Protecting newborns: Research lays the groundwork for a lifesaving vaccine
2024-01-09
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Researchers from Binghamton University, State University of New York are unraveling the workings of Group B Strep (GBS) infections in pregnant women, which could someday lead to a vaccine.
One in five pregnant women carry Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Strep or GBS) in the vaginal tract, which is typically harmless — except when it isn’t.
The bacterial infection poses serious and even fatal consequences for newborns, including pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis, which can have long-term effects on the child’s cognitive function.
Researchers ...
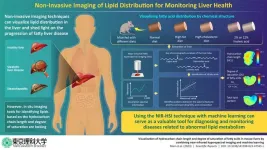
New study unveils machine learning-aided non-invasive imaging for rapid liver fat visualization
2024-01-09
Steatotic liver disease (SLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which includes a range of conditions caused by fat build-up in the liver due to abnormal lipid metabolism, affects about 25% of the population worldwide, making it the most common liver disorder. Often referred to as “silent liver disease,” SLD progresses without noticeable symptoms and can lead to more severe conditions like cirrhosis (liver scarring) and liver cancer.
A liver biopsy—an invasive procedure involving liver tissue sample extraction from the body—is ...
Towards more accurate 3D object detection for robots and self-driving cars
2024-01-09
Robotics and autonomous vehicles are among the most rapidly growing domains in the technological landscape, with the potential to make work and transportation safer and more efficient. Since both robots and self-driving cars need to accurately perceive their surroundings, 3D object detection methods are an active area of study. Most 3D object detection methods employ LiDAR sensors to create 3D point clouds of their environment. Simply put, LiDAR sensors use laser beams to rapidly scan and measure the ...
How fruit bats got a sweet tooth without sour health
2024-01-09
Levi Gadye, 628-399-1046
Levi.Gadye@ucsf.edu | @UCSF
Video: https://ucsf.app.box.com/s/i3atd54ye4m1z1spi0qf59axq7tq7640
Subscribe to UCSF News
A high-sugar diet is bad news for humans, leading to diabetes, obesity and even cancer. Yet fruit bats survive and even thrive by eating up to twice their body weight in sugary fruit every day.
Now, UC San Francisco scientists have discovered how fruit bats may have evolved to consume so much sugar, with potential implications for the 37 million Americans with diabetes. The findings, published on Tuesday, Jan. 9, 2024 in Nature Communications, point to adaptations ...
Vaccine demonstrates potential in delaying relapse of KRAS-mutated pancreatic and colorectal cancers
2024-01-09
HOUSTON ― A vaccine showed potential to prevent relapse of KRAS-mutated pancreatic and colorectal cancers for patients who had previously undergone surgery, according to a Phase I trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Results were published today in Nature Medicine.
In the trial, patients with pancreatic and colorectal cancer who were considered at high risk of relapse received a maximum of 10 doses of the ELI-002 vaccine targeted toward KRAS G12D and G12R mutations. T cell responses were seen in 84% of all patients and in 100% of those in the two highest dose cohorts, including those who ...
Smart skin bacteria are able to secrete and produce molecules to treat acne
2024-01-09
International research led by the Translational Synthetic Biology Laboratory of the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University has succeeded in efficiently engineering Cutibacterium acnes -a type of skin bacterium- to produce and secrete a therapeutic molecule suitable for treating acne symptoms. The engineered bacterium has been validated in skin cell lines and its delivery has been validated in mice. This finding opens the door to broadening the way for engineering non-tractable bacteria to address skin alterations and other diseases using living therapeutics.
The research team is completed by scientists from the Bellvitge Biomedical Research ...
Stranger than friction: A force initiating life
2024-01-09
As the potter works the spinning wheel, the friction between their hands and the soft clay helps them shape it into all kinds of forms and creations. In a fascinating parallel, sea squirt oocytes (immature egg cells) harness friction within various compartments in their interior to undergo developmental changes after conception. A study from the Heisenberg group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), published in Nature Physics, now describes how this works.
The sea is full of fascinating life forms. From algae and colorful fish to marine snails and sea squirts, a completely different world reveals itself underwater. Sea squirts or ascidians in particular are very unusual: ...
Different biological variants discovered in Alzheimer's disease
2024-01-09
Dutch scientists have discovered five biological variants of Alzheimer's disease, which may require different treatment. As a result, previously tested drugs may incorrectly appear to be ineffective or only minimally effective. This is the conclusion of researcher Betty Tijms and colleagues from Alzheimer Center Amsterdam, Amsterdam UMC and Maastricht University. The research results will be published on 9 January in Nature Aging.
In those with Alzheimer's disease, the amyloid and tau protein clump in the brain. In addition to these clumps, other biological processes such as inflammation and nerve ...
