What if cows could talk?
2024-01-16
You may not know it, but cows share information every time they burp, moo, and chew that speaks volumes about their health and welfare.
Through the work of researchers in Virginia Tech’s College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, we may soon know more about what cows are “telling” us and be able to use that information to improve their well-being.
James Chen, an animal data sciences researcher and assistant professor in the School of Animal Sciences is using a $650,000 grant from the U.S. Department ...
Allen Fawcett named Director of the Joint Global Change Research Institute
2024-01-16
By Greg Koller
COLLEGE PARK, Md.— Allen Fawcett — an energy expert and economist who has played a leading role in formulating and coordinating U.S. climate policy — is the new director of the Joint Global Change Research Institute.
Fawcett joined the Environmental Protection Agency in 2003 and, since 2012, served as the chief of EPA’s Climate Economics Branch, which advances the science of climate economics to inform policy. From 2010 to 2011, Fawcett took leave from EPA to serve as the deputy associate director for energy ...
Parents more likely to attempt suicide in first years after child’s cancer diagnosis
2024-01-16
Parents who have a child with cancer are more likely to attempt suicide during the first years after diagnosis, according to a new study conducted by Qianwei Liu of Southern Medical University, China, and colleagues, published January 16th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
Receiving a cancer diagnosis for a child is an incredibly stressful and distressing experience for parents. These parents, especially mothers, face an increased risk of psychiatric disorders, but little is known about the risk of suicide. In the new study, researchers looked at the number of suicide attempts ...
Energy-starved breast cancer cells consume their surroundings for fuel
2024-01-16
New study from the University of Sheffield identifies a novel mechanism employed by breast cancer cells to survive in the challenging environment within tumours
The findings provide a new insight into a previously unknown mechanism of cancer cell survival and may offer a new target for developing therapies
The research found breast cancer cells take advantage of nutrients in the extracellular matrix in times of nutrient starvation
Energy starved breast cancer cells ingest and consume their surroundings to overcome starvation, a new study has found.
The research, conducted by scientists at the University of Sheffield and published today (Tuesday 16 January ...
How did free wi-fi help unlock Hanoi wet markets’ mysteries?
2024-01-16
Researchers at the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT and their collaborators have been working on how to harness the power of the estimated 549 million Wifi hotspots worldwide, resulting in a project that used anonymized data gathered from free Wi-Fi to better understand the impact of COVID-19 on Hanoi’s wet markets during the first stage of the Covid-19 pandemic.
In the paper “Using free Wi-Fi to assess impact of COVID-19 pandemic on traditional wet markets in Hanoi” published in December 2023 in the scientific journal Food Security, the researchers analyzed and interpreted mobile device tracking ...
Smooth operation of future nuclear fusion facilities is a matter of control
2024-01-16
As researchers around the world work to develop viable alternatives to fossil fuels, the prospect of nuclear fusion—harnessing the same energy-generating reactions that power the sun—has grown increasingly attractive to private equity firms.
In 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy launched a partnership with investors in the private sector to accelerate the development of fusion energy, in part through the development of a fusion pilot plant, or FPP, in the United States.
The FPP and ITER—the world’s largest nuclear fusion reactor, currently being ...
Microfossils shed light on the long fossil record of euglenoids
2024-01-16
Hiding in the shadows, euglenoids are a fascinating group of single-celled protists that are neither plant nor animal. Plants photosynthesize, and animals eat. Euglenoids do both. Spiraling along the murky bottoms of shallow fresh-water ponds with their long flagella, they eat organic goop, while also using their chloroplasts to convert CO2 and water with light into sugars. Because of this in-between status, euglenoids have been placed close to the very base of the eukaryotic branch on the tree-of-life that includes ...
Amnesia caused by head injury reversed in early mouse study
2024-01-16
WASHINGTON - A mouse study designed to shed light on memory loss in people who experience repeated head impacts, such as athletes, suggests the condition could potentially be reversed. The research in mice finds that amnesia and poor memory following head injury is due to inadequate reactivation of neurons involved in forming memories.
The study, conducted by researchers at Georgetown University Medical Center in collaboration with Trinity College Dublin, Ireland, is reported January 16, 2024, in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Importantly for diagnostic and treatment purposes, the researchers found that the memory loss attributed to head injury was not a permanent pathological event driven by ...
