New research establishes enduring connection between racial segregation, childhood blood lead levels
2023-08-30
Living in a racially segregated neighborhood puts Black children at a higher risk of having elevated blood lead levels, and this association has persisted over more than two decades, according to new research from the Children’s Environmental Health Initiative, which is led by University of Illinois Chicago Chancellor Marie Lynn Miranda.
The study, published in Pediatrics, analyzed data from the early 1990s and from 2015 from blood lead level tests of more than 320,000 children younger than 7 in North Carolina. Researchers ...
Pandemic pushed half-million kids into grandparents’ homes
2023-08-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – Grandparents appeared to serve as an important private safety net when COVID-19 first hit the U.S., according to a study led by a Washington State University researcher.
The pandemic’s arrival in 2020 coincided with a surge of nearly 510,000 children living in “doubled-up” households, co-residing with other adults in addition to their parents or parents’ partners. While these living arrangements had already been increasing before COVID-19, this was an additional increase beyond what would be expected based on previous trends ...
Stress and insomnia linked to irregular heart rhythms after menopause
2023-08-30
Research Highlights:
A study of more than 83,000 questionnaires by women ages 50-79, found more than 25% developed irregular heart rhythms, known as atrial fibrillation, which may increase their risk for stroke and heart failure.
Stressful life events and insomnia were strongly linked to the development of atrial fibrillation, highlighting the need for mental well-being evaluations to be included with physical health examinations.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Aug. 30, 2023
DALLAS, Aug. 30, 2023 — After menopause an estimated 1 in 4 women may develop irregular heart rhythms — known as atrial fibrillation – ...
New principles for patient data use balance research benefits, individual privacy
2023-08-30
Statement highlights:
This statement emphasizes that policies for patient data sharing should be interpreted and applied respectfully toward patients and research participants, equitable in impact both in terms of risks and potential benefits, and beneficial across broad and demographically diverse communities in the United States.
The statement outlines six new principles focused on encouraging the generalizability of research advances, good stewardship across the translational spectrum, transparency, education and involvement of patients, access and privacy protections.
Embargoed until 4:00 ...
Blood cell insights offer potential boost to lung cancer therapies
2023-08-30
Fresh discoveries about a type of immune cells could give lung cancer patients a more accurate prognosis and better identify who will benefit from immunotherapies.
Researchers found that the location in and around tumours of cytotoxic T cells, which play a key role in fighting cancer, may help predict patient survival and indicate whether or not treatments will work.
The findings could help to pave the way for improved immunotherapies - powerful but expensive life-extending treatments which currently fail in 80 per cent of cases - allowing them to work more effectively in more patients, researchers say.
Experts ...
Climate extremes hit stressed economies even harder
2023-08-30
"The unprecedented societal interruptions during the Covid-19 pandemic of 2020 and onward took their toll on economic activity. Lockdowns disrupted supply chains and caused economic losses with implications for private households," lead author Robin Middelanis from PIK explains. "Global stress like this reduces the economic capacity to cope with additional shocks from weather extremes that put even more pressure on already stressed societies.” For an individual climate disaster, impacts from local production losses can be flexibly reduced to a certain extent by the support ...
Engaging in administrative payment tasks may correlate with treatment delays and nonadherence in cancer care
2023-08-30
Bottom Line: Engaging in administrative tasks to estimate costs or pay for care among a cohort of cancer patients and survivors was associated with an 18% increase in cost-related treatment delays or nonadherence.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Meredith Doherty, PhD, LCSW, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Social Policy & Practice (SP2)
Background: Navigating the U.S. health care system ...
Alcohol makes you more likely to approach attractive people but doesn’t make others seem better looking: Study
2023-08-30
PISCATAWAY, NJ — It’s “liquid courage,” not necessarily “beer goggles”: New research indicates that consuming alcohol makes you more likely to approach people you already find attractive but does not make others appear more attractive, according to a report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
The conventional wisdom of alcohol’s effects is that intoxication makes others seem better looking. But, according to the new study, this phenomenon has not been studied systematically. Earlier research typically ...
Lead service lines in New York City disproportionately impact Hispanic/Latino communities and children already at risk of lead exposure
2023-08-30
Results from a study just released by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health show major inequities in the location of lead service lines across New York City. Communities with large numbers of Hispanic/Latino residents and those with children who are already highly vulnerable to lead exposure from numerous sources are disproportionately impacted by water service lines that may contain lead. The study findings are published online in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
There is no safe level of lead exposure for children. Even at lower levels of exposure, lead is associated with impaired cognitive function, attention-related behavioral problems, and diminished academic ...
