Chasing the light: Sandia study finds new clues about warming in the Arctic
2024-01-15
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Arctic, Earth’s icy crown, is experiencing a climate crisis like no other. It’s heating up at a furious pace — four times faster than the rest of our planet. Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories are pulling back the curtain on the reduction of sunlight reflectivity, or albedo, which is supercharging the Arctic’s warming.
The scientists are not armed with parkas and shovels. Instead, they have tapped into data from GPS satellite radiometers, capturing the sunlight bouncing off the Arctic. This ...
Physicists identify overlooked uncertainty in real-world experiments
2024-01-15
The equations that describe physical systems often assume that measurable features of the system — temperature or chemical potential, for example — can be known exactly. But the real world is messier than that, and uncertainty is unavoidable. Temperatures fluctuate, instruments malfunction, the environment interferes, and systems evolve over time.
The rules of statistical physics address the uncertainty about the state of a system that arises when that system interacts with its environment. But they’ve ...
Kessler Foundation receives grant to investigate impact of combining aerobic exercise and virtual reality for individuals with multiple sclerosis
2024-01-15
East Hanover, NJ – January 15, 2024 – Kessler Foundation received a $39,994 grant from the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers to investigate the impact of a unique combination of a single bout of aerobic cycling and virtual reality (VR) on processing speed in persons with multiple sclerosis (MS) and mobility disability.
Processing speed is the most common cognitive problem in persons with MS and may actually contribute to broader cognitive difficulties, according to the grant recipient, Carly Wender, PhD, research scientist in the Center for Neuropsychology ...
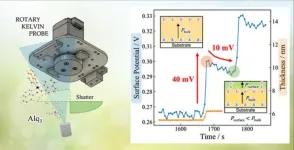
The power of pause: Controlled deposition for effective and long-lasting organic devices
2024-01-15
Organic optoelectronic devices, such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), use molecules with specific structures arranged on thin films. Additionally, the arrangement of these molecules on any surface is crucial for various processes that occur within these devices. This arrangement is guided by two primary factors: the deposition rate (how fast the molecules are placed) and the surface temperature. Slower deposition rates and higher temperatures facilitate the proper arrangement, resulting in more stable structures. Finding the right time scale for this process is also critical, and ...
Going beyond plastic: Chung-Ang University team explores tara gum as a green polymer
2024-01-15
Synthetic, non-biodegradable plastics are major sources of environmental pollution and have prompted a rising interest in sustainable, biodegradable alternatives derived from natural polymers. “Tara gum,” derived from the seeds of the tara tree (Caesalpinia spinosa), stands out as a promising solution. This natural, water-soluble substance contains polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates), including the widely used “galactomannan,” which is employed in coatings, edible films, and as a stabilizer and thickener. The biocompatibility, biodegradability, and safety of tara gum also make it valuable in industries like food and drug delivery. ...
Sahmyook University researchers open doors to next-generation memristive devices
2024-01-15
Memristive devices constitute a category of devices capable of retaining their internal resistance, thus offering superior performance compared to conventional devices that use integrated circuits. Several materials have been explored to manufacture these devices. In recent years, transition metal oxides have gradually become widely popular for this purpose.
Due to their increasing application in diverse domains like artificial intelligence systems, memristive devices must now overcome several issues related to data retention, endurance, and a large number of conductance states. Moreover, the individual fabrication ...
Study quantifies how aquifer depletion threatens crop yields
2024-01-15
Three decades of data have informed a new Nebraska-led study that shows how the depletion of groundwater — the same that many farmers rely on for irrigation — can threaten food production amid drought and drier climes.
The study found that, due in part to the challenges of extracting groundwater, an aquifer’s depletion can curb crop yields even when it appears saturated enough to continue meeting the demands of irrigation. Those agricultural losses escalate as an aquifer dwindles, the researchers reported, so that its ...
When bees nourish their microbiota
2024-01-15
Two teams from UNIL and EPFL have succeeded in demonstrating that the insect synthesizes nutrients for native gut microbes. A study published in « Nature Microbiology ».
Bacteria have adapted to all terrestrial environments. Some have evolved to survive in the gut of animals, where they play an important role for their host; they provide energy by degrading indigestible food, they train and regulate the immune system, they protect against invasion by pathogenic bacteria, and they synthesize neuroactive molecules that regulate the behavior and cognition of their host.
These are great ...
Accelerating how new drugs are made with machine learning
2024-01-15
Researchers have developed a platform that combines automated experiments with AI to predict how chemicals will react with one another, which could accelerate the design process for new drugs.