Alzheimer Europe adopts position on anti-amyloid therapies for Alzheimer’s disease, issuing a call to action for timely, safe and equitable access
2024-01-09
Luxembourg, 9 January 2024 – In a new position paper, and following engagement with its national members and the European Working Group of People with Dementia (EWGPWD), Alzheimer Europe calls for concrete actions to enable timely, safe and equitable access to anti-amyloid drugs, for patients who are most likely to benefit from these innovative new treatments for Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
The growing prevalence and impact of AD has catalysed huge investments in research on its causes, diagnosis, treatment and care. After many high-profile ...
Improved cellular recycling could benefit patients with neurodegenerative conditions
2024-01-09
For the first time, a research team at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) has uncovered a way to potentially reduce the amount of toxic cellular waste accumulating in patients with Zellweger Spectrum Disorder (ZSD).
ZSD is a group of rare, neurodegenerative genetic conditions caused by genetic variations that reduce the number of peroxisomes – the parts of cells that are responsible for, among other tasks, breaking down fats. ZSD varies in severity and is characterized by progressive neurodegeneration as well as symptoms that range from visual impairments, such as cataracts, to liver and kidney disfunction.
Like all living ...
Green ammonia could decarbonize 60% of global shipping when offered at just 10 regional fuel ports
2024-01-09
A study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability has found that green ammonia could be used to fulfil the fuel demands of over 60% of global shipping by targeting just the top 10 regional fuel ports. Researchers at the University of Oxford looked at the production costs of ammonia which are similar to very low sulphur fuels, and concluded that the fuel could be a viable option to help decarbonise international shipping by 2050.
Around USD 2 trillion will be needed to transition to a green ammonia fuel supply chain by 2050, primarily to finance ...
Samsung leads again in U.S. patents while Qualcomm leaps into second place; overall grants dip 3.4%
2024-01-09
New Haven, Conn., Jan. 9, 2024—U.S. patent grants declined 3.4% from 2022, the lowest level since 2019, and Samsung held onto the top spot for the second year in a row according to IFI CLAIMS Patent Services, world leader in tracking patent application and grant data.
IFI CLAIMS Patent Services is a Digital Science company that compiles and tracks data from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and other patent-issuing agencies around the globe. IFI translates its world-leading data into an annual U.S. Top 50 and IFI Global 250 patent rankings, providing valuable insights into companies’ R&D activity.
Other findings in IFI’s latest rankings include patent powerhouse ...
Severe MS predicted using machine learning
2024-01-09
A combination of only 11 proteins can predict long-term disability outcomes in multiple sclerosis (MS) for different individuals. The identified proteins could be used to tailor treatments to the individual based on the expected severity of the disease. The study, led by researchers at Linköping University in Sweden, has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
“A combination of 11 proteins predicted both short and long-term disease activity and disability outcomes. We also concluded that it’s important to measure ...
Combining anti-tumor drugs with chemo may improve rare children’s cancer outcomes
2024-01-09
Children who develop neuroblastomas, a rare form of cancer which develops in nerve cells, may benefit from receiving certain anti-tumour drugs as well as chemotherapy, a new trial has found.
The results of the BEACON trial conducted by the Cancer Research UK Clinical Trials Unit at the University of Birmingham found that combining anti-angiogenic drugs, which block tumours from forming blood vessels, alongside various chemotherapy drugs led to more young people seeing their tumours shrinking, from 18% in the control group to 26% among those on Bevacizumab.
The findings are published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology today. The trial saw 160 young ...
EBRAINS research infrastructure secures €38 million in funding for new phase of digital neuroscience
2024-01-09
The European Commission has accepted the EBRAINS 2.0 proposal submitted in response to the INFRASERV call, granting €38 million for the further development of services of the EBRAINS research infrastructure.
The European Commission has signed a grant agreement to fund EBRAINS with €38 million until 2026. Over the next three years, the infrastructure will continue to develop tools and services to widely serve research communities in neurosciences, brain medicine, and brain-inspired technologies.
EBRAINS (European Brain Research Infrastructures) is an EU co-funded collaborative research platform designed to advance neuroscience and brain ...
Train your brain to overcome tinnitus
2024-01-09
An international research team has shown that the debilitating impact of tinnitus can be effectively reduced in just weeks by a training course and sound therapy delivered via a smartphone app.
The team from Australian, New Zealand, French and Belgian universities report these findings today in Frontiers in Audiology and Otology.
It offers some hope for millions affected by tinnitus who:
have been told that there is nothing they can do about it
face long queues waiting for treatment, or
can’t afford the costs of specialist support.
The initial trial worked with 30 sufferers, of whom almost two thirds experienced a ‘clinically ...
A chemical reaction key to various industries just got greener
2024-01-09
Osaka, Japan – From alleviating your allergy symptoms to optimizing herbicide performance, alkylamines are molecules that have many uses. Unfortunately, common methods of producing alkylamines result in harmful waste byproducts. A method of synthesizing alkylamines in a sustainable yet cost-effective way has thus been highly sought after.
