A secret for boosting hotel bookings: analyze online user reviews for your hotel and your competitors
2023-09-06
Researchers from Texas Christian University, University of South Carolina, and RealPage published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the impact of online reviews on hotel booking performance with a specific focus on the competitive effects of reviews.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “The Competitive Effects of Online Reviews on Hotel Demand” and is authored by Sanghoon Cho, Pelin Pekgun, Ramkumar Janakiraman, and Jian Wang.
Recent reports indicate that a majority of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations when deciding to book a hotel. A 2019 study ...
Rubber plumbing seals can leak additives into drinking water, study says
2023-09-06
As drinking water flows through pipes and into a glass, it runs against the rubber seals inside some plumbing devices. These parts contain additives that contribute to their flexibility and durability, but these potentially harmful compounds can leak into drinking water, according to a small-scale study in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters. The authors report that the released compounds, which are typically linked to tire pollution, also transformed into other unwanted byproducts.
To enhance rubber’s strength and durability, manufacturers typically mix in additives. Scientists have shown that tire dust ...
Mount Sinai announces partnership with the Brazilian Clinical Research Institute to advance cardiovascular disease research and medical education
2023-09-06
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai announced today that it has signed a memorandum of understanding with the Brazilian Clinical Research Institute (BCRI) to focus on advancing cardiovascular disease research, innovation, and medical education.
"This partnership is part of a broader initiative to expand Mount Sinai Heart’s reach globally, and Latin America is an important part of that goal," said Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Dr. Valentin Fuster Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine at Icahn Mount Sinai. "Our partnership ...
Recent advances in melon and gourd research
2023-09-06
As summer draws to a close, the long vines and tendrils of most melons and gourds in the Cucurbitaceae family snake their way along the ground. And they’re dotted with fruits, such as cucumbers or pumpkins. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into melons’ potential health impacts, pathogens and contaminants. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
“Nanoparticles Loaded with a Carotenoid-Rich Extract from Cantaloupe Melon Improved Hepatic Retinol Levels in a Diet-Induced Obesity Preclinical Model”
ACS ...
Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard announces a new research alliance with Novo Nordisk to identify therapeutic targets for type 2 diabetes and cardiometabolic diseases
2023-09-06
Cambridge, MA (September 6, 2023) — The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard today announced a new research alliance with Novo Nordisk aimed at addressing critical unmet clinical needs in diabetes and cardiometabolic diseases. The collaboration will focus on advancing three programs over the next three years. Two programs aim to identify drug targets for clinically important subtypes of type 2 diabetes, which affects more than 37 million people in the United States alone, and one program aims to unravel the genetic roots of cardiac fibrosis, or scarring of the heart, which occurs in many cardiovascular diseases that can lead to ...
MD Anderson and Panacea launch Manaolana Oncology to develop antibody-based therapies for cancer
2023-09-06
HOUSTON and SAN MATEO, Calif. ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Panacea Venture today announced the launch of Manaolana Oncology Inc., a new company created to develop and advance antibody-based therapies against novel cancer antigens.
Manaolana Oncology seeks to build upon the innovative antibody production capabilities and intellectual property of MD Anderson to research and develop novel monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and other antibody-based therapies for a variety of cancer types, with the goal of advancing promising therapies into ...
Obesity-related cardiovascular disease deaths tripled between 1999 and 2020
2023-09-06
Research Highlights:
Obesity-related cardiovascular disease deaths tripled between 1999 and 2020 in the U.S.
Such deaths were higher among Black individuals (highest among Black women) compared with any other racial group, followed by American Indian/Alaska Native people.
Black adults who lived in urban communities experienced more obesity-related cardiovascular disease deaths than those living in rural areas, whereas the reverse was true for all other racial groups.
This news release has been updated to include ...
Switching from harmful to helpful fungi
2023-09-06
Mold and diseases caused by fungi can greatly impact the shelf life of fruit and vegetables. However, some fungi benefit their hosts by aiding plant survival. Colletotrichum tofieldiae (Ct) is a root mold which typically supports continued plant development even when the plant is starved of phosphorus, an important nutrient for photosynthesis and growth. Researchers studied a unique pathogenic strain of the fungi, called Ct3, which conversely inhibits plant growth. By comparing the beneficial and harmful strains Ct strains, they found that activation of a single fungal secondary metabolism gene cluster determined the negative impact of the fungus on the host ...
Does cyberbullying affect adolescents’ risk of developing eating disorders?
