Charging ahead: New electrolyte goes extra mile for faster EV charging
2023-09-12
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers are taking fast charging for electric vehicles, or EVs, to new extremes.
A team of battery scientists recently developed a lithium-ion battery material that not only recharges 80% of its capacity in 10 minutes but keeps that ability for 1,500 charging cycles.
When a battery operates or recharges, ions move between electrodes through a medium called the electrolyte. ORNL’s Zhijia Du led a team who developed new formulations of lithium salts with carbonate solvents to form an electrolyte that maintains better ion flow over time and performs well when high current heats up the battery ...
Smartphone technology expected to advance assessment of neurological soft signs in schizophrenia
2023-09-12
September 12, 2023 — Since the 1980s, we have known that neurological soft signs (NSS) can distinguish people with schizophrenia from psychiatrically healthy individuals. NSS are subtle neurological impairments that principally manifest as decreased sensory integration (trouble receiving and responding to information transmitted to the brain through the senses) and difficulties with balance, rapid successive movements, and right–left orientation.
NSS doesn't always cause impairment of daily living, but identifying them could improve the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia and enhance understanding of the ...
Kessler Foundation receives $725,000 grant for study to accelerate functional recovery in multiple sclerosis
2023-09-12
East Hanover, NJ – September 12, 2023 – Carly Wender, PhD, associate research scientist in the Center for Neuropsychology and Neuroscience Research at Kessler Foundation received a three-year $725,499 grant from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society for her study, “A Novel Combinatory Approach to Maximize Functional Recovery of Learning and Memory in Multiple Sclerosis.”
Cognitive impairment is a common symptom in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) that can be particularly ...
Older adults with digestive diseases experience higher rates of loneliness, depression
2023-09-12
While life expectancy rates for older Americans are rising, nearly 40% of adults report living with a digestive disease of some kind.
“Many people don’t realize that these conditions are very common in ambulatory care,” said Michigan Medicine gastroenterologist Shirley Ann Cohen-Mekelburg, M.D., who specializes in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
“Ultimately, this creates an excess in health care spending in the United States. Not only are these conditions debilitating for the millions of people living with them, ...
Mount Sinai receives NIH grant to develop vaccines that can protect against many different types of coronaviruses
2023-09-12
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has awarded the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai a five-year, $13 million grant to bring together experts from multiple disciplines across five research institutions to create better vaccines against current as well as emerging coronaviruses.
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has infected 280 million people and caused more than five million deaths worldwide since late 2019. While considerable progress has been made to develop interventions (i.e., monoclonal antibodies, antivirals, vaccines) to treat and prevent COVID-19, ...
Setting the gold standard in diagnosis of lupus nephritis
2023-09-12
In the ever-perilous autoimmune disease world of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus), up to 60% of adult patients and 80% of children will develop lupus nephritis (LN), and up to half of those will move on to end-stage renal disease. LN occurs when the immune system wrongly attacks the kidneys, preventing them from doing their job, i.e., cleaning blood, balancing body fluids and controlling hormones that impact blood pressure.
Unfortunately, the most precise way to diagnose LN hasn’t been ...
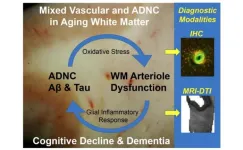
Contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-09-12
“The molecular mechanisms that mediate enhanced dysfunction of white matter parenchymal arterioles when vascular dysfunction and ADNC coincide remain elusive.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 12, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 16, entitled, “Microvascular contributions to white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease.”
In their new editorial, researchers Zsolt Bagi, ...
Accelerating knowledge exchange in biodiversity genomics and bioinformatics
2023-09-12
Since its inception in 2021, the African BioGenome Project (AfricaBP), has made significant gains towards its ambitious goal of sequencing 100,000 endemic African species within the next 10 years. Recently, AfricaBP reported the successful implementation of the Open Institute in the journal Nature Biotechnology (https://rdcu.be/dlXYT), a pioneering biodiversity genomics and bioinformatics knowledge exchange programme.
The AfricaBP Open Institute’s framework will establish openly accessible workshops across Africa, crafted in close collaborations with local African Institutions. ...
Call: "Journalist in Residence“ program at Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA)
2023-09-12
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) is offering science journalists the opportunity for a paid three-month "Journalist in Residence“ program starting in April 2024. Applications are open until Oct. 31, 2023.
The Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) in Klosterneuburg – in the immediate vicinity of Vienna – is a Ph.D.-granting research institute. Opened in 2009, the Institute is dedicated to basic research in the natural sciences, mathematics and computer sciences. It has a total of 1000 employees and 75 different research ...