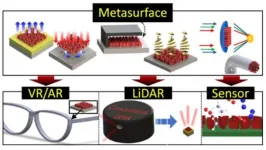
Vision for future micro-optical technology based on metamaterials
2023-08-30
Metasurfaces, also known as invisibility cloak technology, are an artificial material adept at manipulating. With metasurfaces allowing for lenses to be reduced to one 10,000th the size of conventional lenses, they are generating considerable interest as optical components allowing miniaturization of optical systems for the next generation of virtual and augmented reality as well as LiDAR. If metasurfaces become commercially viable, overcoming the challenges of complex manufacturing processes and high production costs, Korea could gain a significant technological edge ...
No worries: online course to help you stop ruminating
2023-08-30
An online course designed to curb negative thinking has had strong results in helping people reduce the time they spend ruminating and worrying, a new study from UNSW Sydney has shown.
And researchers say the online course, which will soon be hosted on the Australian Government funded online clinic This Way Up and is free with a prescription from a clinician, was found to significantly improve the mental health of the people who participated in the study. The trial was part of a collaboration between UNSW, the Black Dog Institute and The Clinical Research Unit for Anxiety and Depression at St ...
Boosting neuroscience training to help children flourish
2023-08-30
Professionals working with children and young people will be offered training in brain science in an Australia-first initiative between The University of Queensland (UQ) and the Australian Research Alliance for Children and Youth (ARACY) through the Thriving Queensland Kids Partnership (TQKP).
Thriving Kids Brain Builders is a neuroscience translation initiative being developed with UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute (QBI) for people working across the health, education, social and community services, justice and housing sectors.
QBI ...
Exercise could help one of prostate cancer treatment’s most-common and devastating side effects
2023-08-30
Prostate cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer in the world, but not only does it put the lives of those diagnosed at risk, but can also severely impact patient quality of life due to side-effects of treatment.
One such side-effect commonly reported by patients is sexual dysfunction – however, a new long-term clinical trial led by Edith Cowan University (ECU) and presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Breakthrough Meeting in Japan, has revealed there is a therapy which may help combat this ...
Can this forest survive? Predicting forest death or recovery after drought
2023-08-30
How long can trees tolerate drought before the forest dies?
Researchers from UC Davis can now predict which forests could survive despite future drought. Their new method links precipitation to tree growth, and it can help people decide where to put their resources as climate change affects patterns of snow and rainfall that impact the health of forests.
“If a forest is doing OK, but in the future we know it’s likely to get only half the average rainfall it used to get, we can calculate the likelihood ...
How Norway is helping to restore humanity inside U.S. prisons
2023-08-30
As part of an innovative prison reform program, the Oregon State Penitentiary created a healing garden on its grounds to provide some respite from the concrete and resemble the outside world. One incarcerated man who had spent most of the past two decades in solitary confinement described going to the garden as, “the first time I walked on grass in 20 years.”
“Many of us have found beauty in weeds and flowers growing through the cracks in the pavement,” he told UC San Francisco researchers, who helped institute and then evaluated the reforms. “There is both beauty and inspiration in knowing that we, ...
Statistics can help us figure out how historic battles could have turned out differently, according to experts
2023-08-30
Quantifying Counterfactual Military History probes whether historic battles and military interventions could have turned out quite differently
Oxford, U.K., 30 August 2023 – Statistical methods can evaluate whether pivotal military events, like the Battle of Jutland, American involvement in the Vietnam war or the nuclear arms race, could’ve turned out otherwise, according to a new book.
Military historical narratives and statistical modelling bring fresh perspectives to the fore in ...
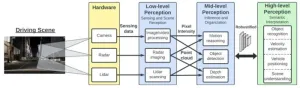
Using neuroscience to stop phantom braking
2023-08-29
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Recently, when customers began complaining that their vehicles with driver-assistance technologies were “phantom braking” or slamming on the brakes without any visible obstacles present, researchers at Michigan State University wanted to learn more about this phenomenon — why it happens and how to stop it.
