Telecare cuts costs, boosts quality of life for dementia patients
2023-09-18
A UCSF telecare program that improves outcomes for patients with dementia and lightens the load for unpaid caregivers also has the surprising bonus of cutting Medicare costs, according to UC San Francisco research.
In the study, publishing in JAMA Internal Medicine on Sept. 18, 2023, researchers, led by UCSF, compared the Medicare costs of 780 patients with dementia. The patients were randomized 2:1 to receive Care Ecosystem support – which included medical and practical assistance – or their usual care for a 12-month period. Both groups were similar in age, severity of dementia ...
Higher buprenorphine doses associated with improved retention in treatment for opioid use disorder
2023-09-18
Individuals with opioid use disorder who were prescribed a lower buprenorphine dose were 20% more likely to discontinue treatment than those on a higher dose, according to a study of patients prescribed buprenorphine in Rhode Island from 2016 to 2020, as fentanyl became widely available. The study, published today in JAMA Network Open, was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, and conducted by researchers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island; NIDA and the Rhode Island ...
Tracking down the formation of cardenolides in plants
2023-09-18
Plants produce an impressive array of metabolites, including many medically valuable steroids. Well-known examples of this class of substances obtained from plants are cardenolides. As early as 1785, the British physician William Withering (1741-1799) published a book on the red foxglove and its use in medicine (An account of the foxglove, and some of its medical uses: with practical remarks on dropsy, and other diseases. Birmingham 1785). He had found out in experiments that taking extracts ...
The surprising origin of a deadly hospital infection
2023-09-18
Hospital staff spend a significant amount of time working to protect patients from acquiring infections while they are being cared for in the hospital. They employ various methods from hand hygiene to isolation rooms to rigorous environmental sanitation. Despite these efforts, hospital-onset infections still occur—the most common of which is caused by the bacterium Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff, the culprit of almost half a million infections in the U.S. each year.
Surprising findings from a new study in Nature Medicine suggest that the burden of C. diff infection may be less a matter of hospital transmission and more a result of characteristics associated ...
Mature sperm lack intact mitochondrial DNA, study finds
2023-09-18
New research provides insight about the bedrock scientific principle that mitochondrial DNA — the distinct genetic code embedded in the organelle that serves as the powerplant of every cell in the body — is exclusively passed down by the mother.
The study, a collaboration among Oregon Health & Science University and other institutions, published today in the journal Nature Genetics.
Scientists have long recognized the fact that mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA, comes exclusively from egg cells in humans, meaning only the mother contributes the genetic code carried by ...
Research identifies new potential hurdle for nano-based therapies
2023-09-18
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered that certain nano-based cancer therapies may be less effective in younger patients, highlighting the need for further investigation into the impact of aging on the body’s ability to respond to treatment.
The researchers found age-related differences are due to how effectively the liver filters the bloodstream. Younger livers are more efficient at this process, which helps limit toxins in the blood but also filters out beneficial treatments, potentially rendering them ineffective.
The study, published today in ...
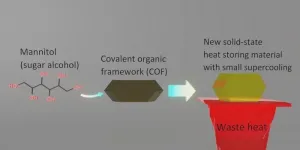
Improving the properties of sweeteners for enhanced thermal energy storage
2023-09-18
As we seek more efficient utilization of waste thermal energy, use of “phase change materials (PCMs)” is a good option. PCMs have a large latent heat capacity and the ability to store-and-release heat as they change from one state of matter to another. Among many PCMs, sugar alcohols (SAs), a class of organic compounds commonly used as sweeteners, stand out due to their low cost, non-toxic, non-corrosive, and biodegradable nature. In particular, SAs generally have their melting point in 100–200 °C, which is an important temperature range where a huge amount of waste heat exists but is currently ...
Ohio State leads new global climate center on AI for biodiversity change
2023-09-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The Ohio State University will lead a new multimillion dollar international center devoted to using artificial intelligence to help understand climate impacts on biodiversity.
The AI and Biodiversity Change (ABC) Global Climate Center will bring together ecologists and computer scientists from six universities in the United States and Canada, with partners in UK, Europe, and Australia, to develop new AI-enabled, data-supported approaches to study how changes in climate are impacting life – including animals, plants and insects – on Earth.
$5 ...