Predicting how molecules will react is vital for the discovery and manufacture of new pharmaceuticals, but historically this has been a trial-and-error process, and the reactions often fail. To predict how molecules will react, chemists usually simulate electrons and atoms in simplified models, a process which is computationally expensive and often inaccurate.
Now, researchers from the University of Cambridge ...
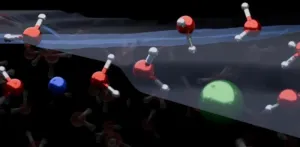
Water molecule discovery contradicts textbook models
2024-01-15
Textbook models will need to be re-drawn after a team of researchers found that water molecules at the surface of salt water are organised differently than previously thought.
Many important reactions related to climate and environmental processes take place where water molecules interface with air. For example, the evaporation of ocean water plays an important role in atmospheric chemistry and climate science. Understanding these reactions is crucial to efforts to mitigate the human effect on our planet.
The distribution of ions at the interface of air and water can affect atmospheric processes. However, a precise understanding of ...
U.S. air pollution rates on the decline but pockets of inequities remain
2024-01-15
Over the last decades, air pollution emissions have decreased substantially; however, the magnitude of the change varies by demographics, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The results indicate there are racial/ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in air pollution emissions reductions, particularly in the industry and energy generation sectors. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research provides a national investigation of air pollution emission changes in the 40 years following the enactment of the Clean Air ...
New Scientific Reports publication reveals major difference in genomes of American and Chinese chestnut
2024-01-15
The chromosomes of American and Chinese chestnut are not so similar after all, at least in one key region of the genome – the nucleolus organizing region (NOR).
The finding, published in a forthcoming article in Scientific Reports, has major implications for anyone with the goal of conferring blight-resistance to American chestnuts through hybridization with the Chinese chestnut.
“This is an unprecedented finding in the field of plant cytology,” says Nurul Faridi, a Forest Service geneticist and lead author of the study.
Traditional ...
Solid-state qubits: Forget about being clean, embrace mess
2024-01-15
New findings debunk previous wisdom that solid-state qubits need to be super dilute in an ultra-clean material to achieve long lifetimes. Instead, cram lots of rare-earth ions into a crystal and some will form pairs that act as highly coherent qubits, shows paper in Nature Physics.
Clean lines and minimalism, or vintage shabby chic? It turns out that the same trends that occupy the world of interior design are important when it comes to designing the building blocks of quantum computers.
How to make qubits that retain their quantum information long enough to be useful is one of the major barriers to practical quantum computing. It’s widely accepted that the ...
Bladder tumors reduced by 90% using nanorobots
2024-01-15
Bladder cancer has one of the highest incidence rates in the world and ranks as the fourth most common tumour in men. Despite its relatively low mortality rate, nearly half of bladder tumours resurface within 5 years, requiring ongoing patient monitoring. Frequent hospital visits and the need for repeat treatments contribute to making this type of cancer one of the most expensive to cure.
While current treatments involving direct drug administration into the bladder show good survival rates, their therapeutic efficacy remains low. A promising alternative involves the use of nanoparticles capable of delivering therapeutic agents directly to the tumour. ...
Research sheds new light on Moon rock formation solving major puzzle in lunar geology
2024-01-15
New research has cracked a vital process in the creation of a unique rock type from the Moon. The discovery explains its signature composition and very presence on the lunar surface at all, unravelling a mystery which has long eluded scientists.
The study, published today in Nature Geoscience, reveals a key step in the genesis of these distinctive magmas. A combination of high temperature laboratory experiments using molten rocks, together with sophisticated isotopic analyses of lunar samples, identify a critical reaction that controls their composition.
This reaction took place in the deep lunar interior some three and a half ...
Priming, shaping and polishing: In search of a HIV vaccine
2024-01-15
Worldwide, an estimated, 40 million people live with HIV. Two-thirds of this group on the African continent. In 2022, more than 600,000 people died from HIV-related causes and more than 1.3 million were infected. There is no vaccine against the world's second most deadly infection, after TB. Thanks to a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Amsterdam UMC's Rogier Sanders leads a project that aims to develop the first effective HIV vaccine.
"We hope to be able ...
Vigilant monitoring is needed to manage cardiac risks in patients using antipsychotics, doctors say
2024-01-15
Philadelphia, January 15, 2024 – The use of the antipsychotic drugs quetiapine and haloperidol is associated with an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death (SCD) caused by drug-induced QT prolongation, reports a new study in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society, published by Elsevier. Caution is advised to manage cardiac risks in patients prescribed ...
