicians and other health care professionals on the fundamentals of nutrition, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has launched a new article series titled Nutrition for the Clinician. The effort supports the White House National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health and its directives to expand nutrition knowledge of health care providers, an effort long supported by the American Society for Nutrition. Nancy Krebs, MD, MS, Professor of Pediatrics, University of Colorado ...
New research shows that most early galaxies looked like breadsticks rather than pizza pies or dough balls
2024-01-17
Columbia researchers analyzing images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found that galaxies in the early universe are often flat and elongated, like breadsticks—and are rarely round, like balls of pizza dough. “Roughly 50 to 80% of the galaxies we studied appear to be flattened in two dimensions,” explained Viraj Pandya, a NASA Hubble Fellow at Columbia University, and the lead author of a new paper slated to appear in The Astrophysical Journal that outlines the findings. “Galaxies that look like long, thin breadsticks seem to be very common in the early universe, which is surprising, since they are uncommon among galaxies ...
[1] ... [1443]
[1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
1451
[1452]
[1453]
[1454]
[1455]
[1456]
[1457]
[1458]
[1459]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.