IU researchers identify new gene mutation that alters Alzheimer’s disease risk
2023-09-06
INDIANAPOLIS—A groundbreaking study led by experts from Indiana University School of Medicine has shed new light on the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer's disease. The team's research, rooted in human genetics studies, has unearthed a critical mutation within a key gene operating in the brain's immune cells, potentially elevating the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
The research team included several IU investigators within Stark Neurosciences Research Institute—Gary Landreth, PhD, the Martin Professor of Alzheimer’s Research; Bruce Lamb, PhD, executive director of Stark Neuroscience Research Institute; Stephanie Bissel, PhD, assistant ...
NIH investigates multidrug-resistant bacterium emerging in community settings
2023-09-06
New “hypervirulent” strains of the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae have emerged in healthy people in community settings, prompting a National Institutes of Health research group to investigate how the human immune system defends against infection. After exposing the strains to components of the human immune system in a laboratory “test tube” setting, scientists found that some strains were more likely to survive in blood and serum than others, and that neutrophils (white blood cells) are more likely to ingest and kill some strains than others. The study, published in mBio, was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
“This ...
Study reports discovery of new cell type in thymus
2023-09-06
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- It came as a surprise to Professor David Lo and his graduate student Diana Del Castillo when they were recently consulted by researchers in Israel for their expertise on specialized cells called Microfold cells, or M cells, which are mostly known for their presence in the intestinal epithelium. The Israeli group had identified similar cells in the thymus, an organ located just above the heart that makes lymphocytes — white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system and protect the body against infection.
Lo, a distinguished professor of biomedical sciences in the UC Riverside School of Medicine, and Del Castillo, ...
Devices offers long-distance, low-power underwater communication
2023-09-06
MIT researchers have demonstrated the first system for ultra-low-power underwater networking and communication, which can transmit signals across kilometer-scale distances.
This technique, which the researchers began developing several years ago, uses about one-millionth the power that existing underwater communication methods use. By expanding their battery-free system’s communication range, the researchers have made the technology more feasible for applications such as aquaculture, coastal hurricane prediction, and climate change modeling.
“What started as a very exciting ...
Beauty salon–based intervention increases trust of PrEP among Black cisgender women
2023-09-06
September 6, 2023 — Among African American and other Black cisgender women, a beauty salon–based intervention improved knowledge and awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) against HIV and increased trust in it, according to a pilot study published in the September issue of The Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care (JANAC), the official journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care. JANAC is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, most study participants did not self-identify as requiring PrEP or having risk factors for HIV. "Like ...
Pumping like the heart
2023-09-06
Pumping liquids may seem like a solved problem but optimizing the process is still an area of active research. Any pumping application—from industrial scales to heating systems at home—would benefit from a reduction in energy demands. Researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now showed how pulsed pumping can reduce both friction from and energy consumption of pumping. For this, they took inspiration from a pumping system intimately familiar to everyone: the human heart.
According to an international study, nearly twenty percent of global electric power are used for pumping liquids around—ranging from industrial applications ...
Chinese paleontologists find new fossil link in bird evolution
2023-09-06
Birds descended from theropod dinosaurs by the Late Jurassic, but our understanding of the earliest evolution of the Avialae, the clade comprising all modern birds but not Deinonychus or Troodon, has been hampered by a limited diversity of fossils from the Jurassic.
As of now, no definitive avialans have been reported except from the Middle–Late Jurassic Yanliao Biota in northeast China (166–159 million years ago; Ma) and the slightly younger German Solnhofen Limestones, which preserve Archaeopteryx. Consequently, there is a gap of about 30 million years before the oldest ...
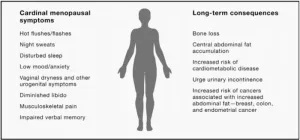
Review of over 70 years of menopause science highlights research gaps and calls for individualized treatment
2023-09-06
Although about half of people go through menopause, less than 15% of them receive effective treatment for their symptoms. Treatment options for people experiencing irritating or severe menopause symptoms are often under researched, and some have questionable efficacy, or cause harmful side effects. In a comprehensive review publishing in the journal Cell on September 6, a team of world-renowned menopause experts summarizes what we know about menopause, calls for more research into the timeline and treatment of menopause, ...
Commercialization of cannabis linked to increased traffic injuries
2023-09-06
Ottawa, ON, September 5, 2023 – Annual rates of emergency department visits for cannabis-involved traffic injury increased by 475 percent over 13 years, according to a new study from The Ottawa Hospital, Bruyère Research Institute, and ICES.
