Emily Rogalski joins UChicago to lead new center for healthy brain aging, Alzheimer's and related diseases
2023-09-13
The University of Chicago will launch a pioneering new center aimed at shifting the popular narrative around the physical and cognitive impacts of aging.
Headed by leading neuroscientist Emily Rogalski, PhD, the new University of Chicago Healthy Aging & Alzheimer's Research Care (HAARC) Center will focus on building deep multidisciplinary expertise and bridging the gap between scientific disciplines to accelerate breakthroughs in cognitive resilience.
“We want to increase awareness and the scientific probability ...
Illuminating the path to sustainable wellbeing
2023-09-13
IIASA is proud to announce the launch of its Flagship Report, "Systems Analysis for Sustainable Wellbeing. 50 Years of IIASA Research, 40 Years After the Brundtland Commission, Contributing to the Post-2030 Global Agenda” on Wednesday, 13 September 2023 at an official UN event in the framework of the 78th session of the UN General Assembly and the Sustainable Development Goals mid-term review.
The IIASA Flagship Report chronicles the extraordinary 50-year journey of IIASA, a globally renowned institute providing systems analytical expertise on complex global challenges. Co-sponsored by the Permanent Missions of Austria and South Africa ...
Study finds that state-mandated civics test policy does not improve youth voter turnout
2023-09-13
Washington, September 13, 2023—The United States has the largest age gap in voter turnout among advanced democracies. Youth voter turnout remained low, at 48 percent, in 2020. Scholars, educators, and policymakers often recommend civic education as a solution to low youth voter turnout.
However, new research finds that a commonly used state-mandated civics test policy—the Civics Education Initiative (CEI)—does not improve youth voter turnout, at least in the short term. The study, by Jilli Jung and Maithreyi Gopalan, both at Pennsylvania State University, was published today in Educational ...
Groundbreaking research unveils genetic characteristics and improved prognosis of triple negative apocrine carcinoma
2023-09-13
Breast cancer research takes a significant stride forward as Professor Semin Lee and his research team from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Ji-Yeon Kim and Professor Young-Hyuck Im from the Division of Hematology-Oncology at Samsung Medical Center in Seoul, delves into the exploration of triple negative apocrine carcinoma. This rare breast cancer subtype has garnered attention due to its unique genetic characteristics and improved prognosis when compared to other forms of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Triple negative ...
Inflammatory signs for adolescent depression differ between boys and girls
2023-09-13
New research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has found that depression and the risk of depression are linked to different inflammatory proteins in boys and girls.
When inflammation occurs in the body a host of proteins are released into the blood called cytokines. Previous research has shown that higher levels of cytokines are associated with depression in adults, but little is known about this relationship in adolescence.
Researchers investigated sex-differences in the relationship between inflammatory proteins and depression. Published in the Journal of ...
The effect of crowdsourcing contests on a company's stock and the idiosyncratic risks they create for investors
2023-09-13
Researchers from University of Colorado Denver, Iowa State University, and Arizona State University published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the stock market effects on these contests and the contest characteristics that may enable such contests to pay off.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “When Do Marketing Ideation Crowdsourcing Contests Create Shareholder Value? The Effect of Contest Design and Marketing Resource Factors” and is authored by Zixia Cao, Hui Feng, and Michael A. Wiles.
Crowdsourcing contests for marketing ideas such as new ads, graphics, and products have become quite popular ...
Some spiders can transfer mercury contamination to land animals, study shows
2023-09-13
Sitting calmly in their webs, many spiders wait for prey to come to them. Arachnids along lakes and rivers eat aquatic insects, such as dragonflies. But, when these insects live in mercury-contaminated waterways, they can pass the metal along to the spiders that feed on them. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters have demonstrated how some shoreline spiders can move mercury contamination from riverbeds up the food chain to land animals.
Most mercury that enters waterways ...
National awards recognize 19 students, schools, and educators’ commitment to health
2023-09-13
DALLAS, September 13, 2023 — On Tuesday, Sept. 12, the American Heart Association, a global force for healthier lives for all, recognized 19 students, schools and educators for their commitment to end cardiovascular disease, the nation’s no. 1 killer, through the Association’s in-school programs, Kids Heart Challenge™ and American Heart Challenge™. The annual National Awards Ceremony, held virtually, was joined by program participants from coast to coast and ...
