The first book to combine mineral nutrition and plant disease gets updated
2023-09-05
Approximately 95% of the world’s food supply is directly or indirectly produced on soil, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Soil health is therefore critical to the health of all living organisms—especially plants. Equally as critical, resources that consider the overlap between soil’s mineral nutrition and plant diseases have been scarce, until members of the American Phytopathological Society (APS) recognized this gap.
APS PRESS has newly published an updated edition of the first book to successfully combine the two important plant science disciplines of nutrition and pathology. Mineral Nutrition and Plant Disease, ...
IKIDS child health research gets another boost in funding
2023-09-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Seven years after an initial $17.9 million award from the National Institutes of Health, the Illinois Kids Development Study at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign will receive approximately $13.7 million – awarded in two phases – to continue its work for another seven years. The money coming to Illinois is part of a national collaborative effort to explore how environmental exposures influence child development, cognition, growth and health.
IKIDS is part of Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes, a national initiative to study five ...
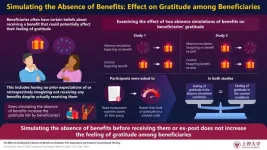
Does a “surprise” factor in gift-giving affect beneficiaries’ gratitude? Scientists answer
2023-09-05
Gratitude is a strong emotion, usually felt by a person who benefits from an intentional good deed of another person. Receiving gifts or benefits can instill a feeling of gratitude in people who receive them, i.e., beneficiaries, encouraging them to be more prosocial, while also helping to create a bond with their benefactors. This has led several researchers to examine the determinants of gratitude. Interestingly, beneficiaries often have preconceived beliefs about receiving a benefit. For instance, they may have no prior expectations of receiving a ...
Clarissa Campbell and Barbara Maier at CeMM receive ERC Starting Grants
2023-09-05
Two scientists at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences have received prestigious ERC Starting Grants from the European Commission: Clarissa Campbell and Barbara Maier. In Clarissa Campbell's laboratory, researchers are working to better understand the interplay between the immune system and metabolism. Barbara Maier and her team are researching the role of lymph nodes in the context of cancer.
(Vienna, 5 September 2023) The ERC grants are among the most prestigious and competitive research grants offered ...
Faster postal service linked to better voter turnout
2023-09-05
PULLMAN, Wash. – A more efficient U.S. Postal Service can increase voter turnout in all states regardless of their mail voting laws, according to a Washington State University study.
WSU researcher Michael Ritter analyzed election data from 2012 through 2020, when the pandemic encouraged many more people than usual to vote by mail. He found that in general more accessible mail voting laws, such as universal mail-in voting and no-excuse mail voting, increased the probability that individuals would vote. Restrictive laws, such as requiring ...
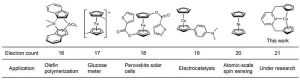
Scientists synthesize new organometallic “sandwich” compound capable of holding more electrons
2023-09-05
Organometallic compounds, molecules made up of metal atoms and organic molecules, are often used to accelerate chemical reactions and have played a significant role in advancing the field of chemistry.
Metallocenes, a type of organometallic compound, are known for their versatility and special "sandwich" structure. Their discovery was a significant contribution to the field of organometallic chemistry and led to the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973 to the scientists who discovered and explained their sandwich structure.
The ...
Study confirms it: Opposites don't actually attract
2023-09-05
Opposites don’t actually attract.
That’s the takeaway from a sweeping CU Boulder analysis of more than 130 traits and including millions of couples over more than a century.
“Our findings demonstrate that birds of a feather are indeed more likely to flock together,” said first author Tanya Horwitz, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience and the Institute for Behavioral Genetics (IBG).
The study, published Aug. 31 in the journal Nature Human Behaviour, confirms what individual studies have hinted at for decades, defying the age-old adage that “opposites ...
Poor water quality disproportionately affects socially vulnerable communities
2023-09-05
A new study published in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research Letters examines the links between drinking water quality violations and social vulnerability in the United States, revealing that these violations disproportionately affect the most vulnerable communities. Approximately 70% of the population affected ranked in the highest social vulnerability category, with many different social parameters, beyond income, linked to different drinking water quality violations.
The study, led by researchers from the Jackson School of Geosciences, University of Texas in Austin, used new water quality data ...
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on emergency department use in British Columbia
2023-09-05
A new study showing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and mitigation strategies used to manage the virus on emergency department (ED) visits in British Columbia can help with future planning. The study is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221516.
"Evaluation of the effects of the pandemic and associated measures can provide a historical account and inform health care service planning for both postpandemic recovery and mitigation of potential consequences ...
