Xidian University researchers develop optimal design method for microwave power transmission
2024-01-09
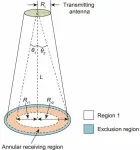
A team of researchers from Xidian University in China has achieved a new result in the field of microwave power transmission. Their study, published in Engineering, introduces an optimal design method for antenna aperture illumination with an annular collection area, with the goal of maximizing the power radiated on the collection area.
The research, led by Professor Baoyan Duan from Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Space Solar Power Station System, Xidian University, focused on formulating the aperture amplitude distribution using a unique set of series. ...
Racial and ethnic disparities in receipt of general anesthesia for cesarean delivery
2024-01-09
About The Study: Racial disparities in rates of general anesthesia continue to exist; however, the findings of this study including 35,000 patients who underwent cesarean delivery suggest that, for laboring patients who had labor epidural catheters in situ, no disparity by race or ethnicity existed. Future studies should address whether disparities in care that occur prior to neuraxial catheter placement are associated with higher rates of general anesthesia among patients from ethnic and racial minority groups.
Authors: Caroline Leigh Thomas, M.D., of ...
Perinatal depression and risk of suicidal behavior
2024-01-09
About The Study: In this study of 952,000 participants, women with perinatal depression were at an increased risk of suicidal behavior, particularly within the first year after diagnosis with persistent risk elevations throughout the 18 years of follow-up, highlighting the need for vigilant clinical monitoring of this vulnerable group.
Authors: Hang Yu, M.Sc., and Donghao Lu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.50897)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
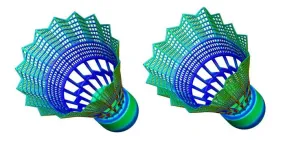
Rallying for a better badminton birdie
2024-01-09
WASHINGTON, Jan. 9, 2024 – Badminton traces its roots back more than a millennium, but the modern version of the racket game originated in the late 19th century in England. Today, it is the second most popular sport in the world behind soccer, with an estimated 220 million people who enjoy playing. For the last three decades, badminton has been a competitive Olympic sport, and with “bird” speeds topping 300 mph in “smash” shots, it certainly makes for exciting spectator sport.
Shuttlecocks, also known as birdies or birds, are ...
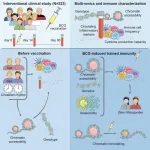
Vaccine boosts innate immunity in people with dormant immune cells
2024-01-09
Humans are protected by two branches of the immune system. Innate immunity provides built-in defense against widespread characteristics of bacteria and viruses, while adaptive immunity memorizes individual pathogens that a person has already encountered. Vaccines teach the adaptive immune system about new pathogens without having to go through an actual infection. This has greatly contributed to human health, but requires a specific vaccine for each major pathogen.
Some vaccines not only teach the adaptive immune system ...
New research shows mobile methadone units are most impactful in rural areas
2024-01-09
While mobile methadone units make a difference in expanding methadone use for patients with opioid addictions, they are likely to be most impactful in rural areas, according to new research.
The research was published today in Health Services Research and focused on the impact of adding new treatment services exclusively to rural Louisiana, where like in many other remote parts of the country, there are limited healthcare infrastructures and barriers to transportation. They compared this data to the impact of ...
PNNL kicks off multi-year energy storage, scientific discovery collaboration with Microsoft
2024-01-09
The urgent need to meet global clean energy goals has world leaders searching for faster solutions. To meet that call, the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory has teamed with Microsoft to use high-performance computing in the cloud and advanced artificial intelligence to accelerate scientific discovery on a scale not previously demonstrated. The initial focus of the partnership is chemistry and materials science—two scientific fields that underpin solutions to global energy challenges.
“The intersection of AI, cloud and high-performance computing, along with human scientists, we believe is key to accelerating the path to meaningful scientific ...
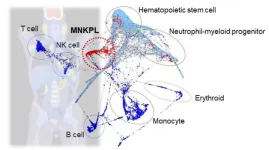
The hidden identity of leukemia
2024-01-09
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use various technologies to better characterize a rare form of leukemia on the molecular level
Tokyo, Japan – Leukemia is a common term used to refer to a form of blood cancer. However, there are different types of leukemia depending on the cell type involved. One unique form is myeloid/natural killer (NK) cell precursor acute leukemia (MNKPL). Because of its rarity, there is no consensus on the specific characteristics needed to clinically identify this disease. In a recent article ...