Ohio State researchers publish national guidelines for ALS genetic testing, counseling
2023-09-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine led the creation of evidence-based consensus guidelines for genetic testing and counseling for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a neurodegenerative disease that affects the cells in the brain and spine.
These evidence-based, consensus guidelines provide clinicians with a framework for the offer of genetic testing and outline the information that should be provided to persons with ALS before and after testing. In addition, the guidelines provide specific recommendations regarding ...
Study: Admissions policies that consider grades and test scores in context of available opportunities are linked to college success
2023-09-18
Indicators of high school grades and standardized test scores that take into account the levels of school, neighborhood, and family resources available to students are strongly associated with those students’ success in college, according to new research published today. The study, published in AERA Open, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association, emerges against the backdrop of the recent Supreme Court decision to ban race-conscious admissions in higher ...
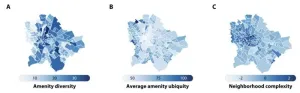
Unlocking urban diversity: The magnetism of complex amenities
2023-09-18
Diversity fuels prosperity in cities, but where do people from diverse backgrounds meet? A study from the Complexity Science Hub now indicates that locations offering a range of rare shops and services may hold the key.
Extensive research consistently underscores a common factor in successful cities: diversity. Encouraging interactions between individuals of different backgrounds fosters the exchange of ideas, leading to innovation and economic success. “However, segregation persists in urban ...
Latest blood cancer treatment updates presented at annual NCCN event during Blood Cancer Awareness Month
2023-09-18
SAN FRANCISCO, CA [September 18, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) 2023 Annual Congress: Hematologic Malignancies™ returns to San Francisco this week, for the first time since 2019. The meeting features insights from world-renowned experts on providing optimal, evidence-based treatment for various blood cancers, plus best practices for protecting vulnerable populations in a changing healthcare landscape.
The live event is taking place September 22-23, 2023, at the Hilton San Francisco Union Square. ...
How do suicide risk or depression screenings compare to identify patients at risk?
2023-09-18
Editor’s Note: September is National Suicide Prevention Month.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Research led by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and Wesleyan University found that depression screening tools outperformed suicide risk screenings under most conditions.
“We compared the effectiveness of multiple depression and suicide risk screening methods for the purpose of identifying primary care patients who subsequently attempted suicide. Our findings may generate a lot of discussion within the suicide prevention community, as it contradicts long-held assumptions ...
Atomic layer deposition route to scalable, electronic-grade van der Waals Te thin films
2023-09-18
A research team, led by Professor Joonki Suh in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Semiconductor Materials and Devices Engineering at UNIST, has made a significant breakthrough in thin film deposition technology. By employing an innovative atomic layer deposition (ALD) process, Professor Seo successfully achieved regular arrangement of tellurium (Te) atoms at low temperatures as low as 50 degrees Celsius.
The ALD method is a cutting-edge thin film process that enables precise stacking ...
NIH launches $2 million prize competition to spur innovation in fetal diagnostic and monitoring technologies
2023-09-18
The National Institutes of Health will award up to $2 million in cash prizes to accelerate development of diagnostic and monitoring technologies that improve fetal health outcomes in low-resource settings. The Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics Technology (RADx® Tech) Fetal Monitoring Challenge calls on scientists, engineers, and clinicians around the country to submit their innovative approaches and compete for prizes and additional resources to support technology development and clinical impact. The challenge is sponsored by the NIH’s National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), ...
Incubator or barrier? Exploring the links between agriculture, biodiversity and the spread of pathogens
2023-09-18
Many pathogens, including the virus that causes COVID-19, are thought to have originated in wild animals before spilling into human populations.
Agriculture is often blamed for accelerating this process, which is known as zoonotic spillover, through deforestation and habitat fragmentation that reduce biodiversity and increase the likelihood of contact between infected wildlife and humans.
But in a Perspectives article published online Sept. 15 in the journal One Earth, University of Michigan ecologist Ivette Perfecto and her colleagues argue that agriculture can both help and hinder: ...
FAU receives $750,000 philanthropic grant for Alzheimer’s disease
2023-09-18
More than 720,000 Floridians will be living with Alzheimer’s disease by 2025. Currently, Florida has the second highest prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States and is the sixth leading cause of death in Floridians 65 and older.