THE LANCET PLANETARY HEALTH: Experts warn 'green growth' in high income countries is not happening, call for 'post-growth' climate policies to meet Paris targets
2023-09-05
Peer-reviewed / Empirical study
New study challenges political claims that some high-income countries have achieved “green growth”– revealing that under current growth-oriented strategies, emission reductions in these nations fall drastically short of meeting the climate goals and fairness requirements of the Paris Agreement.
If current trends continue, even the 11 high-income countries that have "decoupled" carbon emissions from GDP growth would on average take over 200 years to get their emissions close to zero, and would emit more than 27-times their fair share of the “global carbon budget” ...
Pharmacy discount card programs like Amazon Prime and GoodRx gold could save patients millions of dollars in out-of-pocket costs for commonly prescribed generic medications
2023-09-04
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 04 September 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. New ACP paper addresses ethical issues in determining death; recommends clarification to the Uniform Determination ...
Farms that create habitat key to food security and biodiversity
2023-09-04
It seems intuitive that forests would provide better habitat for forest-dwelling wildlife than farms. Yet, in one of the longest-running studies of tropical wildlife populations in the world, Stanford researchers found that over 18 years, smaller farms with varying crop types – interspersed with patches or ribbons of forest – sustain many forest-dependent bird populations in Costa Rica, even as populations decline in forests.
In a paper published Sept. 4 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Nicholas Hendershot and colleagues ...
The art of wandering in vertebrates: new mapping of neurons involved in locomotion
2023-09-04
For those fortunate enough to walk normally, wandering is such an expected behavior that we hardly consider that it involves complex, partly involuntary processes. “Animals move to explore their environment in search of food, interaction with others, or simply out of curiosity. But the perception of danger or a painful stimulus can also activate an automatic flight reflex”, Martin Carbo-Tano, a post-doctoral fellow at Paris Brain Institute, explains. In both cases, movement initiation relies on the activation of so-called reticulospinal control neurons, which form an intertwined network in ...
Most species are rare. But not very rare
2023-09-04
Halle/Saale, Fort Lauderdale. More than 100 years of observations in nature have revealed a universal pattern of species abundances: Most species are rare but not very rare, and only a few species are very common. These so-called global species abundance distributions have become fully unveiled for some well-monitored species groups, such as birds. For other species groups, such as insects, however, the veil remains partially unlifted. These are the findings of an international team of researchers led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg ...
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
2023-09-04
Extreme El Niño weather saw South America’s forest carbon sink switch off
Hot and dry conditions resulted in increased tree death
Evidence that most forest areas withstand periods of severe drought
Greatest impact in forests with drier climates
Tropical forests in South America lose their ability to absorb carbon from the atmosphere when conditions become exceptionally hot and dry, according to new research.
For a long time, tropical forests have acted as a carbon sink, taking more ...
Blowing snow contributes to Arctic warming
2023-09-04
When it comes to global warming trends, the Arctic is a troubling outlier. The Arctic warms nearly four times faster than the global average, and aerosols play an important role in that warming. Scientists have long known that pollutants from other regions can accumulate in the Arctic atmosphere where they alter atmospheric chemistry, absorb sunlight, and affect local weather patterns, leading to localized warming that melts ice and snow. Sea salt particles dominate aerosol mass concentration, but their production mechanisms and impact on Arctic climate have remained unclear.
Atmospheric scientists led by Jian Wang, director of the Center for Aerosol ...
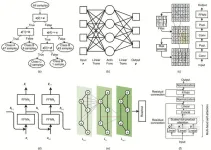
Innovative solutions for chemical challenges: Harnessing the potential of machine learning
2023-09-04
In a review published in Engineering, scientists explore the burgeoning field of machine learning (ML) and its applications in chemistry. Titled “Machine Learning for Chemistry: Basics and Applications,” this comprehensive review aims to bridge the gap between chemists and modern ML algorithms, providing insights into the potential of ML in revolutionizing chemical research.
Over the past decade, ML and artificial intelligence (AI) have made remarkable strides, bringing us closer to the realization of intelligent machines. The advent of deep learning methods and enhanced data storage capabilities has played a pivotal role in this progress. ML has already demonstrated success ...
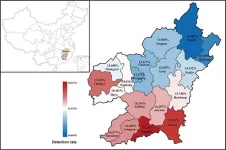
Uncovering thalassemia diversity in southern china through next-generation sequencing
2023-09-04
Around 5.2% of the global population carries abnormal hemoglobin genes [1]. Each year, 300,000 to 500,000 children are born with severe hemoglobinopathies worldwide, with approximately 80% of these cases occurring in developing countries [2]. Thalassemia is the most common hereditary hemoglobinopathy and occurs in 4.4 out of every 10,000 live births [3]. It is prevalent in Mediterranean coastal areas, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
A previous study indicated that Ganzhou, the southernmost city in Jiangxi province, had a thalassemia prevalence ...
