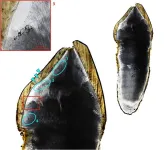
Prognostic significance of senescence-related tumor microenvironment genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
2024-01-31
“These findings provided evidence for the role of senescence in the tumor microenvironment [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- January 31, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “Prognostic significance of senescence-related tumor microenvironment genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.”
The impact of the senescence related microenvironment on cancer prognosis and therapeutic response remains poorly understood. In this new study, researchers Young Chan Lee, Yonghyun Nam, Minjeong Kim, ...
UTIA trade expert elected president of SAEA
2024-01-31
Andrew Muhammad, professor and Blasingame Chair of Excellence in Agricultural Policy at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, has been elected president of the Southern Agricultural Economics Association. The newly elected president will be recognized at the Association’s upcoming annual meeting in Atlanta, Georgia, from February 3-6.
“We are excited for Dr. Muhammad in this important leadership role,” says Bill Johnson, interim department head for UT’s Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics. “His previous experience with SAEA and his global perspective on agriculture ...
Diabetes medication class tied to lower risk of kidney stones
2024-01-31
Rates of kidney stones are on the rise in the United States and around the world. Type 2 diabetes is associated with increased risk of kidney stones, but some forms of treatment for this condition may also have the benefit of lowering risk of kidney stones. In a study led by investigators from Mass General Brigham, researchers found that there was an association between the use of sodium-glucose contratransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and a lower risk of developing kidney stones. Their findings are reported in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts ...
Engineers develop hack to make automotive radar hallucinate
2024-01-31
DURHAM, N.C. – A black sedan cruises silently down a quiet suburban road, driver humming Christmas carols quietly while the car’s autopilot handles the driving. Suddenly, red flashing lights and audible warnings blare to life, snapping the driver from their peaceful reprieve. They look at the dashboard screen and see the outline of a car speeding toward them for a head-on collision, yet the headlights reveal nothing ahead through the windshield.
Despite the incongruity, the car’s autopilot grabs control and swerves into a ditch. Exasperated, the driver looks around the vicinity, ...
Strong European backing for Ukraine leaves “little space” for exploitation of pro-Russian politics, study shows
2024-01-31
Strong support for Ukraine means there is “little space” for European politicians to exploit pro-Russia foreign policy messages, a new study shows.
Researchers have found widespread backing for Ukraine across the continent, and for policies that help the nation, such as imposing sanctions on Russia.
But public opinion is more mixed on the approach NATO should take and whether Ukraine should become a member.
Experts found European nations can be classified into three distinct groups. Citizens ...
Did dementia exist in ancient Greek and Rome?
2024-01-31
You might think age-related dementia has been with us all along, stretching back to the ancient world.
But a new analysis of classical Greek and Roman medical texts suggests that severe memory loss — occurring at epidemic levels today — was extremely rare 2,000 to 2,500 years ago, in the time of Aristotle, Galen and Pliny the Elder.
The USC-led research, published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, bolsters the idea that Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias are diseases of modern environments and lifestyles, with sedentary behavior and exposure to air pollution largely to blame.
“The ancient Greeks had very, very few — but we found them ...
Surgeons’ choice of skin disinfectant impacts infection risk, Canadian-American study shows
2024-01-31
Does the type of solution used by surgeons to disinfect skin before surgery impact the risk of surgical site infection? According to new research from an international trial jointly led by McMaster University and the University of Maryland School of Medicine – yes, it does.
Researchers of the PREPARE trial, which enrolled nearly 8,500 participants at 25 hospitals in Canada and the United States, found the use of iodine povacrylex in alcohol to disinfect a patient’s skin could prevent surgical site infection in thousands of patients undergoing surgery for a closed ...
Trees struggle to ‘breathe’ as climate warms, researchers find
2024-01-31
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Trees are struggling to sequester heat-trapping carbon dioxide (CO2) in warmer, drier climates, meaning that they may no longer serve as a solution for offsetting humanity’s carbon footprint as the planet continues to warm, according to a new study led by Penn State researchers.
“We found that trees in warmer, drier climates are essentially coughing instead of breathing,” said Max Lloyd assistant research professor of geosciences at Penn State and lead author on the study recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “They are sending CO2 right back into the ...
New study has promising results for anti-aging effects from enzymatically modified isoquercitrin
2024-01-31
From the study:
This research examines the anti-aging potential of the flavonoid derivative of isoquercitrin known as enzymatically modified isoquercitrin (EMIQ).
