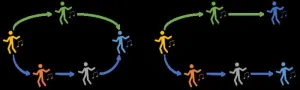
What do neurons, fireflies and dancing the Nutbush have in common?
2023-09-08
Computer scientists and mathematicians working in complex systems at the University of Sydney and the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences in Germany have developed new methods to describe what many of us take for granted – how easy, or hard, it can be to fall in and out of sync.
Synchronised phenomena are all around us, whether it is human clapping and dancing, or the way fireflies flash, or how our neurons and heart cells interact. However, it is something not fully understood in engineering and science.
Associate Professor Joseph Lizier, expert in complex systems at the University of Sydney, said: “We know ...
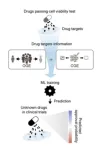
Drug approvals in clinical trials were correlated with the cells/humans discrepancy in gene perturbation effects
2023-09-08
Developing new drugs is paramount in discovering innovative treatments and preventing diseases. This is vital not only for advancing medicine but also for the overall health and well-being of humanity. Yet, even when drugs demonstrate safety and efficacy in cell and animal models, they frequently encounter hurdles in clinical trials on human.
A single setback for a drug during clinical trials, which involves diverse population groups, can result in significant economic losses. To address this, it is imperative to understand why certain drugs, despite passing the preclinical stages, falter during clinical ...
Unveiling the causes of the 1931 Yangtze River Deluge
2023-09-08
In the summer of 1931, an unprecedented calamity unfolded along the Yangtze River basin in eastern China - the 1931 Yangtze River flood, known as one of history's deadliest natural disasters. This cataclysmic event submerged a staggering 180,000 km2, affected 25 million lives, and tragically claimed over 2 million lives.
Despite its immense societal impact, the origins of this monumental flood have remained largely unexplored, a challenge compounded by the scarcity of historical records and pre-1950s meteorological data in China. Recent access to crucial historical datasets has, however, unlocked the ability to investigate the 1931 Yangtze River flood.
A recent study published ...
Physical activity boosting resources support classroom performance
2023-09-08
DALLAS, September 8, 2023 — This back to school season the American Heart Association and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with its 32 NFL clubs, are offering students exciting ways to move more with NFL PLAY 60™. Physical activity is important as students return to the classroom. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, active kids learn better, focus more, think more clearly, react to stress more calmly, and perform and behave better in the classroom[1].
The ...
New study highlights feasibility and optimization of ammonia-based power generation for carbon neutrality
2023-09-08
Ammonia is emerging as a promising energy source to achieve carbon neutrality due to its inherent carbon-free nature. A recent study, led by Professor Hankwon Lim in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering and the Graduate School of Carbon Neutrality at UNIST, has evaluated the feasibility of ammonia-based power generation through techno-economic and carbon footprint analyses. The research focuses on an integrated system combining ammonia decomposition and phosphoric acid fuel cells.
The study, conducted using a commercial process simulator, unveils significant findings regarding the efficiency and economic viability of utilizing ammonia ...
UTSA researchers explain plant’s medicinal power against COVID and glioblastoma
2023-09-08
Vibrant green leaves sprout from tall fragrant plants sitting neatly in two rows of terracotta pots in Valerie Sponsel’s UTSA biology laboratory. One floor just above her is the chemistry lab of Francis Yoshimoto, who is extracting the plant’s leaves for medicinal compounds. Soon, the researchers will meet with UTSA researcher Annie Lin, who will test the extracted compounds on cancer cells.
The plant is Artemisia annua, or Sweet Annie, and it contains medicinal compounds. UTSA researchers are studying the plant to understand the bioactive properties of one of these compounds, Arteannuin B, in cancer cells and COVID, the ...
Benchtop NMR spectroscopy can accurately analyse pyrolysis oils
2023-09-08
Benchtop NMR spectroscopy can accurately analyse pyrolysis oils
Pyrolysis bio-oils have the potential to be widely used as alternative fuels but are very complex to analyse
Cheaper, simpler, low-field, or ‘benchtop’, NMR spectrometers were able to accurately quantify key oxygen-containing components of pyrolysis bio-oils for the first time
More accessible analysis could help develop the potential of bio-oils as an alternative to fossil fuels
EMBARGOED UNTIL FRIDAY 8TH SEPTEMBER at 9am UK time 2023 | Birmingham, UK
A team of researchers at Aston University ...