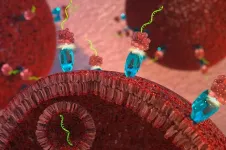
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop novel tumor-targeting nanospheres with the potential to dramatically improve light-based cancer diagnosis and treatment
2023-09-04
Abu Dhabi, UAE (September 4, 2023) – In a breakthrough in cancer therapeutics, a team of researchers at the Magzoub Biophysics Lab at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) has made a significant advance in light-based therapies – biocompatible and biodegradable tumor-targeting nanospheres that combine tumor detection and monitoring with potent, light-triggered cancer therapy to dramatically increase the efficacy of existing light-based approaches.
Non-invasive, light-based therapies, photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) have the potential to be safe and effective alternatives to conventional cancer treatments, which are beset by a ...
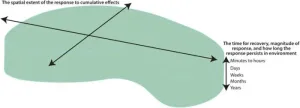
Ecosystem footprint concept and its potential applications in environmental management
2023-09-04
Traditionally, the impact of human activity on an ecosystem has lacked context when planning restorative ecosystem mitigation and management strategies. Multiple human activities over time and space, the resilience of a particular ecosystem, and the stress caused by many individual or related, overlapping activities that generate cumulative effects may affect the overall "ecosystem response footprint," or ability of an ecosystem to adapt and change to human activity.
A team of marine scientists reviewed the most recent perspectives on ecological footprints to rigorously define the term "ecosystem response footprint" as the ...
First-in-class targeted microRNA therapy slows cancer tumor growth
2023-09-04
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new cancer therapy developed by Purdue University researchers attacks tumors by tricking cancer cells into absorbing a snippet of RNA that naturally blocks cell division. As reported today in Oncogene, tumors treated with the new therapy did not increase in size over the course of a 21-day study, while untreated tumors tripled in size over the same time period.
Cancer can begin almost anywhere in the human body. It is characterized by cells that divide uncontrollably and that may be able to ignore signals to ...
Invasive Alien Species Pose Major Global Threats to Nature, Economies, Food Security and Human Health: IPBES report
2023-09-04
The severe global threat posed by invasive alien species is underappreciated, underestimated, and often unacknowledged. According to a major new report by the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), more than 37,000 alien species have been introduced by many human activities to regions and biomes around the world. This conservative estimate is now rising at unprecedented rates. More than 3,500 of these are harmful invasive alien species – seriously threatening nature, nature’s contributions to people and good quality of life. Too often ignored until it is too late, invasive alien species are a ...
Korean Scientific payload for observing the lunar space environment begins its transfer to the US for the scheduled 2024 launch
2023-09-04
The Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Jong-Ho Lee, hereinafter referred to as 'MSIT') and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (Director Young-Deuk Park, hereinafter referred to as 'KASI') announced the beginning of the transfer of the lunar space environment monitor, 'LUSEM'(Lunar Space Environment Monitor) that will be aboard United States’ unmanned lunar lander in 2024, has began on September 4th.
LUSEM is a payload developed by the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) in participation with the U.S. NASA's CLPS(Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative ...
IOP Publishing appoints Dr. David Gevaux as Chief Editor of Reports on Progress in Physics
2023-09-04
IOP Publishing (IOPP) has appointed Dr. David Gevaux as the first Chief Editor of Reports on Progress in Physics. Taking up the post from the 4th of September, Dr. Gevaux will lead on ambitious plans for the journal, as its scope expands to include groundbreaking new research content alongside the authoritative reviews for which it is well known across all areas of physics.
Working closely with Professor Subir Sachdev, the Editor in Chief of Reports on Progress in Physics, Dr. Gevaux will champion the editorial ...
New study uncovers the Causes of the Qing Dynasty's Collapse
2023-09-04
The Qing Dynasty in China, after over 250 years, crumbled in 1912. Led by the Complexity Science Hub (CSH), an international research team has pinpointed key reasons behind the collapse, revealing parallels to modern instability and offering vital lessons for the future.
China is considered today to be the world's largest economy (in terms of PPP). However, this position is not new. In 1820, China's economy already held the top spot, accounting for 32.9% of the global GDP. In the interim, there was a period of decline followed by a resurgence. In 1912, after over 250 years in power, the Qing Dynasty collapsed despite being considerably wealthier at the time ...
[1] ... [1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
[1716]
[1717]
[1718]
1719
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
[1725]
[1726]
[1727]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.