Alive without a pulse: Evolution of durable left ventricular assist devices
2023-09-11
https://www.scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/CVIA.2023.0056
Announcing a new article publication for Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications journal. Durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) offer a viable option for patients with advanced heart failure and have been demonstrated to be superior to optimal medical therapy in terms of both mortality and quality of life, in selected patients. However, durable LVADs can be associated with severe morbidity. Because the rates of cardiac ...
Doctoral student’s "fear of positivity" research could assist with effective depression treatments
2023-09-11
STARKVILLE, Miss.—How can positive experiences seem like the opposite for some?
A doctoral student in Mississippi State University’s Clinical Psychology program believes this phenomenon is true, and his recent research is featured in an upcoming issue of The Journal of Behavioral Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry.
Michael R. Gallagher’s article “A network analytic investigation of avoidance, dampening, and devaluation of positivity” focuses on how behaviors related to processing positive experiences may play a role ...
Stem cell-derived components may treat underlying causes of PCOS
2023-09-11
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a pervasive endocrine disorder that affects millions of women globally, impacting their hormonal balance, fertility and overall well-being. It is notoriously difficult to treat, with widely varying symptoms and mysterious, complex underlying causes. Researchers at the University of Chicago recently unveiled a potential new PCOS treatment that may improve multiple PCOS symptoms by regulating body systems and reducing inflammation.
Recently published results demonstrate the promise ...
Urban parks built on former waste incineration sites could be lead hotspots
2023-09-11
DURHAM, N.C. – For much of the last century, many cities across the United States and Canada burned their trash and waste in municipal incinerators. Most of these facilities were closed by the early 1970s due to concerns about the pollution they added to the air, but a new Duke University study finds that their legacy of contamination could live on in urban soils.
“We found that city parks and playgrounds built on the site of a former waste incinerator can still have greatly elevated levels of lead in their surface soils many decades after the incinerator was closed,” ...
You can leave your gloves on: Rice-developed material burns viruses, safe for skin
2023-09-11
HOUSTON – (Sept. 11, 2023) A new material that packs deadly heat for viruses on its outer surface while staying cool on the reverse side could transform the way we make and use personal protective equipment (PPE), cutting down the pollution and carbon footprint associated with current materials and practices.
The composite, textile-based material developed by Rice University engineers uses Joule heating to decontaminate its surface of coronaviruses like SARS-CoV-2 in under 5 seconds, effectively killing at least 99.9% of viruses. Wearable items made from the material can handle hundreds of uses with the potential for a single pair of gloves to prevent nearly ...
Not too big: Machine learning tames huge data sets
2023-09-11
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Sept. 11, 2023 — A machine-learning algorithm demonstrated the capability to process data that exceeds a computer’s available memory by identifying a massive data set’s key features and dividing them into manageable batches that don’t choke computer hardware. Developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory, the algorithm set a world record for factorizing huge data sets during a test run on Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Summit, the world’s fifth-fastest supercomputer.
Equally efficient on laptops and supercomputers, ...
UArizona Cancer Center researchers discover iron-targeting approaches to halt proliferation of cancer cells
2023-09-11
Researchers at the University of Arizona Cancer Center discovered a new class of iron-targeting compounds that hamper the proliferation of cultured malignant cells in a laboratory setting. The results of the study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Cancer cells are what we call ‘addicted’ to iron, and so we are making compounds that are able to interfere with the availability of iron in cancer cells,” said Elisa Tomat, PhD, professor in the Department of Chemistry ...
Experimental physicist David Weld to investigate the role of feedback and measurement in quantum systems
2023-09-11
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Experimental physicist David Weld’s experimental research interest lies in a question that has been around for a long time, but which we’re only now approaching the ability to investigate.
“There’s a really old interest in the quantum act of measurement,” he said. “It’s something that’s at the foundations of quantum mechanics and has been puzzling people for more than a century.”
Called the “measurement problem” and famously illustrated by Erwin Schrödinger’s ...
ORNL teams receive funding through DOE BRaVE initiative to study biopreparedness
2023-09-11
The Department of Energy’s Office of Science has selected three Oak Ridge National Laboratory research teams to receive funding through DOE’s new Biopreparedness Research Virtual Environment, or BRaVE, initiative.