2023-09-06
In a study of US adolescents, both victims and perpetrators of cyberbullying were more likely than other youth to experience eating disorder symptoms. The findings are published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders.
In the study of 10,258 adolescents aged 10–14 years, participants answered questions about whether they had experienced cyberbullying victimization and perpetration, as well as whether they had experienced eating disorder symptoms.
Cyberbullying victimization was associated with worrying about weight ...
Are children’s growing pains tied to migraines?
2023-09-06
New research published in Headache reveals that, in children and adolescents, pain in the lower limbs—what are often called “growing pains” by clinicians and are commonly attributed to rapid growth—may indicate the presence or risk of migraines.
The study included 100 children and adolescents born to mothers with migraines seen at a headache clinic, with half of the youth experiencing growing pains.
“In families of children with growing pains, there is an increased prevalence of other pain syndromes, especially migraine ...
Are antipsychotic drugs being appropriately prescribed to homebound patients with dementia?
2023-09-06
New research published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society indicates that antipsychotics are likely overprescribed and used inappropriately among patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) receiving home health care, and such use is linked to worse patient outcomes.
Antipsychotic drugs are not approved for the treatment of dementia—they are mostly used off-label to manage the symptoms that many people with ADRD experience, such as agitation, aggression, and psychosis that are called “behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia.” In addition, ...
New method enables efficient isolation of raccoon-borne food poisoning pathogen
2023-09-06
Osaka, Japan – As cute as raccoons may look, their behaviors are troublesome, and so are their droppings. Known to contain Escherichia albertii—a harmful enteropathogen—raccoon feces challenge zoonotic researchers who grapple to isolate this bacterium for further study. Fortunately, Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have come up with a novel culture medium for efficient isolation of E. albertii, making progress toward alleviating this particular raccoon-conveyed threat.
Due ...
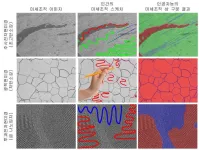
Easier and faster materials microstructure analysis through human-AI collaboration!
2023-09-06
The research team led by Dr. Se-Jong Kim and Dr. Juwon Na of the Materials Data Management Center in the Materials Digital Platform Division together with the research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee of POSTECH has developed a technology that can automatically identify and quantify materials microstructure from microscopic images through human-in-the-loop machine learning. KIMS is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Microscopic imaging systems visualize material structure information at multiple ...
Psychedelic rock gecko among dozens of species in need of further conservation protection in Vietnam
2023-09-06
Further conservation measures are required to protect Vietnamese reptiles, such as the psychedelic rock gecko (Cnemaspis psychedelica), from habitat loss and overharvesting, concludes a new report, published in the open-access scientific journal Nature Conservation.
Having identified areas of high reptile diversity and large numbers of endangered species, the study provides a list of the 50 most threatened species as a guide for further research and conservation action in Vietnam.
The study, based on the bachelor thesis of Lilli Stenger (University of Cologne, Germany), recommends IUCN CPSG’s ...
MCG Anesthesiology Externship Program helps grow profession
2023-09-06
A unique program that sees students at the Medical College of Georgia working as anesthesia technologists throughout their four years of medical school can influence more of them to pursue the specialty as a career, investigators report.
The MCG Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine’s nearly 100-year-old Externship Program is one of only five or six in the country and allows interested medical students to work nights, weekends and holidays, as a critical part of the anesthesia and operating room teams. Anesthesia techs are typically responsible for sterilizing, cleaning, assembling, calibrating, testing and troubleshooting various pieces of machinery in the operating ...
Non-binary and transgender Californians suffered alarming levels of physical and sexual violence in the past year
2023-09-06
WASHINGTON (September 6, 2023) – An annual survey of physical and sexual violence suffered by Californians documents for the first time the higher incidence of violence among non-binary and transgender people. One in 20 California adults has experienced physical violence (5%) in the past year, a decrease from 8% in 2022, according to The California Violence Experiences Study (CalVEX); but the reported rates for non-binary and transgender individuals were notably higher, 14% and 27%, respectively.
“The new data we have in this year’s report show that rates of violence have declined since levels seen during the pandemic, but these experiences remain too ...
New Myriad Genetics survey reveals widespread confusion and misconceptions about ovarian cancer screening among a majority of women
2023-09-06
SALT LAKE CITY, Sept. 6, 2023 – Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ:MYGN), a leader in genetic testing and precision medicine, today revealed new nationwide survey results indicating widespread confusion and misconceptions about ovarian cancer screening among a majority of women.