The study examined cannabis-involvement in emergency department (ED) visits for traffic injuries between 2010 and 2021 and looked for changes after the legalization of cannabis in October 2018 and following the commercialization of the legal market (expanded cannabis products and retail stores), which overlapped with the ...
The discovery of a new kind of cell shakes up neuroscience
2023-09-06
Neuroscience is in great upheaval. The two major families of cells that make up the brain, neurons and glial cells, secretly hid a hybrid cell, halfway between these two categories. For as long as Neuroscience has existed, it has been recognized that the brain works primarily thanks to the neurons and their ability to rapidly elaborate and transmit information through their networks. To support them in this task, glial cells perform a series of structural, energetic and immune functions, as well as stabilize physiological constants. Some of these glial cells, known as astrocytes, ...
Enhanced recovery program successfully reduced opioid use after pancreatic cancer surgery
2023-09-06
By improving hospital care pathways, researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center successfully reduced inpatient opioid use by 50% after pancreatic cancer surgery and cut the median opioid prescription volumes at discharge to zero. This approach, described in a study published today in JAMA Surgery, could help reduce the risk of long-term opioid dependence in patients.
In this cohort study, which involved 832 patients undergoing pancreatic resection surgery, the researchers investigated how making incremental modifications to post-surgery procedures affected the amounts of opioids used by inpatients and at the point of discharge. In less ...
Study finds increase in travelers to Massachusetts seeking abortion care post-Dobbs
2023-09-06
Analysis led by Brigham researchers showed an increase in out-of-state abortion travelers to Massachusetts from other states including Texas, Louisiana, Florida, and Georgia after Dobbs.
Use of non-profit funding by charitable organizations for abortion care more than doubled among out-of-state travelers
A rigorous analysis by researchers confirms a rise in out-of-state travelers coming to Massachusetts to seek abortion care. In a new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member ...
Incidence of in situ and invasive cutaneous melanomas during the pandemic
2023-09-06
About The Study: Researchers identified decreases of in situ and invasive melanoma diagnoses during 2020, which may reflect decreased skin cancer screening examinations or access to dermatologic care during the pandemic, both of which may lead to reduced melanoma diagnoses. This study adds to the current literature by highlighting that the relative increase in thick melanomas in 2020 was primarily associated with a marked decrease in thin melanomas, rather than an absolute increase in thicker melanomas.
Authors: Rebecca I. Hartman, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Cannabis-involved traffic injury emergency department visits after cannabis legalization and commercialization
2023-09-06
About The Study: This study found large increases in cannabis involvement in emergency department visits for traffic injury over time in Ontario, Canada, which may have accelerated following nonmedical cannabis commercialization. Although the frequency of visits was rare, they may reflect broader changes in cannabis-impaired driving. Greater prevention efforts, including targeted education and policy measures, in regions with legal cannabis are indicated.
Authors: Daniel T. Myran, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Ottawa in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31551)
Editor’s ...
Furthest ever detection of a galaxy’s magnetic field
2023-09-06
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have detected the magnetic field of a galaxy so far away that its light has taken more than 11 billion years to reach us: we see it as it was when the Universe was just 2.5 billion years old. The result provides astronomers with vital clues about how the magnetic fields of galaxies like our own Milky Way came to be.
Lots of astronomical bodies in the Universe have magnetic fields, whether it be planets, stars or galaxies. “Many people ...
The first organic oscillator that makes catalysis swing
2023-09-06
Oscillating chemical systems are present at nearly every popular chemistry exhibition – especially the ones that display striking colour changes. But so far there are very few practical uses for these types of reactions beyond timekeeping. In nature, on the other hand, many important life processes such as cell division and circadian rhythms involve oscillations. Scientists at the University of Groningen have now developed an oscillating system that contains a catalyst, and exhibits periodic catalytic activity: this synthetic chemical oscillator can do more than just keep time. A description of this ...
Scripps Research chemists devise a method for C-H activation of alcohols
2023-09-06
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research chemists have extended a powerful molecule-building method—called C-H activation—to the broad class of chemicals known as alcohols.
The synthetic chemistry feat, reported in Nature on September 6, 2023, follows the development of C-H activation techniques for the three other major classes of organic molecule—amines, acids and ketones—that are used to construct pharmaceuticals. It gives chemists a versatile new toolkit for making drugs and other valuable compounds now using the alcohol chemical class; moreover, its ...