Singapore study reveals impact of early life adversity on a child’s brain development
2024-01-15
Leveraging neuroimaging data from the Growing Up in Singapore Towards healthy Outcomes (GUSTO) cohort, researchers from A*STAR’s Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) identified an association between early life adversity and the pace of brain development in childhood.
SINGAPORE – A study led by researchers from A*STAR's Singapore Institute for Clinical Sciences (SICS) has found evidence suggesting that children exposed to elevatec levels of early life adversity (ELA) exhibit an accelerated pattern of brain development during the preschool years. When exposed to ELA, such as a mother's mental and ...
Researchers propose revised scoring system for recognising outstanding NHS clinicians
2024-01-15
A team of researchers has developed a new scoring system for a nationwide scheme, overseen by the Advisory Committee on Clinical Impact Awards (ACCIA), to recognise and reward senior doctors and dentists in England and Wales.
There has been a scheme in place since 1948 to reward senior clinicians who make an outstanding contribution to supporting the delivery of NHS goals. The awards have been known, through various iterations, as merit awards, clinical excellence awards, and, most recently, clinical impact awards.
Published ...
Few older adults use direct-to-consumer health services; many who do don’t tell their regular provider
2024-01-14
Only a small percentage of older Americans have jumped on the rising trend of getting health care services and prescriptions directly from an online-only company, rather than seeing their usual health care providers in person or via telehealth, a new poll finds.
But that could change rapidly, the University of Michigan survey suggests.
In all, 7.5% of people between the ages of 50 and 80 have used at least one direct-to-consumer health care service from an online-only provider, according to the new findings from the National Poll on Healthy Aging.
Of those who did ...
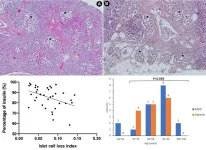
Loss of cells in pancreas in the elderly may cause age-related diabetes
2024-01-13
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have studied pancreatic islet cell loss in people with no previous pancreatic problems. They identified key trends in the types of cells lost due to islet cell loss in different age groups and sexes, finding that ICL in the elderly population was largely due to insulin-producing beta cell loss. This may be the cause of age-related diabetes and help inform new preventative treatments.
The pancreas is an incredibly important part of the human digestive system, particularly for regulating blood sugar levels by secreting the hormone insulin. ...
African women living with HIV have an effective option to prevent malaria during pregnancy
2024-01-13
In women living with HIV, preventive treatment with DHA-PPQ is a safe and effective strategy to prevent malaria during pregnancy, according to the final results of MAMAH, a clinical trial funded by the European & Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP) and coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The study, published in the Lancet Infectious Diseases, could help protect the health of the estimated one million pregnant women who suffer from a double infection with malaria ...
The fate of novel ideas
2024-01-13
Innovation may be what drives progress in the arts, business, sciences and technology, but the novel ideas that drive innovation often face headwinds that hinder or even prevent their adoption.
Why did some good ideas, such as hand sanitizing in 19th-century hospitals or racial integration in the 20th century, take years to win widespread embrace? University of Utah postdoctoral researcher Wayne Johnson set out to identify the hurdles.
His research team’s program of five studies, which featured analyses of evaluations of films screened at Utah’s Sundance Film ...
Are bugs bugging humans or the other way around? Study reveals a few surprises
2024-01-13
Insects and spiders often receive little attention from people, except when we’re swatting them away. However, as arthropods — creatures distinguished by a hard exoskeleton and jointed legs— they play an essential role in sustaining the ecosystems humans rely on. Remarkably, arthropods make up approximately 84% of all known animal species.
A study published recently in Scientific Reports reveals how human activity affects biodiversity among arthropods and how nonbiological factors, such as daily temperature swings and proximity to the ocean, affect arthropod biodiversity in urban areas.
The research uncovered a few ...
Could an already approved drug cut down on opioid use after surgery?
2024-01-12
Researchers in the Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) have found that an FDA-approved drug may help to decrease pain after surgery. In the pilot study published in Pain Management, spinal surgery patients who received N-acetylcysteine (NAC) during surgery in addition to standard pain control treatments reported lower pain scores and requested fewer opioids after surgery than patients given a placebo.
Opioids are often given for a short time after ...
[1] ... [1444]
[1445]
[1446]
[1447]
[1448]
[1449]
[1450]
[1451]
1452
[1453]
[1454]
[1455]
[1456]
[1457]
[1458]
[1459]
[1460]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.