Although the epidemic of age-related brain dysfunction – of which Alzheimer’s disease is a major factor – is growing at an alarming rate, there is a disconnect between the existing care model designed for urgent care and the progressive nature of this chronic condition, which tends to worsen over time.
To address this widespread health concern, Florida Atlantic University’s Schmidt College ...
Study shows nearly 300% increase in ADHD medication errors
2023-09-18
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is among the most common pediatric neurodevelopmental disorders. In 2019, nearly 10% of United States (U.S.) children had a diagnosis of ADHD. Approximately 3.3 million children, or roughly 5 out of every 100 children in the U.S., are currently prescribed medication for ADHD.
In a new study, published today in Pediatrics, researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy and Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital investigated the characteristics ...
KICT develops road pothole filtering program based on AI
2023-09-18
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) has developed a 'Road Pothole Filtering Program' to establish an emergency road restoration system for frequent pothole occurrences.
Commonly referred to as 'the landmine of the road,' potholes are a road damage phenomenon in which parts of the asphalt sink into bowl-like depressions. Potholes occur when a significant amount of rainwater infiltrates the road surface, weakening the ground below and causing the asphalt ...
New online tool available to help health care providers identify a hard to diagnose breast cancer
2023-09-18
A new diagnostic scoring system, developed by renowned breast cancer experts, is now available as an easy-to-use online tool through Susan G. Komen®, the world’s leading breast cancer organization. This tool will help health care providers recognize and effectively diagnose a rare and aggressive breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer.
The new Inflammatory Breast Cancer (IBC) Scoring System online tool is available at https://www.komen.org/ibc and may help to increase diagnostic accuracy, predict outcomes, guide treatment decisions ...
Pearl Harbor: Bombed battleships’ boost for climate science
2023-09-18
Weather data from several ships bombed by Japanese pilots at Pearl Harbor has been recovered in a rescue mission that will help scientists understand how the global climate is changing.
Crew members aboard various vessels - such as the USS Pennsylvania and the USS Tennessee - died when their battleships were targeted in December 1941. Despite these losses, many boats returned to service during the Second World War and US naval servicemen continued their daily duties, which included recording weather data.
A new research paper, published in Geoscience Data ...
Brigham researchers uncover ‘circular logic’ of RNAs in Parkinson’s disease
2023-09-18
Investigators found and catalogued mysterious RNA circles that are linked to brain cell identity
Findings show that circular RNA is produced by brain cells damaged in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease
Circular RNA production from one Parkinson’s gene DNAJC6 was abnormal even prior to symptom onset
Researchers are gaining new insights into neurological diseases by studying circular RNAs (circRNAs) in brain cells. A new study by investigators from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General ...
Engineered compound shows promise in preventing bone loss in space
2023-09-18
A new study published in a Nature Partner Journal, npj Microgravity, finds an engineered compound given to mice aboard the International Space Station (ISS) largely prevented the bone loss associated with time spent in space. The study, led by a transdisciplinary team of professors at the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Forsyth Institute in Cambridge, Massachusetts, highlight a promising therapy to mitigate extreme bone loss from long-duration space travel as well as musculoskeletal ...
European funding for the treatment of Type 1 diabetes using 3D bioprinting
2023-09-18
Javier Ramón Azcón, an ICREA research professor and the leader of the Biosensors for Bioengineering group at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), has been granted an "ERC Proof of Concept Grant." This prestigious grant is awarded by the European Research Council (ERC) and aims to explore the commercial and societal potential of research projects that have been previously funded by the ERC. Recipients use this type of funding to verify the practical viability of scientific concepts, explore business opportunities or prepare patent applications.
Ramón's project has been named "Uniink" and centers ...
National Poll: 2 in 3 parents say their kids have experienced poor air quality
2023-09-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – As smoke from Canada's historic wildfires triggers poor air quality alerts across the country, many parents worry about the impact on their child’s health, a new national poll suggests.
Two-thirds of parents say over the past two years they have experienced at least one day with poor or unhealthy air quality in their area, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
In response to poor air quality alerts, most parents kept their windows closed and limited ...
[1] ... [1684]
[1685]
[1686]
[1687]
[1688]
[1689]
[1690]
[1691]
1692
[1693]
[1694]
[1695]
[1696]
[1697]
[1698]
[1699]
[1700]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.