COVID-19 can trigger auto-immune disorders-related antibodies, causing thrombosis and other complications
2023-09-12
An article published in NPJ Aging, a Springer Nature journal, reveals that natural production of auto-antibodies increases with age and that infection by SARS-CoV-2 can exacerbate production of auto-antibodies relating to auto-immune diseases, helping to explain why aging increases the chances of developing severe COVID-19. The study also discovered some of the factors that associate the severe form of the disease with blood clotting disorders such as thrombosis.
“These findings open the door to a better ...
Alzheimer’s: An M.D./Ph.D. graduate student’s request for Yuhua Song as mentor leads to two NIH R01 awards totaling $5 million
2023-09-12
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In the summer of 2018, graduate student Hunter Dean from the Medical Scientist Training Program came to Yuhua Song, Ph.D., with a research idea. He wanted to pursue his doctoral research at the University of Alabama at Birmingham in Alzheimer’s disease — under the joint mentorship of Song, who had never worked in Alzheimer’s, and Erik Roberson, M.D., Ph.D., an Alzheimer’s expert in the UAB Department of Neurology and the Center for Neurodegeneration and Experimental Therapeutics, or CNET.
That collaboration brought Song, a professor in the UAB Department of ...
Recommendations for addressing health-related social needs in cancer care introduced at NCCN Policy Summit
2023-09-12
Today, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—presented new recommendations for screening and addressing health-related social needs (HRSN) in people with cancer during a policy summit in Washington, D.C. The event included a keynote address from Ellen Lukens, Deputy Administrator and Director, The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI), and other speakers representing a diverse group of patient advocates, providers, and policymakers.
The new recommendations for measuring and addressing HRSNs were ...
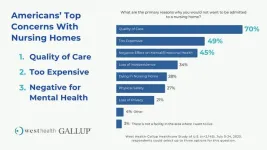
West Health-Gallup Poll: 70% of Americans uncomfortable with prospect of being admitted to nursing home
2023-09-12
WASHINGTON, D.C. — September 12, 2023 — More than 40% of Americans say nursing homes are unsafe and 7 in 10 say they would be uncomfortable ever having to be admitted to one even if they needed such care, while more than six in 10 (61%) feel similarly anxious about the prospect of admitting family members, according to the latest survey from West Health and Gallup.
Safety was a particular area of perceived concern; 41% of respondents say nursing homes are not safe, 26% say they are, and about a third say they don’t know. Notably, the survey found that people over 35 were much ...
UTHealth Houston researcher to present abstract detailing new mouse model for brain arteriovenous malformations at NIH meeting
2023-09-12
An abstract unveiling a new mouse model for brain arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) developed by UTHealth Houston researchers has been selected for a poster presentation at the second annual National Institutes of Health (NIH) Investigator Meeting for Interoception Research in November.
Eunsu Park, PhD, assistant professor in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, will present the abstract at the meeting, hosted by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) at the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland, on Nov. ...
Combination of stressors key to testing perovskite solar cells
2023-09-12
Perovskite solar cells should be subjected to a combination of stress tests simultaneously to best predict how they will function outdoors, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
Solar cells must endure a set of harsh conditions—often with variable combinations of changing stress factors—to judge their stability, but most researchers conduct these tests indoors with a few fixed stressing conditions. While these tests provide some necessary insight, understanding which stressor applied during indoor tests provided predictive correlations ...
Communicating stability, strong connections to stakeholders versus shareholders are priorities in Chinese financial reporting, Rotman research finds
2023-09-12
September 12, 2023 Toronto - It’s commonly accepted that U.S. and Chinese companies treat financial reporting and disclosure differently.
New research not only confirms that but digs into the motivations behind the distinction, using surveys with more than 200 Chinese executives who hold reporting responsibility. An overriding interest in communicating long-term stability and inspiring confidence in the company’s prospects among a diverse range of stakeholders, and not primarily shareholders, as in the U.S., was a signature driver for the Chinese business leaders.
“Acknowledging differences in approaches and incentives ...
Morris Animal Foundation funds 6 new studies to advance canine cancer research
2023-09-12
DENVER/Sept. 12, 2023 – Recent findings from the Golden Retriever Lifetime Study confirm the enormous impact of hemangiosarcoma on golden retrievers. To address critical gaps in disease detection and treatment, Morris Animal Foundation announced it is funding six studies focused on this deadly form of canine cancer.
“We are committed to providing resources to the top research teams in the world that can advance our understanding of hemangiosarcoma," said Dr. Kathy Tietje, Chief Program Officer at Morris Animal Foundation. "These innovative research ...
ReMDO grants support commercialization of regenerative medicine therapies
2023-09-12
WINSTON-SALEM, NC, September 12, 2023 - When the RegenMed Development Organization (ReMDO) offered its grant opportunity related to regenerative medicine manufacturing and commercialization, the result exceeded expectations.