Domesticating plants impacts their microbiome, study finds
2024-01-16
New research led by the University of Oxford indicates that human domestication of crops can alter the communities of microorganisms that are associated with plants. Intriguingly, independent domestication events were found to have similar impacts on the plant microbiome. The results have been published today in Current Biology.
Lead researcher Dr Riccardo Soldan (Department of Biology, University of Oxford) said: 'Our study provides evidence that regardless of where and how domestication took place, domesticated ...
Reductive carboxylation of glutamine as a potential target in AML
2024-01-16
“Identification and validation of novel and targetable metabolic weaknesses in AML is ongoing.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 16, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on December 1, 2023, entitled, “Reductive carboxylation of glutamine as a potential target in acute myeloid leukemia.”
In this new editorial, researchers Alessia Roma, Lawrence D. Goodridge and Paul A. Spagnuolo from the University of Guelph discuss acute myeloid leukemia (AML) — an aggressive cancer of the blood and bone marrow ...
Identity concealment in sexual minority men may have impeded mpox care
2024-01-16
ITHACA, N.Y. – Openly gay, bisexual and other sexual minority men were more likely than those who conceal their sexual orientation to seek care for mpox during a global outbreak of the disease last year that disproportionately affected their community, researchers from Cornell University and the University of Toronto found.
It wasn’t necessarily concern over being “outed” that kept some sexual minority men from seeking care for the disease, formerly known as monkeypox. According to the researchers, it was an information gap, partially attributable to separation from community due to identity concealment.
“The resource knowledge and community-connected ...
BSC predicts that global-mean temperature could reach the 1.5ºC warming level threshold in 2024
2024-01-16
2023 has just been confirmed as the hottest year on record, with global average temperatures exceeding pre-industrial conditions by 1.48°C, as stated by the Copernicus Programme of the European Union. Climate scientists from the Barcelona Supercomputing Center-Centro Nacional de Computación (BSC-CNS), based on the BSC decadal forecast system, were capable of predicting a year ago that 2023 had a high probability of being the warmest year on record.
After the record-smashing conditions in 2023, the imminent question is how the year 2024 and the following years will ...
New study aims to unlock secrets of the human brain
2024-01-16
The inner workings of the human brain are a gradually unraveling mystery and Dr. Richard Naud of the University of Ottawa’s Faculty of Medicine has led a highly compelling new study that brings us closer to answering these big questions. The study’s results have important implications for theories of learning and working memory and could potentially help lead to future developments in artificial intelligence (AI) since AI developers and programmers watch the work of Dr. Naud and other leading neuroscientists.
Published in Nature Computational Science, the study tackles the many-layered mystery ...
Pudukotai Dinakarrao studying ways to protect autonomous vehicle supply chains
2024-01-16
Sai Manoj Pudukotai Dinakarrao, Assistant Professor, Electrical and Computer Engineering, received funding for the project: "Cyber Sentinel: Safeguarding Autonomous Vehicle Supply Chains against Backdoors in Hardware."
Pudukotai Dinakarrao is working with University of Virginia researchers who aim to deploy a backdoor attack mitigation and avoidance approach for vehicles.
Haiying Shen, Associate Professor, Computer Science; Associate Professor, Electrical and ...
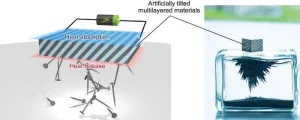
Thermoelectric permanent magnet opens new possibilities in thermal management technologies
2024-01-16
1. A NIMS research team has demonstrated that the transverse thermoelectric conversion (i.e., energy conversion between charge and heat currents that flow orthogonally to each other) can be greatly enhanced by applying magnetic fields or utilizing magnetism. In addition, the team developed a thermoelectric permanent magnet—a new functional material capable of thermoelectric cooling and power generation—by combining permanent magnets and thermoelectric materials into a hybrid structure. These results may guide in achieving thermal ...
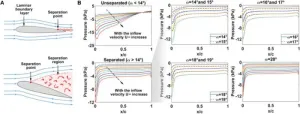
Quantum computing and machine learning are effective tools in fluid dynamics
2024-01-16
To prevent aircraft stalls, engineers have long studied the flow of air over airfoils such as airplane wings to detect the angles when flow separation occurs. Recently, a team of researchers at Shanghai Jiao Tong University including Xi-Jun Yuan and Zi-Qiao Chen investigated the use of quantum computing in connection with machine learning as a more accurate way of solving such problems. Their research was published Nov. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The use of a quantum support vector machine rather than a classical support vector machine increased the accuracy of classification of flow separation from 81.8% ...