Now, in a study recently published in Green Chemistry, a research team led by Osaka University has found a way. The team has developed a method of alkylamine synthesis that works under mild conditions and produces ...
Spanish butterflies better at regulating their body temperature than their British cousins
2024-01-09
Butterfly populations in Catalonia in northern Spain are better than their UK counterparts at regulating their body temperature by basking in the sunshine, but rising global temperatures due to climate change may put Spanish butterflies at greater risk of extinction.
An international study, led by the University of Cambridge and the Institut de Biologia Evolutiva (IBE) in Barcelona, found that butterflies use different methods to regulate their body temperature. In Catalonia, butterflies tend to angle ...
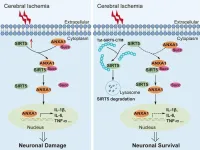
A novel cell-penetrating peptide exerts therapeutic effects against ischemic stroke
2024-01-09
This study is led by Dr. Xing Li and Dr. Yilin Zhao (Department of Anesthesiology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Geriatric Anesthesia and Perioperative Brain Health, and Wuhan Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Anesthesia, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology). The team's previous research found that the increase in SIRT5 in microglia induced by ischemic stroke causes annexin-A1 (ANXA1) desuccinylation, which decreases ANXA1 membrane recruitment and secretion but promotes ANXA1 nuclear translocation, resulting in the production of proinflammatory ...
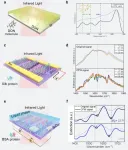
Ultrasensitive molecular sensing with synthesize complex-frequencey waves
2024-01-09
Sensors are essential tools for detecting and analyzing trace molecules in a variety of fields, including environmental monitoring, food safety, and public health. However, developing sensors with high enough sensitivity to detect these tiny amounts of molecules remains a challenge.
One promising approach is surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), which uses plasmonic nanostructures to amplify the infrared signals of molecules adsorbed on their surface. Graphene is a particularly promising material for SEIRA because of its high ...
Creating novel amino acid nanoparticles with enhanced anticancer activity
2024-01-09
Ishikawa, Japan -- Amino acids, such as tyrosine and tryptophan, are the fundamental building blocks that make up proteins. These biomolecules have different chemical groups on each end and side chain, and so, have the natural ability to form a chain through the formation of an amide (peptide) bond. However, such linkages are weak and easily degraded under physiological conditions. This is where the Fmoc-protected amino acids come into the picture.
In a new study now, a research team led by Dr. Eijiro Miyako, Associate ...
A landscape-based approach to urban heritage management: People, spatial biography, and ecosystem
2024-01-09
This article first identifies the current definition of urban heritage that includes both “old” and “young” monuments. Their protection has also shifted from solely preserving “old” values into a more holistic process to retain “old” values and manage the change in their adaptive reuse to gain “new” values, towards a more people-centered and landscape-based approach. Furthermore, a concept of ecosystem for urban planning and development is introduced, ...
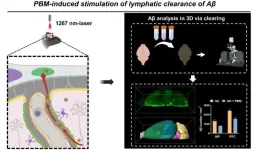
Photostimulation: non-invasive and effective therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease
2024-01-09
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder. β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition in the brain is a crucial contributor to the pathogenesis of AD, mitigating excessive cerebral Aβ burden has been considered as a possible therapeutic strategy for AD. Meningeal lymphatic vessels (MLVs) are recently discovered structures responsible for exchanging soluble components between the cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid, and have been proved to be a potential pathway of Aβ drainage.
Researchers at Huazhong University ...
Love scrambles the brain and scientists can now tell us why
2024-01-09
Love is blind, the saying goes, and thanks to a world-first Australian study, we are now a step closer to understanding why.
It is well known that romantic love changes the brain, releasing the so-called love hormone oxytocin, responsible for the euphoria we feel when falling in love.
Now, researchers from the ANU, University of Canberra and University of South Australia have measured how a part of the brain is responsible for putting our loved one on a pedestal in that first flush of romance.
In the world’s first study investigating the link between the human brain’s behavioural activation ...
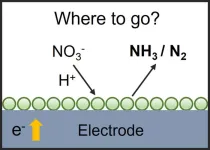
Where to go with nitrate electroreduction reaction?
2024-01-09
Ammonia is a necessary feedstock to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and polymers. To date, about 80% of global ammonia is used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers which relates to 50% of global food production. The global production of ammonia is about 180 million metric tons per year through the carbon-intensive and highly energy-consuming Haber-Bosch process. The high energy consumption, high carbon intensity, and high capital investment of the Haber-Bosch process make the development of environmentally sustainable and affordable routes for ammonia synthesis under ambient conditions more urgent. The electrochemical ammonia ...
[1] ... [1448]
[1449]
[1450]
[1451]
[1452]
[1453]
[1454]
[1455]
1456
[1457]
[1458]
[1459]
[1460]
[1461]
[1462]
[1463]
[1464]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.