American Society for Microbiology announces ‘gain of function’ recommendations from top scientists
2023-09-13
Washington, D.C. — Sept. 13, 2023 — The American Society for Microbiology today released consensus recommendations from a workshop of leading scientists who reviewed the benefits and risks of “gain of function” research, as well as related policies and procedures, and proposed a foundation to guide discussions and improve oversight moving forward.
The recommendations – together with a call to action for the scientific community and the general public – are intended to inform assessments of “gain of function research of concern,” which makes up a small fraction of all biological research. ...
Scientists uncover COVID’s weakness
2023-09-13
New UC Riverside research has revealed COVID’s Achilles heel — its dependence on key human proteins for its replication — which can be used to prevent the virus from making people sick.
In a new paper published in the journal Viruses, the UCR research team describes an important discovery. The protein in COVID that enables the virus to make copies of itself, called N, requires the help of human cells to perform its job.
Genetic instructions in our cells are transcribed from DNA to messenger ...
UMass Amherst and Embr Labs develop ‘digital drug’ to predict hot flashes
2023-09-13
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst’s Institute for Applied Life Sciences (IALS) and Embr Labs have created a machine-learning algorithm to predict a hot flash before a person perceives it.
When combined with Embr Labs’ patented wearable device, Embr Wave™, immediate cooling is delivered to mitigate or fully alleviate the event. This first-of-its-kind predictive algorithm is the result of machine learning being applied to the largest data set of digital biomarkers for hot flashes ever collected, which was generated by researchers at UMass Amherst’s Center for Human ...
Socioeconomic status may be an uneven predictor of heart health
2023-09-13
Research Highlights:
The benefits of four measures of socioeconomic status (education, income, employment status and health insurance) on ideal heart health were greater for non-Hispanic white adults compared to Black, Hispanic and Asian adults in the U.S.
The new diverse representative study suggests heart disease prevention efforts should address other non-biological factors that drive cardiovascular health and not rely solely on reducing socioeconomic disparities by race or ethnic group.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2023
DALLAS, ...
No increase in cancer risk for most patients with reflux disease
2023-09-13
Reflux disease manifests as acid regurgitation and heartburn and is a known risk factor for oesophageal cancer. However, a new study published in The BMJ by researchers at Karolinska Institutet now reports that the majority of patients do not have a higher risk of cancer. A large-scale study from three Nordic countries shows that the cancer risk is only elevated in patients whom gastroscopy reveals to have changes in the oesophageal mucosa.
­“This is a gratifying result since reflux disease is a very common condition and most patients are found to have a completely normal mucus membrane on gastroscopic examination,” says the study’s ...
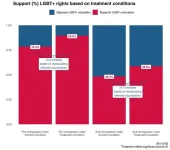
Study uncovers link between anti-immigrant prejudices and support for LGBT+ rights
2023-09-13
Cross-national research carried out by the University of Southampton and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VUA) into public opinion on LGBT+ rights has shown that anti-immigrant prejudices, particularly towards Muslims, contributes to explaining some of the widespread shifts in tolerance towards the LGBT+ community. Findings of a new study show this was especially evident among socially conservative voters.
The rise of tolerance towards LGBT+ individuals in Western democracies could be seen as remarkable, according to the researchers. Whereas a majority of citizens rejected the idea of same-sex marriage a couple of decades ago, a majority of ...
Rapid acting, oral vaccines are coming soon
2023-09-13
A new paper in Biology Methods and Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, indicates that researchers studying SARS-CoV-2 may have developed new methods to administer vaccines orally, which would be both easier to administer and more effective at combatting illnesses.
The best way to neutralize viruses is before they can enter inside human cells but are only on the external surface of epithelial cells that line and produce mucus in the lungs, nose, and mouth. A specific class of antibodies known as Immunoglobulin A operate in mucus and can disable viruses. However, production of specific immunoglobulins/antibodies for a ...
Certain proteins in breast milk found to be essential for a baby’s healthy gut
2023-09-13
More than 320 million years of mammalian evolution has adapted breast milk to meet all the physiological needs of babies: it contains not only nutrients, but also hormones, antimicrobials, digestive enzymes, and growth factors. Furthermore, many of the proteins in breast milk, for example casein and milk fat globule membrane proteins, aren’t just sources of energy and molecular building blocks, but also directly stimulate immunity, at least under preclinical conditions.
Likewise, the gut microbiome, composed of bacteria, archaea, and fungi, plays a vital role in the regulation of the immune system. This raises the possibility that the immune-boosting function ...