The Regenerative Medicine Manufacturing grant call encouraged small, medium, and large companies to submit letters of interest with an accompanying white paper that addressed a gap in technical capabilities for one or more of the following topic areas: Cell and Biomaterial Manufacturing, Standards and Quality Control, Additive Manufacturing and Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation.
The grant opportunity will ...
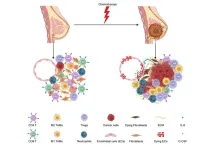
Breast cancer recurrence may be triggered by chemotherapy injury to non-cancer cells
2023-09-12
A standard chemotherapy drug injures surrounding non-cancer cells, which can then awakens dormant cancer cells and promotes cancer growth, according to a new study publishing September 12th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Ramya Ganesan of Emory University, US, and colleagues. The finding is important for understanding cancer recurrence and may point to important new targets to prevent it.
Advances in cancer treatment, including chemotherapy, have dramatically reduced mortality for many types of cancer, including breast cancer. Nonetheless, up to 23% of breast cancer patients experience recurrence within the first five years. Treatment is meant to kill all cancer cells, ...
Disease-resistant rice and wheat plants may modulate disease susceptibility in their neighbors
2023-09-12
Growing several plant varieties in the same field for disease resistance is a longstanding agricultural practice, but can have unpredictable results. A study publishing September 12th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Jean-Benoit Morel at Institut National de Recherche pour l'Agriculture l'Alimentation et l'Environnement, Montpellier, France, and colleagues suggests that plant-to-plant interactions may confer disease immunity in both wheat and rice.
Neighbor-Modulated Susceptibility (NMS) occurs when healthy, same-species ...
Umass Amherst research finds benefits, risks in state-mandated school-based BMI assessments
2023-09-12
A University of Massachusetts Amherst resource economist finds mandated in-school Body Mass Index (BMI) assessments adopted in varying forms by 24 states to combat childhood obesity have the potential to improve the health of some students while introducing body-image issues for others. The research is believed to be the first to assess these policies as a whole, rather than in single states or school districts.
“In states that passed these laws, overweight and obese teens were more likely to correctly describe their bodies as such, compared to states ...
UNIST and University of Ulsan College of Medicine to introduce groundbreaking HST curriculum in Korea!
2023-09-12
In a significant collaboration, UNIST and the University of Ulsan College of Medicine (hereinafter ‘U of U College of Medicine’) have successfully developed a joint curriculum aimed at cultivating professionals with interdisciplinary expertise. This unique program seeks to bridge the gap between engineering and medicine, producing graduates who possess both medical knowledge and engineering understanding. The collaboration aims to contribute effectively to advancements in healthcare technology and innovation.
The jointly developed curriculum consists of seven courses, including ‘Introductions to Medical Science AI‘ and ‘Brain and Cognitive ...
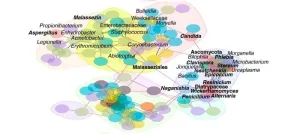
How the respiratory tract microbiome influences the severity of bacterial pneumonia
2023-09-12
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung alveoli caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. It is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, representing a clinical and economic burden and a global public health problem. The microbial ecosystem (or microbiome) of the human respiratory tract colonizes different niches. The respiratory tract microbiome is of interest to scientists as it contributes to human health by stimulating the immune system and protecting against infection by pathogens. Scientists ...
Researchers develop new method for mapping the auditory pathway
2023-09-12
Researchers have developed a non-invasive method for mapping the human auditory pathway, which could potentially be used as a tool to help clinicians decide the best surgical strategy for patients with profound hearing loss.
The findings, published today in eLife, highlight the importance of early interventions to give patients the ability to hear and understand speech, so that their auditory-language network can develop properly and their long-term outcomes are improved.
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) occurs when the sensitive hair cells inside the cochlea are damaged, or when there is damage to the auditory nerve which transmits sound to the brain. A person with profound hearing ...
FAIRer knowledge about biodiversity with AI-friendly nanopublications
2023-09-12
Earlier this year, in a pilot project, the teams of high-tech startup Knowledge Pixels and open-access scholarly publisher and technology provider Pensoft released a novel workflow to publicly share and future-proof scientific findings by means of nanopublications.
Nanopublications complement human-created narratives of scientific knowledge with elementary, machine-actionable, simple and straightforward scientific statements that prompt sharing, finding, accessibility, citability and interoperability. By making it easier to trace individual findings back to their origin and/or follow-up updates, it also helps to better understand the provenance of biodiversity ...
[1] ... [1693]
[1694]
[1695]
[1696]
[1697]
[1698]
[1699]
[1700]
1701
[1702]
[1703]
[1704]
[1705]
[1706]
[1707]
[1708]
[1709]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.