BRaVE, announced earlier this year, aims to build on biopreparedness research that delivered high-impact results in the fight against COVID-19. In the height of the pandemic, DOE national laboratory scientists combined fields such as biology, high-performance computing and manufacturing to bolster the national supply of personal protective equipment and improve virus testing and treatment.
“The advances made ...
Self-reported “night owls” more likely to have unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, significantly increased diabetes risk
2023-09-11
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 11 September 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. Self-reported “night owls” more likely to have ...
Big teeth, bigger data
2023-09-11
Virginia Tech researchers in the College of Natural Resources and Environment are assessing the efficacy of shark sanctuaries by developing a modeling system that utilizes publicly accessible fishing data to determine shark catch and mortality rates. Published in the journal Science Advances, their findings represent an important step in utilizing data science to tackle oceanic conservation challenges.
“Shark sanctuaries are coastal areas designated by countries as places where the targeted ...
Article: Doctors treating patients with Parkinson’s disease must focus on stigma and emotional impacts as well as motor symptoms
2023-09-11
Even the best treatment approaches for Parkinson’s disease are inadequate if they do not address patients’ feelings of social rejection, isolation, loneliness and other psychosocial effects of stigma, according to a report from experts specializing in Parkinson’s and other movement disorders.
A new report co-authored by UCLA Health neurologist and researcher Dr. Indu Subramanian says many misconceptions and biases cause patients with Parkinson’s to be stereotyped, devalued and shunned, which, along with a progressive loss of functionality and independence, often lead to “self-stigma,” with declining self-esteem and increasing anxiety and depression. The ...
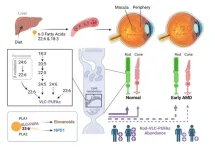
LSU Health New Orleans researchers discover a key failure in amd that may lead to progression and vision loss
2023-09-11
New Orleans, LA – Research led by Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor, Ernest C. and Yvette C. Villere Chair for the Study of Retinal Degeneration, and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, suggests that age-related macular degeneration (AMD) decreases an essential fatty acid, preventing the formation of a class of protective molecules and reducing repair potential. The discovery may also open new therapeutic avenues for AMD. The findings are published in Experimental Eye Research, ...
Virginia Tech has seismic role in earthquake center
2023-09-11
A Virginia Tech professor has an integral role in the establishment of a new center to study earthquakes in the Cascadia Subduction Zone off the coast of Oregon.
The project will create an earthquake center to study subduction zones — fault lines where one tectonic plate slips beneath another — to enable collaborative research and community connections for increased hazard awareness.
The Division of Earth Sciences in the Directorate for Geosciences at the National Science Foundation has awarded a $15 million grant over five years to establish the Cascadia Region ...
3D printing with coffee: Turning used grounds into caffeinated creations
2023-09-11
Coffee can do a lot of things: Wake you up, warm you up and lessen that existential dread. According to a new study, it could also help reduce the waste from 3D printing.
That’s the vision behind a new project led by Michael Rivera, an assistant professor in the ATLAS Institute and Department of Computer Science at the University of Colorado Boulder. He and his colleagues have developed a method for 3D printing a wide range of objects using a paste made entirely out of old coffee grounds, water and a few other sustainable ingredients.
The team has already experimented with using coffee grounds to craft jewelry, pots for plants and even, ...
Firms address corporate scandal with lengthy codes of ethics, study shows
2023-09-11
Corporate scandals have been on the rise for the past decade.
In 2019, Strategy& (the strategy consulting business unit of PricewaterhouseCoopers) found that for the first time in the history of its annual survey, more CEOs were dismissed for ethical concerns than for poor firm performance or internal board struggles.
There has been no shortage of highly publicized scandals, including the BP oil spill in 2010, the Target data breach in 2013 and abuses of financial incentives at Wells Fargo in 2016. A number of CEOs have resigned following alleged inappropriate relations, including Brian Krzanich at Intel, Leslie Moonves at CBS, ...
Atmospheric scientists reveal much of Houston’s ozone exceedance due to air flows from the north
2023-09-11
University of Houston atmospheric science researchers have found that while local emissions play a role in the rise of ozone levels in Houston, most of the pollutants can be carried in from other regions across the country, leading to excess ozone pollution. Their findings offer insights into strategies to mitigate future ozone pollution for the region.
