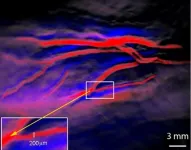
Genetic alterations in thyroid cancer mediate resistance to BRAF inhibition and anaplastic transformation
2024-01-29
“An improved understanding of the molecular basis of thyroid cancer has led to the development of new targeted agents.”
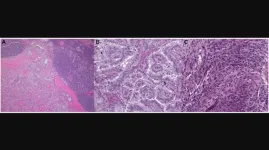
BUFFALO, NY- January 29, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 24, 2024, entitled, “Genetic alterations in thyroid cancer mediating both resistance to BRAF inhibition and anaplastic transformation.”
In this new paper, researchers Mark Lee and Luc GT Morris from New York Presbyterian Hospital and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center discuss thyroid cancer. A subset of thyroid cancers present at advanced stage or with dedifferentiated histology and have limited response to standard therapy. ...
Psychology research: Women more sensitive to cocaine
2024-01-29
Previous studies focused on cocaine use have found that women are more likely than men to develop an addiction, try cocaine at a younger age, use larger amounts of the drug, and suffer from overdose.
Now, a new study from researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington in the journal Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior finally validates what scientists have long suspected: The female sex hormone estradiol (a synthetic version of the naturally occurring estrogen) is responsible for why women are more susceptible to cocaine addiction than men.
“For the first time, we have shown that estradiol enhances the cocaine-conditioned reward,” said Linda Perrotti, ...
When Chinese citizens are surveyed anonymously, support for party and government plummets
2024-01-29
By Ileana Wachtel January 29, 2024
Chinese citizens who rarely voice open criticism of their government reveal stronger negative views when they can answer questions anonymously, according to a new study published in The China Quarterly.
The study by researchers at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences shows an enormous drop in citizen support for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and government policies when citizens are surveyed using a method that hides their identities and makes them feel more anonymous than a typical survey.
Why ...
Students are missing more school, and school nurses may be well-positioned to help
2024-01-29
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- School nurses are more than just health care heroes. They also play a key role in identifying students who are at risk for chronic absenteeism — a growing problem that diminishes academic success and can hurt students’ health and lead to a variety of negative long-term life outcomes.
A recent study by a University of Missouri researcher found that school nurses are often well-positioned to identify students at-risk for chronic school absenteeism. The finding could help schools implement assessments and interventions to ultimately better support students ...
Re-energizing mitochondria to treat Alzheimer’s disease
2024-01-29
LA JOLLA, CA — Nerve cells in the brain demand an enormous amount of energy to survive and maintain their connections for communicating with other nerve cells. In Alzheimer’s disease, the ability to make energy is compromised, and the connections between nerve cells (called synapses) eventually come apart and wither, causing new memories to fade and fail.
A Scripps Research team, reporting in the journal Advanced Science on January 18, 2024, has now identified the energetic reactions in brain cells that malfunction and lead to neurodegeneration. By using a small molecule ...
Rice scientists pull off quantum coup
2024-01-29
HOUSTON – (Jan. 29, 2023) – Rice University scientists have discovered a first-of-its-kind material, a 3D crystalline metal in which quantum correlations and the geometry of the crystal structure combine to frustrate the movement of electrons and lock them in place.
The find is detailed in a study published in Nature Physics. The paper also describes the theoretical design principle and experimental methodology that guided the research team to the material. One part copper, two parts vanadium and four parts sulfur, the alloy features a 3D pyrochlore lattice consisting ...
Spatial model predicts bumblebee exposure to pesticide use
2024-01-29
It has long been known that agricultural pesticides are one of the greatest threats to bees and other essential pollinators. What farmers have lacked is an understanding of how different pesticides, applied at various times on a variety of crops, affect the risk of exposure to bees living near the fields.
Researchers have drawn from real-world data to try to address this gap, developing and testing a spatial model for predicting pesticide exposure in bumblebees. The journal Science of the Total Environment published the work, based on the interactions of the yellow-faced bumblebee (Bombus vosnesenskii) ...
A firm eye on the proboscis
2024-01-29
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, 29 JANUARY 2024, 21:00 CET (20:00 LONDON TIME, 15:00 U.S. EASTERN TIME)
Have you ever seen a hummingbird hawk moth? When people encounter this moth for the first time, they are usually intrigued: Looking like a cross between a butterfly and a bird – hence the name – this animal has the amazing ability to hover like a helicopter for long periods. On closer inspection, another feature of the hummingbird hawk moth quickly catches the eye: the spiralling curled proboscis, which is as long as the entire animal.
The moth uses its proboscis ...