A 28-day clinical trial with 30 volunteers aged 31–55 years highlighted EMIQ's effectiveness. Participants using EMIQ-containing Essence displayed reduced facial trans-epidermal water loss and skin roughness, alongside improved skin elasticity. This study emphasizes EMIQ's potential as an anti-photoaging ingredient in cosmetics, warranting further research. The findings pave the way for developing innovative skincare products addressing photoaging effects. ...
Ketamine helped many severely depressed veterans, study shows
2024-01-31
Ketamine has received a lot of attention as a potential treatment for depression, but few studies have revealed how well it works in real world settings, especially in patients with complex mental health needs.
Now, a new study of data from veterans who had tried many depression treatments but still had severe symptoms suggests a series of intravenous doses of ketamine gave many at least partial relief. For a minority, it led to full remission.
Nearly half of 215 veterans with treatment resistant depression who received ...
Bringing order to disordered proteins
2024-01-31
Protein molecules lie at the heart of biology. Our typical understanding of proteins states that each type of protein has a specific three-dimensional shape that enables it to perform its function. This dogma is challenged by intrinsically disordered proteins which make up one third of all proteins and have central biological functions even though their shapes are constantly changing. Until now, our understanding of the structural properties of this intriguing class of proteins has been based on studies ...
A cholesterol precursor mediates sensitivity to cell death by ferroptosis
2024-01-31
A team of scientists from the University of Ottawa, and researchers from other universities and research centres around the world, have discovered that 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) is an endogenous suppressor of ferroptosis, which could have important implications for the treatment of cell death-related diseases.
Ferroptosis is a form of cell death that is characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides and iron-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells. It is a regulated process that is distinct from other forms of cell death, such as apoptosis and necrosis.
The researchers identified a pro-ferroptotic activity of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7) ...
Rice study shows how allyship can combat discrimination in STEM for Blacks, Latinos
2024-01-31
Calling out discriminatory behavior is an effective way for white students to help combat racism against Black and Latino science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) students, according to new research from Rice University.
“(Absent) Allyship in STEM: Can Psychological Standing Increase Prejudice Confrontation?” appears in a recent edition of the Journal of Business and Psychology. The research, led by Eden King and Mikki Hebl from Rice, examines whether Black and Latino college students face discrimination when studying STEM and how allies can help combat racist behavior in these situations.
“There is already a serious lack of representation ...
Drug overdose cardiac arrests involve younger, healthier people than other cardiac arrests
2024-01-31
Research Highlights:
An analysis of cardiac arrest records in a U.S. registry revealed that people with drug overdose cardiac arrests were more likely to be younger, have fewer health conditions and have higher survival rates with better neurologic outcomes compared to people who experience cardiac arrest from other causes.
In addition, drug overdose cardiac arrests were less likely to be witnessed and less likely to present with a shockable first monitored heart rhythm, meaning a heart rhythm that is able to respond to a defibrillator.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, January 31, 2024
DALLAS, Jan. 31, 2024 — An analysis of data for more ...
Exposure to even moderate levels of radon linked to increased risk of stroke
2024-01-31
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 31, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Now a new study has found exposure to this invisible, odorless gas is also linked to an increased risk of stroke. The study, which examined exposures in middle age to older female participants, found an increased risk of stroke among those exposed to high and even moderate concentrations of the gas compared to those exposed to the lowest concentrations. The study is published in the January 31, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, ...
Polycystic ovary syndrome tied to memory, thinking problems
2024-01-31
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 31, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People with polycystic ovary syndrome may be more likely to have memory and thinking problems in middle age, according to new research published in the January 31, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that polycystic ovary syndrome causes cognitive decline. It only shows an association.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a hormonal disorder that is defined by irregular menstruation and elevated levels of a hormone called androgen. Other symptoms may include excess hair growth, acne, infertility and poor metabolic ...
Advanced simulations to provide new understanding of supermassive black holes
2024-01-31
Rochester Institute of Technology scientists will be the lead researchers on a $1.8 million NASA grant to study electromagnetic signals from merging supermassive black holes.
RIT’s Manuela Campanelli, Distinguished Professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics and director of the Center for Computational Relativity and Gravitation, will lead the collaborative project with help from Yosef Zlochower, professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics. The project will also include researchers from the University of Idaho, Johns Hopkins University, and the Goddard Space Flight Center.
The team will combine astrophysical knowledge with state-of-the-art ...