The climate crisis could reshape Italian mountain forests forever
2023-09-08
As a result of the climate crisis, future forests may become unrecognizable. Trees that currently make up European woods may no longer be seen — or they may have moved several hundred meters uphill. Scientists writing in Frontiers in Forests and Global Change have mapped the forests of five vulnerable mountain areas in Italy and modelled the future of these fragile ecosystems.
“If I imagine my daughter walking with me as an old man, in our mountain forests, I can imagine that we can see the initial stage of a profound ...
Disney princesses can be good for a child’s self-image, UC Davis researchers suggest
2023-09-08
Children have loved Disney princesses since Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs premiered in theaters in 1937. While this adoration continues to grow in terms of princess movie ratings, some parents may wonder what effects these idealized images of young women might have on how their children feel about and express themselves.
According to new research from the University of California, Davis, a favorite princess improved — but did not harm — young children’s ...
University of Miami upgrades Atmospheric Chemistry Observatory in Barbados
2023-09-08
The observatory has been used to document the transport of Saharan dust particles across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean, creating the longest-running dust data set in existence. Scientists from many different disciplines use the data to understand how dust particles impact everything from coral reef health to cloud formation and tropical storms.
Through a grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF), the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science recently completed a major upgrade to its Barbados Atmospheric Chemistry Observatory (BACO), expanding its capability ...
Beaver activity in the Arctic increases emission of methane greenhouse gas
2023-09-08
The climate-driven advance of beavers into the Arctic tundra is causing the release of more methane — a greenhouse gas — into the atmosphere.
Beavers, as everyone knows, like to make dams. Those dams cause flooding, which inundates vegetation and turns Arctic streams and creeks into a series of ponds. Those beaver ponds and surrounding inundated vegetation can be devoid of oxygen and rich with organic sediment, which releases methane as the material decays.
Methane is also released when organics-rich permafrost thaws as the result of heat carried by the spreading water.
A study linking Arctic beavers to an increase in the release of methane was ...
Labour laws need updating now remote work is here to stay
2023-09-08
Australia’s employment laws and regulations must be updated to reflect the changing nature of work, with many people continuing to work from home long after the COVID-19 pandemic.
That’s according to University of South Australia Associate Professor of Organisational Behaviour Dr Ruchi Sinha who says labour laws and protections should be updated to clarify issues related to work hours, overtime, and breaks in a remote work context, now that almost half of all employees are working from home at least once a week.
The Australian Institute of Health and Welfare ...
UArizona scientists investigate new frontiers of sound with $30M center
2023-09-08
The National Science Foundation has granted the University of Arizona $30 million over five years to establish a new NSF Science and Technology Center. The New Frontiers of Sound Science and Technology Center, which comes with an additional $30 million funding option over the following five years, will bring together researchers working in topological acoustics.
With topological acoustics, researchers exploit the properties of sound in ways that could vastly improve computing, telecommunications and sensing. Applications could include reaching quantum-like computing speeds, reducing the power usage of smartphones, and sensing changes in aging infrastructure or the natural ...
Artificial intelligence could help build pollen jigsaw of present and ancient flora
2023-09-08
An emerging system which combines rapid imaging with artificial intelligence could help scientists build a comprehensive picture of present and historic environmental change – by swiftly and accurately analysing pollen.
Pollen grains from different plant species are unique and identifiable based on their shape. Analysing which pollen grains are captured in samples such as sediment cores from lakes helps scientists understand which plants were thriving at any given point in history, potentially dating back thousands to millions of years.
Up to now, scientists have manually ...
Distance from clinic influences abortion pill access
2023-09-08
Women who live farther from a medical clinic and those who identify as multiracial are more likely to use telemedicine to get abortion pills than to visit a clinic, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The findings were published Sept. 1 in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the main takeaways,” said lead author Anna Fiastro, a family medicine research scientist at UW Medicine, “is that the further patients are from a brick-and-mortar clinic, the more ...
Study links epigenetic changes to historic trauma in Alaska Native communities
2023-09-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers investigated the relationship between historical traumatic events experienced by Alaska Native communities and epigenetic markers on genes that previous studies have linked to trauma. The new study found a similar pattern among Alaska Native participants, with specific epigenetic differences observed in those who reported experiencing the most intense symptoms of distress when reflecting on historic losses.
The study also found that individuals who strongly identified with their Alaska Native heritage and participated in cultural activities generally reported better well-being. The new findings are detailed in the International ...
Mums exposed to air pollution give birth to smaller babies, but living in a greener area may mitigate the risks
2023-09-08
Milan, Italy: Women exposed to air pollution give birth to smaller babies, according to research that will be presented at the European Respiratory Society International Congress in Milan, Italy [1]. The research also shows that women living in greener areas give birth to bigger babies and this may help counteract the effects of pollution.