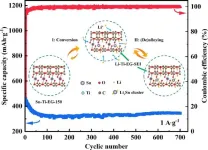
Unique framework of tin bimetal organic compound facilitates stable lithium-ion storage
2024-01-09
Battery capacity is one of the primary bottlenecks in efficient renewable energy storage and significant reductions in carbon emissions. As a battery anode that releases electrons in a lithium-ion battery (LIB), tin (Sn) and Sn-mixture alloys could theoretically store more energy at a higher density than more common carbon-based anodes. Pairing a Sn-Ti bimetal element with inexpensive ethylene glycol (Sn-Ti-EG) mitigated many of the challenges of using Sn as an anode material and produced an inexpensive LIB with excellent storage and performance characteristics.
Sn and Sn alloys, or mixture of another metal with Sn, could outperform other anode materials ...
Attribution of the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk
2024-01-09
Eastern China was hit by an extreme drought in summer 2022 that caused severe economic and agricultural damage. The event has attracted a great deal of attention not only because of its severe intensity and huge social impacts, but also because it is yet another example within the hot topic of the influence of anthropogenic forcing induced warming on drought extremes and how they might change under different scenarios of continued warming in the future.
Recently, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters published ...
Increasing levels of "hype" language in grant applications and publications
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—The success of scientific endeavors often depends on support from public research grants. Successful applicants increasingly describe their proposed research using promotional language ("hype"); however, it remains unclear whether they use hype in their subsequent research publications.
A research team led by the University of Tsukuba analyzed all published research abstracts of projects funded by the US National Institute of Health (NIH) from 1985 to 2020. The analysis covered 139 hype adjectives emphasizing significance ...
Is spa water a fossil of water? Uncover the real ultra-deep water cycles
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Although most natural spa waters primarily originate from atmospheric precipitation, such as rain and snow (known as meteoric water), the present study explored the unique qualities of certain spa waters. By analyzing the stable isotope compositions of hydrogen and oxygen in water molecules, researchers have identified distinct characteristics that indicate the presence of long-trapped lithospheric water. They traced the isotopic evolution of this water through sophisticated numerical modeling, and found that various types of water, including those found deep beneath the ...
Light measurement enables estimation of the chemical attributes of spice extracts
2024-01-09
Tsukuba, Japan—Spices and other plant-derived products contain many active components, such as polyphenols and flavonoids. However, even the slightest variations in conditions can considerably affect the extraction efficiency of these active components, posing challenges in determining the exact quantity of active components in the extract solution.
In this study, researchers comprehensively measured the fluorescence emitted by polyphenols and flavonoids and analyzed the acquired data using machine learning methods. ...
Nemours Children’s Health researchers find Zika virus is effective when used to treat a type of childhood cancer in mice
2024-01-09
ORLANDO, Fla. (Jan. 9, 2024) — Injecting neuroblastoma tumors with Zika virus shrank or eliminated those tumors in studies with mice, suggesting that the virus could someday serve as an effective cancer therapy, according to a study led by Nemours Children’s Health researchers and published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Neuroblastoma is a rare childhood cancer that typically develops in the sympathetic nervous system or the adrenal glands. Only 700 to 800 cases are diagnosed each year in the United States, accounting for ...
Multidisciplinary panel advocates for increased adoption of Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) in peripheral vascular interventions
2024-01-09
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM ET ON JANUARY 9, 2024
WASHINGTON (January 9, 2024) – Proceedings from an expert consensus roundtable that discussed the benefits of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in lower extremity revascularization procedures were released today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI), Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology (JVIR), and Journal of Vascular Surgery - Vascular Insights.
The roundtable focused on the current challenges in diagnosing ...
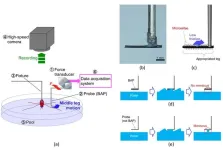
Analysis of rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis
2024-01-09
A research paper by scientists at the Ibaraki University analyzed the rowing force of the water strider middle leg by direct measurement using a bio-appropriating probe and by indirect measurement using image analysis.
The new research paper, published on Nov. 17 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, reported the rowing force of water striders obtained by direct and indirect measurements, and analyzed the maximum force arrival time and the middle leg angular velocity of the direct and indirect force measurements.
“Rowing force of the middle leg of a water ...
Discovering a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis
2024-01-09
Prof. Sun-Uk Lee of the Department of Neurology and Prof. Euyhyun Park of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology from Korea University’s Anam Hospital discovered a new mechanism of vestibular neuritis.
Vestibular neuritis is one of the common diseases causing acute dizziness. It is known to be caused by an inflammation in the vestibular nerve and inner ear, which is responsible for balance and body motion sensation.