Modified soft material promises better bioelectronics
2024-01-16
The scientific community has long been enamored of the potential for soft bioelectronic devices, but has faced hurdles in identifying materials that are biocompatible and have all of the necessary characteristics to operate effectively. Researchers have now taken a step in the right direction, modifying an existing biocompatible material so that it conducts electricity efficiently in wet environments and can send and receive ionic signals from biological media.
“We’re talking about ...
Study reveals key factors in surgeons' opioid prescribing patterns
2024-01-16
Key takeaways
Decreasing trend in opioid prescriptions: There was a notable nationwide reduction in opioid prescriptions after surgery from 2013 to 2017, reflecting a shift in the medical community's approach to pain management.
Social determinants affect opioid prescription rates: At the county level, lower median population age, higher education levels, insufficient sleep, higher health care costs, fewer mental health providers, and higher uninsured rates are linked to higher opioid prescription rates.
No ...
We need a staph vaccine: here’s why we don’t have one
2024-01-16
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is an extremely common bacterial infection; about 30% of people have colonies of SA living in their nose. SA is often harmless, but it is also a leading cause of hospital-acquired and community-associated infections. A vaccine for SA would be a game-changer for public health, but for decades, all vaccine candidates for SA have failed in clinical trials despite successful preclinical studies in mice. Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have finally explained why.
In a new study, published January ...
Analysis of breast cancer mortality in the US
2024-01-16
About The Study: Based on four simulation models, breast cancer screening, treatment of stage I to III breast cancer, and treatment of metastatic breast cancer were each associated with reduced breast cancer mortality between 1975 and 2019 in the U.S.
Authors: Sylvia K. Plevritis, Ph.D., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.25881)
Editor’s ...
Consumption of 100% fruit juice and body weight in children and adults
2024-01-16
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 eligible studies, including 17 among children (n = 45,851) and 25 among adults (n = 268,095), found a positive association between intake of 100% fruit juice and weight gain in children. Analysis of cohort studies in adults found a significant positive association among studies unadjusted for total energy, suggesting potential mediation by calories; an analysis of trials in adults found no significant association between 100% fruit juice consumption and body weight. The findings ...
Employer-sponsored health insurance premium cost growth and its association with earnings inequality among families
2024-01-16
About The Study: The findings of this study of U.S. families receiving employer-sponsored health insurance suggest that three decades of increasing health care premiums were likely associated with reduced annual earnings and increased earnings inequality by race and ethnicity and wage level and were meaningfully associated with wage stagnation.
Authors: Kurt Hager, Ph.D., M.S., of the UMass Chan Medical School in Worcester, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Experiences of interpersonal violence in sport and perceived coaching style among college athletes
2024-01-16
About The Study: The results of this survey study involving 4,119 currently competing U.S. college athletes suggest that interpersonal violence is associated with marked changes in the psychosocial health and emotional well-being of college athletes, particularly those who identify as female and with non-heterosexual sexual orientations. Variations in coaching style have the potential to alter these associations. Ongoing efforts are needed to leverage the unique position that coaches hold to help reduce interpersonal violence and create safe places where all college athletes can thrive.
Authors: Yetsa A. Tuakli-Wosornu, M.D., ...
Largest-ever study of palliative care demonstrates scalable strategy to increase support for seriously ill patients in the hospital
2024-01-16
PHILADELPHIA – Ordering a palliative care consultation by “default” – via an automatic order programmed into the electronic medical record that doctors may cancel if they choose – is an effective strategy to give more hospitalized patients the opportunity to benefit from palliative care, and sooner, according to a new study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Palliative care is specialized medical care focused on relieving the symptoms and stress of a serious illness and improving quality of life, in alignment with a patient’s ...
Cost of employer-sponsored health insurance is flattening worker wages, contributing to income inequality
2024-01-16
The rising cost of health insurance is an ongoing concern in the United States. New research shows that increasing health insurance costs are eating up a growing proportion of worker’s compensation, and have been a major factor in both flattening wages and increasing income inequality over the past 30 years.
In a study from the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, researchers found that the cost of employer-sponsored insurance (ESI) health care benefits increased much faster than workers’ wages since the late 1980s, ...
[1] ... [1446]
[1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
[1451]
[1452]
[1453]
1454
[1455]
[1456]
[1457]
[1458]
[1459]
[1460]
[1461]
[1462]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.