Viral protein fragments may unlock mystery behind serious COVID-19 outcomes
2024-01-29
There are many lingering mysteries from the COVID-19 pandemic. For instance, why does SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind the disease, cause severe symptoms in some patients, while many other coronaviruses don’t? And what causes strange symptoms to persist even after the infection has been cleared from a person’s system?
The world may now have the beginning of answers. In a study published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a UCLA-led multidisciplinary research team explores one way that COVID-19 turns the ...
Endangered seabird shows surprising individual flexibility to adapt to climate change
2024-01-29
New research finds that individual behavioural flexibility and not evolutionary selection is driving the northward shift of Balearic shearwaters.
The findings were revealed through a decade-long study which tagged individual birds.
The results indicate that individual animals may have greater behavioural flexibility to respond to climate change impacts than previously thought.
How individual animals respond to climate change is key to whether populations will persist or go extinct. Many species are shifting their ranges as the environment warms, but up to now the mechanisms underlying ...
Spacing characteristics between vegetation could be a warning sign of degrading dryland ecosystems - study
2024-01-29
Scientists have found that the spatial arrangement of plants in drylands can be a sign of the environment degrading, according to a new study.
One of the iconic features of drylands is the striking appearance of islands of plants surrounded by bare soil. This spatial structure of arid vegetation has long fascinated scientists, but now a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, has shed new light on why these plants group in this way.
An international team of scientists, including from the University of Birmingham, combined field data from 115 sites around the world, and used mathematical models and remote sensing to build a picture of how the ...
Researchers spying for signs of life among exoplanet atmospheres
2024-01-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The next generation of advanced telescopes could sharpen the hunt for potential extraterrestrial life by closely scrutinizing the atmospheres of nearby exoplanets, new research suggests.
The next generation of advanced telescopes could sharpen the hunt for potential extraterrestrial life by closely scrutinizing the atmospheres of nearby exoplanets, new research suggests.
Published recently in The Astronomical Journal, a new paper details how a team of astronomers from The Ohio State University examined upcoming telescopes’ ability to detect chemical ...
People are inclined to hide a contagious illness while around others, research shows
2024-01-29
A startling number of people conceal an infectious illness to avoid missing work, travel, or social events, new research at the University of Michigan suggests.
The findings are reported in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. Across a series of studies involving healthy and sick adults, 75% of the 4,110 participants said they had either hidden an infectious illness from others at least once or might do so in the future. Many participants reported boarding planes, going on dates, and engaging in other social interactions while secretly sick. More than 61% of healthcare workers participating in the study also ...
Racial and ethnic differences in hypertension-related telehealth
2024-01-29
A new study in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health found that hypertension management via telehealth increased among Medicaid recipients regardless of race and ethnicity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Click here to read the article now.
Jun Soo Lee, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and coauthors, reported that from February-April 2023, the number of hypertension-related telehealth outpatient visits per 100 persons increased from 0.01 to 6.13, and the number of hypertension-related in-person visits decreased from 61.88 to 52.63.
The investigators ...
Henry Ford Health helps advance precision medicine research in Michigan
2024-01-29
Michiganders will continue to have the opportunity to advance medical research aimed at advancing individualized health care through a renewed award to Henry Ford Health + Michigan State University Health Sciences from the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) All of Us Research Program. The award includes $18.3 million in initial funding to support a consortium of 8 health care provider organizations with a presence in 16 states.
Henry Ford has led the consortium since 2017. The renewed award allows participation to continue until at least 2028. The multimillion-dollar multi-year award represents the largest NIH research grant in Henry Ford’s 108-year history.
All ...
Jobs and geography may affect hearing: New study maps hearing loss by state and county across the US
2024-01-29
Chicago, IL – January 24, 2024 – The first study to map the prevalence of bilateral hearing loss in the United States by state and county finds that rates of hearing loss are higher among men, non-Hispanic Whites, and residents of rural areas. Bilateral hearing loss is hearing loss in both ears.
West Virginia, Alaska, Wyoming, Oklahoma, and Arizona had the highest rates of hearing loss, while the District of Columbia, New Jersey, New York, Maryland, and Connecticut had the lowest (see top ten highest and ...
UChicago engineer driving key role in Great Lakes water transformation
2024-01-29
The Chicago-based Great Lakes ReNEW coalition has been awarded one of the largest, if not the largest, climate awards in the city’s history – up to $160 million over 10 years as one of the inaugural U.S. National Science Foundation’s Regional Innovation Engines.