Various mechanisms had been suggesting as the cause of vestibular neuritis, such as reactivation of latent herpes virus or peripheral blood circulation disorder in the ...
Researchers developing AI to make the internet more accessible
2024-01-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – In an effort to make the internet more accessible for people with disabilities, researchers at The Ohio State University have begun developing an artificial intelligence agent that could complete complex tasks on any website using simple language commands.
In the three decades since it was first released into the public domain, the world wide web has become an incredibly intricate, dynamic system. Yet because internet function is now so integral to society’s well-being, its complexity also makes it considerably harder to navigate.
Today there ...
Scientists outline a bold solution to climate change, biodiversity loss, social injustice
2024-01-09
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An international team of scientists led by Oregon State University researchers has used a novel 500-year dataset to frame a “restorative” pathway through which humanity can avoid the worst ecological and social outcomes of climate change.
In addition to charting a possible new course for society, the researchers say their “paradigm shifting” plan can support climate modeling and discussion by providing a set of actions that strongly emphasize social and economic justice as well ...
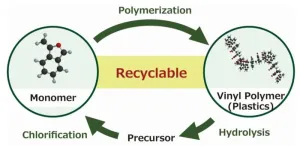
Novel chemical recycling system for vinyl polymers of cyclic styrene derivatives
2024-01-09
Chemical recycling of widely used vinyl polymers (VPs) is one of the key technologies required for realizing a sustainable society. In this regard, a team of researchers from Shinshu University have recently reported a new chemical process that facilitates the depolymerization of cyclic styrene-based VPs, resulting in the recovery of a monomer precursor. This highly efficient chemical recycling system can help with effective resource circulation and the development of new plastic recycling technologies.
Vinyl polymers (VPs) are ...
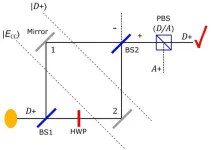
Quantum particles can’t separate from their properties, after all
2024-01-09
The quantum Cheshire cat effect draws its name from the fictional Cheshire Cat in the Alice in Wonderland story. That cat was able to disappear, leaving only its grin behind. Similarly, in a 2013 paper, researchers claimed quantum particles are able to separate from their properties, with the properties travelling along paths the particle cannot. They named this the quantum Cheshire cat effect. Researchers since have claimed to extend this further, swapping disembodied properties between particles, disembodying multiple properties simultaneously, ...
Press passes now available for Discover BMB to be held March 23–26
2024-01-09
Complimentary press passes are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB). Join us March 23–26 in San Antonio to experience an engaging agenda showcasing the newest developments and current trends in the field.
As the flagship meeting for one of the largest molecular life science organizations in the world, #DiscoverBMB brings together researchers in academia and industry from across the globe.
Explore captivating science stories and connect with leading experts during the scientific symposia, which will encompass 12 themes. Topics include:
Exciting ...
New CRISPR Center brings hope for rare and deadly genetic diseases
2024-01-09
Children and adults with rare, deadly genetic diseases have fresh hope for curative therapies, thanks to a new collaboration between the Innovative Genomics Institute (IGI) and Danaher Corporation, a global life sciences and diagnostics innovator.
The new Danaher-IGI Beacon for CRISPR Cures center will use genome editing to address potentially hundreds of diseases, including rare genetic disorders that have no cure. The goal is to ensure treatments can be developed and brought to patients ...
Three researchers awarded $1 million each to study new heart disease treatments, causes
2024-01-09
DALLAS, Jan. 9, 2024 — A physician-scientist from Massachusetts researching whether chemicals naturally occurring in foods could help treat heart disease, a genetics expert from Pennsylvania exploring the molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism and cardiovascular diseases and a California-based professor of cardiovascular medicine studying how vaping impacts the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms are the most recent American Heart Association Merit Award recipients. Over the next five years, each researcher will receive a total of $1 million in funding from the Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and research, ...
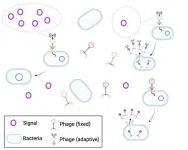
The value of information gathering for phages
2024-01-09
Phages, the viruses that infect bacteria, will pay a high growth-rate cost to access environmental information that can help them choose which lifecycle to pursue, according to a study. Yigal Meir and colleagues developed a model of a bacteria-phage system to investigate how much the viruses should be willing to invest to acquire information about their local environment. A temperate phage, once inside a bacterium, can choose one of two life cycles. In the lytic cycle, the phage turns the bacterium ...
[1] ... [1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
[1451]
[1452]
[1453]
[1454]
1455
[1456]
[1457]
[1458]
[1459]
[1460]
[1461]
[1462]
[1463]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.