The research team focused on two ozone episodes in September 2021 (Sept. 6 – 11 and Sept. 23 – 26). The month of September is the typical annual ozone peak due to high temperatures, lack of rain and air circulation patterns that transport polluted air from the north.
Their analysis revealed that roughly 63% of the excess ...
Paper: Air pollution via wildfire smoke increases suicide risk in rural counties
2023-09-11
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Air pollution poses well-established risks to physical health, but an emerging body of research says that it may also have adverse effects on mental health. New research co-written by a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign economist examining the relationship between air pollution via drifting wildfire smoke exposure and suicide risk found large-scale evidence that air pollution disproportionately elevates the risk of suicide among rural populations in the U.S.
Each 10% increase in airborne particulate matter in rural counties causes monthly suicide rates ...
Ecology and artificial intelligence: stronger together
2023-09-11
Many of today’s artificial intelligence systems loosely mimic the human brain. In a new paper, researchers suggest that another branch of biology — ecology — could inspire a whole new generation of AI to be more powerful, resilient, and socially responsible.
Published September 11 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the paper argues for a synergy between AI and ecology that could both strengthen AI and help to solve complex global challenges, such as disease outbreaks, loss of biodiversity, and climate change ...
Leading asthma groups tackle definition of clinical remission in treatment of asthma
2023-09-11
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (September 11, 2023) – As an increasing number of improved asthma treatments are developed, a greater number of people with asthma are finding their symptoms under control. Their improved status raises an important question for healthcare providers (HCPs) who treat this condition: “What qualifies as clinical remission in the treatment of asthma?”
A panel of 11 experts in asthma care came together to review available literature to create a working definition. The panel included six allergists, three pulmonologists and two pediatricians. The paper outlining their recommendations is published in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, ...
Adult food literacy program increases nutrition habits over time
2023-09-11
Improving food literacy positively influences diet quality and reduces the risk of chronic diseases; however, interpreting the evidence of its effectiveness has been limited. Results of a new study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, found that Foodbank Western Australia’s Food Sensations for Adults (FSA) food literacy program is effective in producing positive changes across a range of food literacy and dietary behaviors in participants ages 18 and older.
Lead author Andrea Begley, DrPH, School of Population Health, Curtin University in Perth, Western Australia (WA), says, “Behavior change takes time to establish. Participants ...
For older men, treating urinary symptoms may lead to lower mortality risk
2023-09-11
Effective treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men aged 50 or older is associated with a lower risk of death over the next few years reports a study in the October issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"We found a small but significant decrease in mortality risk for older men who received medications for treatment of LUTS," comments lead author Blayne Welk, MD, MSc, of Western University ...
Department of Energy announces $73 million for basic research to accelerate the transition from discovery to commercialization
2023-09-11
Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $73 million in funding for eleven projects which focus on the goal of accelerating the transition from discovery to commercialization of new technologies that will form the basis of future industries. This goal will require basic research to be conducted with an eye to an innovation’s end application, considering discovery, creation, and production of materials and technologies with approaches that can be scaled and readily transitioned into new products and capabilities to support the economic health and security of the nation.
“This ...
Wifi can read through walls
2023-09-11
Researchers in UC Santa Barbara professor Yasamin Mostofi’s lab have proposed a new foundation that can enable high-quality imaging of still objects with only WiFi signals. Their method uses the Geometrical Theory of Diffraction and the corresponding Keller cones to trace edges of the objects. The technique has also enabled, for the first time, imaging, or reading, the English alphabet through walls with WiFi, a task deemed too difficult for WiFi due to the complex details of the letters.
For more details ...
Malaria-causing parasites resistant to both treatment and detection have emerged in Ethiopia
2023-09-11
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Scientists have detected new strains of malaria-causing parasites in Ethiopia that are both resistant to current treatments and escape detection by common diagnostic tests — a development that could increase cases and deaths from malaria and make eliminating the persistent disease an even greater challenge.
The authors detailed their findings from a genomic surveillance study in Nature Microbiology. Already, scientists had found in Uganda, Tanzania and Rwanda strains of the parasite ...
[1] ... [1697]
[1698]
[1699]
[1700]
[1701]
[1702]
[1703]
[1704]
1705
[1706]
[1707]
[1708]
[1709]
[1710]
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.