Authorized in the “CHIPS and Science Act of 2022,” the NSF Engines program is designed to support the development of diverse regional coalitions of universities, local governments, the private sector and nonprofits to create solutions to today’s pressing issues.
Selected from an initial pool of more ...
Hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia
2024-01-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- Clinical research led by Indiana University School of Medicine investigators and their collaborators in Uganda has revealed that hydroxyurea significantly reduces infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Their latest findings enhance strong evidence of hydroxyurea’s effectiveness and could ultimately reduce death in children in Africa, the continent most burdened by the disease.
The group’s research, recently published in the journal Blood, revealed that hydroxyurea treatment resulted in a remarkable ...
University of Manchester and SPIE announce $1 million endowment for postgraduate scholarships
2024-01-29
The University of Manchester and SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics have announced the establishment of the SPIE-Manchester Postgraduate Scholarship in Photonics.
The $500k gift from the SPIE Endowment Matching Program will be matched 100% by the University and will be used to support both early-career and returning researchers from the University’s Photon Science Institute in partnership with the Royce Institute, the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation.
The partnership was announced today (29 January) during the SPIE Photonics West conference in San Francisco.
Photonics is the study of light and its interactions ...
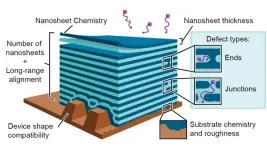
Argonne scientists help scale up nanomaterials for sustainable manufacturing
2024-01-29
New material is self-assembling, long-lasting and recyclable.
As electronic devices get smaller, the materials needed to create them get smaller as well. Nanoscience is the study of extremely small materials that find uses in energy storage, electronics, health and safety applications and more.
Now a team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory has developed a new self-assembly method to fabricate multilayered 2D nanosheets. A nanosheet is an extremely small, lasagna-like material made of ultrathin layers of polymers and nanoparticles.
These nanosheets have significantly ...
OU scientists tests revolutionary imaging technique for pancreatic cancer
2024-01-29
Researchers at OU Health Stephenson Cancer Center at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences have embarked on a revolutionary new research study that could improve the detection of a deadly disease — pancreatic cancer — and give patients a chance to live longer, healthier lives.
The research focuses on an innovative combination of imaging techniques: a newly created contrast agent that recognizes pancreatic cancer cells, paired with Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography, or MSOT. Together, the approach can detect pancreatic cancer cells the width of an eyelash ...
Rising sea levels could lead to more methane emitted from wetlands
2024-01-29
As sea levels rise due to global warming, ecosystems are being altered. One small silver lining, scientists believed, was that the tidal wetlands found in estuaries might produce less methane – a potent greenhouse gas – as the increasing influx of seawater makes these habitats less hospitable to methane-producing microbes.
However, research from biologists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley indicates that these assumptions aren’t always true. After examining the microbial, chemical, and geological features of 11 wetland zones, the team found that a wetland region exposed ...
Study urges people to think twice before going on a diet
2024-01-29
A new qualitative study highlights the negative interpersonal and psychological consequences associated with “yo-yo dieting,” also known as weight cycling. The work underscores how toxic yo-yo dieting can be and how difficult it can be for people to break the cycle.
“Yo-yo dieting – unintentionally gaining weight and dieting to lose weight only to gain it back and restart the cycle – is a prevalent part of American culture, with fad diets and lose-weight-quick plans or drugs normalized as people pursue beauty ...
Astronomers spot 18 black holes gobbling up nearby stars
2024-01-29
Star-shredding black holes are everywhere in the sky if you just know how to look for them. That’s one message from a new study by MIT scientists, appearing today in the Astrophysical Journal.
The study’s authors are reporting the discovery of 18 new tidal disruption events (TDEs) — extreme instances when a nearby star is tidally drawn into a black hole and ripped to shreds. As the black hole feasts, it gives off an enormous burst of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Astronomers have detected previous tidal disruption events by looking for characteristic bursts in the optical and X-ray bands. To date, these searches have ...
The DiAL-Health study will help determine how intermittent fasting and calorie counting can improve a person’s “healthspan”
2024-01-29
January is a time when many people are looking for new diet routines, and intermittent fasting is trending, as are traditional calorie cutting programs.
Research conducted with animal models suggests that intermittent fasting slows aging, and those animals live longer. Researchers at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham are conducting the DiAL-Health study to see if eating for 8 hours and fasting for 16 each day shows similar results in people. These researchers ...
[1] ... [1406]
[1407]
[1408]
[1409]
[1410]
[1411]
[1412]
[1413]
1414
[1415]
[1416]
[1417]
[1418]
[1419]
[1420]
[1421]
[1422]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.