There is a strong relationship between birthweight and lung health, with low birthweight children facing a higher risk of asthma and higher rates of chronic obstructive ...
Stevens INI receives new funding to study small vessel disease in Asian Americans
2023-09-07
Asian Americans are among the fastest growing populations in the U.S. but are significantly underrepresented in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) research. This means there is a significant knowledge gap of ADRD in this particular group at a time when the global Asian population is rapidly aging and the burden of ADRD will likely mirror this growth. Thanks to a new award, the Keck School of Medicine of USC’s Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute (Stevens INI) is perfectly poised to help bridge the gap.
Professor of ...
What’s love got to do with it? An exception to the recognition of musical themes
2023-09-07
New Haven, Conn. — Music can take on many forms in cultures across the globe, but Yale researchers have found in a new study that some themes are universally recognizable by people everywhere with one notable exception — love songs.
“All around the world, people sing in similar ways,” said senior author Samuel Mehr, who splits his time between the Yale Child Study Center, where he is an assistant professor adjunct, and the University of Auckland, where he is senior lecturer in psychology. “Music is deeply rooted in human social interaction.”
For ...
Neurodivergent engineering research at USU funded by the National Science Foundation
2023-09-07
More will soon be known about neurodiversity in engineering students, thanks to funding from the National Science Foundation and the efforts of Utah State University College of Engineering Assistant Professor Marissa Tsugawa.
Tsugawa, along with collaborators from USU and Minnesota State University, received $373,508 in funding for their research in identifying emancipatory language and capturing neurodivergent narratives.
“The term neurodivergent refers to a person with a brain that functions significantly different from the societal norm, such as someone with ADHD or autism,” Tsugawa said. “The term is used to celebrate, ...
Study seeks to explain widespread inequality for developing diabetes mellitus following gestational diabetes
2023-09-07
September 5, 2023-- Racial and ethnic inequities in diabetes have been established following gestational diabetes, but these inequities are substantial and have been an overlooked facet of maternal health equity, according to a new study by epidemiologist Teresa Janevic, PhD, associate professor of Epidemiology at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. Until now there was limited research on racial and ethnic disparities in type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). The findings are published online in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“Very few studies ...
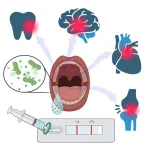
New at-home test for gingivitis protects oral health
2023-09-07
Engineers at the University of Cincinnati have developed a new device that can warn consumers about early risks of tooth decay from diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis, the earliest form of gum disease, is caused by bacteria. But not just any bacteria.
The problem for researchers was getting a device to single out the particular type responsible for the disease, said Andrew Steckl, an Ohio Eminent Scholar and distinguished research professor in UC’s College of Engineering and Applied Science.
“It’s been quite the challenge to get to the point where we can detect this toxin created by the bacteria ...
Internationally recognized computational researcher Spyridon Bakas, PhD, to serve as inaugural director of Division of Computational Pathology
2023-09-07
INDIANAPOLIS—Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Pathology is launching a new Division of Computational Pathology and a Research Center for Federated Learning in Precision Medicine. Both will be led by Spyridon Bakas, PhD, an internationally recognized computational researcher who brings ten years of experience and NIH grant funding to this growing field that combines artificial intelligence and medicine.
“Computational pathology is a growing area of medicine around the world,” Bakas said. “The idea is to leverage information that exists within tissue slides ...
Two in one: FSU researchers develop polymer that can be adapted to high and low temperature extremes
2023-09-07
The modern world is filled with synthetic polymers, long-chained molecules designed by scientists to fill all manner of applications.
Researchers at FAMU-FSU College of Engineering have developed two closely related polymers that respond differently to high and low temperature thresholds, despite their similar design. The polymer pair could be used in applications in medicine, protein synthesis, protective coatings and other fields. Their work is published in Macromolecules.
“Typically, in order to have one thermal behavior, we have to prepare a polymer for that specific application, and if you ...
New stroke treatment in development at UTHSC
2023-09-07
A study at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center aims to develop a new way to treat ischemic stroke, a leading cause of death in adults worldwide.
The study is funded by a $1,155,000 translational grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, part of the National Institutes of Health. Jianxiong Jiang, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and the Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Jiawang Liu, PhD, director of the Medicinal Chemistry ...
[1] ... [1702]
[1703]
[1704]
[1705]
[1706]
[1707]
[1708]
[1709]
1710
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
[1716]
[1717]
[1718]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.