Pitt researchers to study Alzheimer’s disease in marmosets
2023-09-06
PITTSBURGH – To reimagine existing preclinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine neuroscientists created the first non-human primate model of hereditary Alzheimer's in marmoset monkeys, outlining their approach in Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions.
Researchers are now working on characterizing and validating genetic, molecular, functional and cognitive features of aging and Alzheimer’s disease in marmosets that harbor mutations in the same gene that is linked to early-onset disease in humans. Scientists hope to accelerate the pace of the ...
Oral health deteriorates before and after bariatric surgery, study shows
2023-09-06
Oral health deteriorates in morbidly obese people on a diet in preparation for bariatric surgery and patients who have undergone the procedure, with increasing caries, gingivitis and periodontitis. This is the conclusion of a study conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) in Brazil. Articles on the study are published in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation and Clinical Oral Investigations, stressing the importance of participation by a dentist in the assessment of bariatric patients.
The study was funded by FAPESP (projects 17/26400-6 and 16/10940-9), following 100 patients divided into two groups (dietary ...
Patients with AML who received vitamin C/D supplements had fewer complications, but no overall survival benefit seen
2023-09-06
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who received vitamin C and D supplements while undergoing intensive chemotherapy had lower rates of complications, such as infections, bleeding, and inflammation, when compared with similar, previously treated patients who did not receive these supplements. Moreover, while the study showed no difference in survival between the two groups, a subgroup analysis showed that among patients with a genetic mutation known as NPM1 – found in about one in three patients with AML – the risk of death was nearly 50% lower among those ...
University of Colorado ophthalmologists administer novel treatment for single patient facing rare genetic condition
2023-09-06
Thirteen-year-old Grace Hoyt received potentially the best birthday gift ever this month when pediatric ophthalmologists at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Children’s Hospital Colorado administered the first treatment designed specifically to slow her vision loss associated with posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa (PCARP), a rare genetic condition that affects vision and the nervous system.
“It’s so incredible that she has this opportunity,” Susan Hoyt says of her daughter, who received the first treatment Aug. 24. “We’ve known that Grace is going to go blind, but to have ...
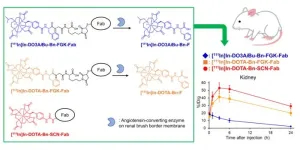
Novel molecular design for enhanced efficacy and safety in radiotheranostics
2023-09-06
Radiotheranostics embodies the convergence of diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals into a unified platform. In cancer treatment, radiotheranostic procedures typically involve the use of antibodies that bind to proteins abundantly found on the surface of cancerous cells. The antibodies are labeled with a suitable radioisotope, which facilitates imaging procedures used to diagnose cancer and can be used to target cancerous cells and bombard them with deadly radiation as a form of treatment.
Although radiolabeled antibodies show promise as a treatment for cancer, several hurdles impede their clinical translation. ...
Potential target for reversing drug resistance in ovarian cancer identified
2023-09-06
For the 314,000 people diagnosed with ovarian cancer each year, hope often comes in the form of platinum-based drugs such as cisplatin.
Cisplatin causes the death of quick-dividing tumour cells, so it is a potent first-line defence in the treatment of the often fatal disease.
However, over half of ovarian cancer patients develop recurrence and become resistant to cisplatin and other platinum-based chemotherapies, contributing to the five-year survival rate of 31%.
It is unclear why this resistance occurs, but a solution is urgently ...
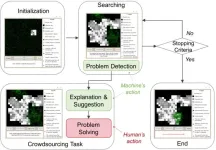
Human-AI collaboration improves source search outcomes
2023-09-06
When artificial intelligence robots that have been designed to use algorithms to complete source search tasks, such as search and rescue operations during a fire, encounter a disturbance, they are often unable to complete their task. Proposed solutions have ranged from trying to improve algorithms to introducing additional robots, but these AI-driven robots still encounter fatal problems.
Researchers have proposed a solution: a human-AI collaboration that takes advantages of the unique skills of the human brain to overcome challenges.
The paper was published in the Journal of Social ...
Teleneurology challenges met by training curriculum
2023-09-06
A new physician-training system in telehealth simulates key parts of traditional, in-person neurological exams that use little reflex hammers, pinpricks, and flashlights to test nerve function. The three-year program, which was designed by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, has trained at least 68 neurology residents since its rollout in 2020. Published online Aug. 3 in Neurology Education, a new analysis of the curriculum identifies challenges to translating in-person exam techniques ...
[1] ... [1707]
[1708]
[1709]
[1710]
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
1715
[1716]
[1717]
[1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.