AACR Cancer Progress Report details exciting advances in cancer research and treatment
2023-09-13
PHILADELPHIA – Today, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) released the 13th edition of its annual Cancer Progress Report, which chronicles how basic, translational, and clinical cancer research and cancer-related population sciences—primarily supported by federal investments in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI)—remain vitally important to improving health and saving lives.
In addition to providing the latest statistics on cancer incidence, mortality, and survivorship, the AACR Cancer Progress Report 2023 offers detailed updates and important ...
Pitt surveillance system detected infection linked to eye drops months before outbreak declared
2023-09-13
An infectious diseases surveillance system created by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists and deployed at a UPMC hospital successfully flagged cases of a drug-resistant infection spread by eye drops months before national public health officials announced an outbreak.
The findings, published today in The Journal of Infectious Diseases, were obtained through a hospital-based program called Enhanced Detection System for Healthcare-Associated Transmission (EDS-HAT). They demonstrate the potential of this technology to detect and stop nationwide outbreaks sooner.
“Our study really showcases the utility of whole genome sequencing surveillance,” ...
Early ovary removal likely to accelerate aging process and health problems
2023-09-13
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 13, 2023)—Increasing concerns regarding potentially harmful long-term effects of premenopausal bilateral oophorectomy (PBO) have caused a decline in the number of women choosing to proactively remove both ovaries as a precaution to protect against ovarian cancer. A new study identified specific chronic medical conditions, such as asthma and arthritis, associated with the procedure. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Hysterectomy is the second-most-frequently performed surgical operation for women after cesarean ...
Discovery of two potential Polar Ring galaxies suggests these stunning rare clusters might be more common than previously believed.
2023-09-13
KINGSTON, September 13, 2023 – A group of international astronomers, including researchers from Queen’s University, has identified two potential polar ring galaxies, according to results published today in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Queen’s researchers Nathan Deg and Kristine Spekkens (Physics, Engineering Physics & Astronomy) led the analysis of data obtained using a telescope owned and operated by CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency. Looking at ...
Freshwater connectivity can transport environmental DNA through the landscape
2023-09-13
A new paper published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B used environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding to analyze fish and zooplankton communities. The study found that the movement of water between freshwater bodies, or freshwater connectivity, can transport eDNA. This highlights the potential of eDNA to provide a comprehensive view of freshwater biodiversity.
Aquatic ecosystems are connected by waterways, which allow fish, plants, and other organisms to move from one place to another. This connectivity is important for the resilience of aquatic populations, but it can also make it difficult ...
Largest historic fire death toll belongs to aftermath of 1923 Japan Earthquake
2023-09-13
Fires that raged in the days following the 1 September 1923 magnitude 7.9 Kantō earthquake killed roughly 90% of the 105,000 people who perished in and around Tokyo, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in history—comparable to the number of people killed in the World War II atomic bombing of Hiroshima.
The story of the conflagration, not well-known outside of Japan, holds important lessons for earthquake scientists, emergency response teams and city planners, according to a new paper published ...
Nature’s great survivors: Flowering plants survived the mass extinction that killed the dinosaurs
2023-09-13
A new study by researchers from the University of Bath (UK) and Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (Mexico) shows that flowering plants escaped relatively unscathed from the mass extinction that killed the dinosaurs 66 million years ago. Whilst they suffered some species loss, the devastating event helped flowering plants become the dominant type of plant today.
There have been several mass extinctions in the Earth’s history, the most famous caused by an asteroid hit 66 million years ago, which has steered the course of life on Earth profoundly.
The ...
Death rates following first heart attack have gone down for those without diabetes or with type 2 diabetes, but not for type 1 diabetes
2023-09-13
*Note- this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) meeting in Hamburg, October 2-6. Please credit the meeting if you use this story*
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) shows that, following a heart attack, there have been falls in the death rates of both people without diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes, but not those with type 1 diabetes. The study is by Dr Linn ...
University of Alberta to offer pioneering AI education to all undergraduate students
2023-09-12
The University of Alberta (U of A), a globally recognized leader in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning, along with Amii (Alberta Machine Intelligence Institute), are breaking new ground with the launch of "Artificial Intelligence Everywhere," a new online introductory course accessible to all U of A undergraduates. The course is the cornerstone for an in-development AI certification, which will be one of the first in Canada.
The course equips students across all disciplines with essential AI literacy skills. With AI permeating sectors from health care to finance, this initiative bridges the AI skills ...
[1] ... [1688]
[1689]
[1690]
[1691]
[1692]
[1693]
[1694]
[1695]
1696
[1697]
[1698]
[1699]
[1700]
[1701]
[1702]
[1703]
[1704]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.