Researchers find enzyme plays much larger role in preventing neurodegenerative diseases
2024-01-31
Indiana University researchers in the College of Arts and Sciences in Bloomington have identified a missing link that can help protect the brain from aging.
Hui-Chen Lu, professor and director of the Linda and Jack Gill Center for Biomolecular Science at IU, alongside graduate students Sen Yang and Zhen Xian Niou, found that nicotinamide nucleotide adenylyl transferase 2, or NMNAT2, provides energy to axons independent of the mitochondria. It does this by propelling glycolysis, a process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. This gives axons enough energy to ...
CU Anschutz researchers identify new biomarker in quality of blood donations
2024-01-31
AURORA, Co. (January 31, 2024) - A collaborative cohort of researchers, led by University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus professor Angelo D’Alessandro, have identified kynurenine as a critical new biomarker in the quality of stored red blood cells (RBCs), a crucial step in the development of more personalized transfusions. Study results published today in the journal Blood.
The transfusion of RBCs is one of the most common in-hospital medical procedures second only to vaccination. The blood supply is dependent on altruistic blood donors, and donated RBCs are stored ...
38% of surveyed Danish owners put their dogs on unlicensed cannabinoids
2024-01-31
In a new study, 38 percent of dog owners surveyed in Denmark reported giving their pups cannabinoids, particularly cannabidiol or CBD. Pernille Holst and colleagues at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on January 31.
Cannabis has become popular for recreational and medical use in humans, and many cannabis-based products are also available for pets. But because cannabis is not legal for veterinary use in countries such as Denmark, pet owners are using it without a prescription. To understand how common unlicensed cannabinoid use for pets is in Denmark, Holst and colleagues distributed an anonymous ...
After big shocks such as the pandemic lockdowns and the invasion of Ukraine, happiness levels may return to normal in as little as 2-3 weeks, per sentiment analysis of tweets in ten countries
2024-01-31
After big shocks such as the pandemic lockdowns and the invasion of Ukraine, happiness levels may return to normal in as little as 2-3 weeks, per sentiment analysis of tweets in ten countries
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295896
Article Title: Reactions to macro-level shocks and re-examination of adaptation theory using Big Data
Author Countries: South Africa, New Zealand
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Non-invasive wearable devices might be able to predict preterm birth by monitoring changes in maternal heart rate variability
2024-01-31
Non-invasive wearable devices might be able to predict preterm birth by monitoring changes in maternal heart rate variability
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0295899
Article Title: Wearable-derived maternal heart rate variability as a novel digital biomarker of preterm birth
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Childhood vitamin D deficiency was likely prevalent during industrialization in England
2024-01-31
Evidence from teeth reveals that vitamin D deficiency during childhood was likely a major issue in industrialized England, according to a study published January 31, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Anne Marie Snoddy of the University of Otago, New Zealand and colleagues.
The 18th and 19th centuries AD were a period of industrialization and urbanization in England. This was also a time of increasing incidence of health issues like vitamin D deficiency (VDD) and associated conditions like rickets, potentially linked to changing social practices ...
Archaeological evidence of seasonal vitamin D deficiency discovered
2024-01-31
Rickets ran rife in children following the Industrial Revolution, but University of Otago-led research has found factory work and polluted cities aren’t entirely to blame for the period’s vitamin D deficiencies.
In a Marsden funded study, just published in PLOS One, researchers from Otago, Durham University, University of Edinburgh, University of Brighton, and University of Queensland, sampled teeth from a cemetery site in industrial era England, looking for microscopic markers of nutritional disease.
Lead author Dr Annie Sohler-Snoddy, Research ...
Jennifer J. Raab named President and CEO of The New York Stem Cell Foundation
2024-01-31
NEW YORK, NY (January 31, 2024) – The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) announced today that, following a nationwide search, its Board of Directors has named Hunter College President Emerita Jennifer J. Raab as its next President and Chief Executive Officer, effective this month.
NYSCF is one of the world’s leading nonprofit stem cell organizations, raising and investing more than $450 million since its founding in 2005 to accelerate cures for the major diseases of our time through stem cell research. The foundation conducts its own pioneering research at the NYSCF Research Institute laboratories in Manhattan, informs and convenes scientists and ...
[1] ... [1412]
[1413]
[1414]
[1415]
[1416]
[1417]
[1418]
[1419]
1420
[1421]
[1422]
[1423]
[1424]
[1425]
[1426]
[1427]
[1428]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.