The Myriad Genetics Cancer Risk survey shows that nearly three out of four women (71%) falsely believe annual pap smears include testing for ovarian cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the “only gynecologic cancer the Pap test screens for is cervical cancer.”
“Ovarian cancer is ...
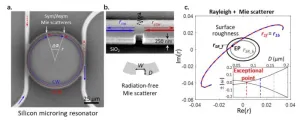
Low loss Mie scatterer enhanced Q and chirality control in silicon microring
2023-09-06
Non-Hermitian systems with their spectral degeneracies known as exceptional points (EPs) have been explored for lasing, controlling light transport, and enhancing a sensor’s response. A ring resonator can be brought to an EP by controlling the coupling between its frequency degenerate clockwise and counterclockwise traveling modes. This has been typically achieved by introducing two or more nano-tips into the resonator’s mode volume. While this method provides a route to study EP physics, the basic understanding of how the nano-tips’ shape and size symmetry impact the system’s non-Hermicity is missing, along with additional loss from both in-plane and out-of-plane ...
Engineering of plant cell wall modifying enzymes opens new horizons
2023-09-06
A newly discovered way of optimising plant enzymes through bioengineering has increased knowledge of how plant material can be converted into biofuels, biochemicals and other high-value products.
The University of Adelaide-led study presents innovative ideas for how the walls of plant cells can be assembled, structured and remodelled by controlling specific enzymes’ catalytic function.
Fundamental plant cell properties – such as structure, integrity, cytoskeletal organisation and stability ...
Researchers awarded $2.5 million to develop brain cancer treatment
2023-09-06
A multidisciplinary team of investigators from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center was awarded a $2.5 million Translational Team Science Award from the Department of Defense to develop a tailored treatment for glioblastoma, a deadly brain tumor with limited treatment options.
The team — including David Nathanson, associate professor of molecular and medical pharmacology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Benjamin Ellingson, director of the UCLA Brain Tumor Imaging Laboratory and professor of radiological ...
Study: Race, ethnicity may play a role in cause of liver cancer
2023-09-06
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL SEPT. 5, 2023 AT 8 P.M. ET) – A new analysis of liver cancer has identified racial and ethnic differences and emerging trends for this highly fatal disease. The study, conducted by researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations, also identified potential targeted interventions to improve control and prevention.
Their extensive review, published Sept. 6 in the journal Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, examined 14,420 confirmed ...
Efforts to restore federal forests in eastern Oregon are working, Oregon State research shows
2023-09-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Forest thinning is improving the robustness of older trees and enhancing native biodiversity on federal lands in eastern Oregon, evidence that collaborative efforts to restore forests are working, research by Oregon State University shows.
The study led by James Johnston of the OSU College of Forestry involved long-term monitoring and research partnerships between OSU, the U.S. Forest Service and local groups in Oregon’s Blue Mountains.
Published today in Forest Ecology and Management, the findings illustrate the collaboration’s success ...
Global surge in cancers among the under 50s over past three decades
2023-09-06
There’s been a striking 79% increase in new cases of cancer among the under 50s around the world over the past three decades (1990-2019), finds research published today in the open access journal BMJ Oncology.
Breast cancer accounted for the highest number of ‘early onset’ cases in this age group in 2019. But cancers of the windpipe (nasopharynx) and prostate have risen the fastest since 1990, the analysis reveals. Cancers exacting the heaviest death toll and compromising health the most among younger adults in 2019 were those of the breast, windpipe, lung, bowel, and stomach.
The findings ...
Strong evidence of ‘threshold effect’ for NHS 18-week waiting list target
2023-09-06
There’s strong evidence of a ‘threshold effect’ in English hospitals’ efforts to comply with the 18-week referral to treatment standard, concludes a long term data analysis of performance against the target, published online in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
The target focused activity on meeting the threshold requirement for patients on the waiting list after which it tailed off—the so-called threshold effect–rather than instigating pervasive improvement in practice, the analysis indicates. Clinical need may be a secondary consideration for meeting the target, suggest the researchers.
In 2012, an 18-week ...
Hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) risk factor for serious mental health issues
2023-09-06
The hyperactivity disorder, usually referred to as ADHD, is an independent risk factor for several common and serious mental health issues, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
It is associated with major depression, post traumatic stress disorder, the eating disorder anorexia nervosa, and suicide attempts, the findings show, prompting the researchers to recommend vigilance by health professionals in a bid to ward off these disorders later on.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition in children and teens that extends into adulthood in up to around two thirds of cases. Worldwide, its prevalence ...
[1] ... [1708]
[1709]
[1710]
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
1716
[1717]
[1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.