“Frequent phantom braking incidents can erode confidence in autonomous driving technologies,” said Qiben Yan, an assistant professor in the College of Engineering. “If riders perceive the technology as unpredictable or unreliable, they’ll be less likely to embrace it.”
Autonomous vehicles have a vision system, ...
Sensitive parenting and preschool attendance may promote academic resilience in late preterm infants
2023-08-29
Late preterm infants, or infants born between 34 and 36-6/7 weeks gestation, are the majority of infants born preterm, and are at greater risk for academic delays compared to full term infants.
Certain factors, including a low level of maternal education, prenatal tobacco use, twins/multiple gestation and male sex increased the risk for deficits in math and reading by kindergarten for late preterm infants, a new study finds.
However, sensitive parenting and preschool enrollment are two possible ways to counter the risk of being born late preterm, and to promote academic resilience.
“Our findings highlight an opportunity for pediatric providers to offer prevention strategies ...
New imaging technique could provide clearer images for oncologists
2023-08-29
A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).A multidisciplinary team lead by University of Texas at Arlington mathematics Assistant Professor Souvik Roy is on a mission to improve medical imaging using a new technique called quantitative photoacoustic tomography (QPAT).
QPAT is an imaging modality that combines ultrasound, which is an imaging technique that uses sound waves to image features inside ...
Neptune's disappearing clouds linked to the solar cycle
2023-08-29
Astronomers have uncovered a link between Neptune's shifting cloud abundance and the 11-year solar cycle, in which the waxing and waning of the Sun's entangled magnetic fields drives solar activity.
This discovery is based on three decades of Neptune observations captured by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii, as well as data from the Lick Observatory in California.
The link between Neptune and solar activity is surprising to planetary scientists because Neptune is our solar system's farthest major planet and receives sunlight with about 0.1% ...
Liver-targeting drug reverses obesity, lowers cholesterol in mice
2023-08-29
A University of Massachusetts Amherst biomedical engineer has used a nanogel-based carrier designed in his lab to deliver a drug exclusively to the liver of obese mice, effectively reversing their diet-induced disease.
“The treated mice completely lost their gained weight, and we did not see any untoward side effects,” says S. Thai Thayumanavan, distinguished professor of chemistry and biomedical engineering. “Considering 100 million Americans have obesity and related cardiometabolic disorders, we became pretty excited about this work.”
Efforts ...
MIND Institute director calls for new approach to equity in autism, fragile X research
2023-08-29
UC Davis MIND Institute Director Leonard Abbeduto is calling for a major shift in the way research into autism and other neurodevelopmental disabilities is conducted. He co-authored a paper titled “Toward Equity in Research on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities” that was the basis for a special issue of the American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. The issue was published today.
Abbeduto, a distinguished professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, argues that researchers ...
Rapid shifts from drought to downpour occurring more often
2023-08-29
New research shows that wild swings from severe drought to heavy rains are becoming more common with climate change in many parts of the world and that feedback loops from the land itself are likely contributing to the trend.
The research looked at four decades of meteorological and hydrological data on a global level and found seven regional hotspots around the world where the trend was getting worse: eastern North America, Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, southern Australia, southern Africa, and southern South America.
“We are especially concerned with the sudden shift from drought to flood,” said coauthor Zong-Liang Yang, a professor at The University of Texas at Austin Jackson ...
Hemp helps to heal
2023-08-29
A few days ago, the federal government took the controversial decision to make the acquisition and possession of small amounts of cannabis exempt from punishment. Provided the German parliament approves the draft bill, the “Cannabis Act” will come into force next year. While some consider this move to be long overdue, others continue to warn strongly against the health risks of cannabis use.
The Jena researchers and their colleagues are now taking a different look at cannabis – at the traditional medicinal ...
Department of Energy announces $24 million for research on quantum networks
2023-08-29
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $24 million in funding for three collaborative projects in quantum network research.
Scientific research infrastructure linked with quantum networks is needed to realize distributed quantum computers. These quantum computers could simulate complex scientific processes inaccessible to computational platforms of today, integrate quantum sensors that promise measurements of unprecedented precision, and address previously inaccessible scientific questions of importance.
“Advances in quantum networking are enabling effective interconnections ...
[1] ... [1703]
[1704]
[1705]
[1706]
[1707]
[1708]
[1709]
[1710]
1711
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
[1716]
[1717]
[1718]
[1719]
... [8819]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.