New research reveals Earth's ancient ‘breath’: Study reveals connection between atmospheric changes and mantle chemistry
2023-08-31
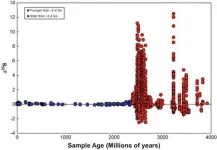
An international team of scientists have uncovered an important link between Earth’s early atmosphere and the chemistry of its deep mantle.
The study, which was led by researchers at the University of Portsmouth and University of Montpellier, sheds new light on the evolution of life on our planet and the rise of atmospheric oxygen.
The team investigated magmas formed in ancient subduction zones, where portions of Earth’s crust sink back into the mantle, from a pivotal moment in Earth's history – the Great Oxidation Event (GOE). This event, which is estimated to have happened between 2.1 ...
Discovery opens possibility of new ion channel-targeting drugs
2023-08-31
Ion channels are attractive drug targets due to their importance in health and disease, but finding ways to target a specific ion channel selectively is a major challenge. Now, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and RMIT University in Australia have discovered that ion channels called BK channels have unique openings in their sides, which drug molecules may be able to access. The finding, published Aug. 31 in Nature Chemical Biology, could lead to the development of selective drugs that target the BK channel to treat ...
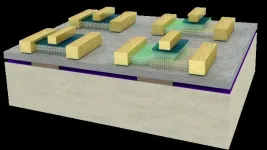
Analog and digital: The best of both worlds in one energy-efficient system
2023-08-31
We live in an analog world of continuous information flow that is both processed and stored by our brains at the same time, but our devices process information digitally in the form of discrete binary code, breaking the information into little bits (or bites). Researchers at EPFL have revealed a pioneering technology that combines the potential of continuous analog processing with the precision of digital devices. By seamlessly integratingultra-thin, two-dimensional semiconductors with ferroelectric materials, the research, published in Nature Electronics, unveils a novel way to improve energy efficiency and add new functionalities in computing. The ...
Coastal fisheries show surprising resilience to marine heat waves
2023-08-31
Rutgers-led research found that marine heat waves – prolonged periods of unusually warm ocean temperatures – haven’t had a lasting effect on the fish communities that feed most of the world.
The finding is in stark contrast to the devastating effects seen on other marine ecosystems cataloged by scientists after similar periods of warming, including widespread coral bleaching and harmful algal blooms.
“There is an emerging sense that the oceans do have some resilience, and while they are changing in response ...
A new breakthrough in obesity research allows you to lose fat while eating all you want
2023-08-31
This is a significant development that brings hope to the one billion individuals with obesity worldwide. Researchers led by Director C. Justin LEE from the Center for Cognition and Sociality (CCS) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have discovered new insights into the regulation of fat metabolism. The focus of their study lies within the star-shaped non-neuronal cells in the brain, known as 'astrocytes'. Furthermore, the group announced successful animal experiments using the newly developed drug 'KDS2010', which allowed the mice to successfully achieve weight loss without resorting ...
New blood test for noncoding RNA significantly improves cancer detection
2023-08-31
Cancer is most treatable in its early stages, so finding innovative and non-invasive methods to diagnose cancer early on is crucial for fighting the disease. Liquid biopsies, which require just a simple blood draw, are an emerging technology for non-invasively testing for cancer using DNA or RNA sequencing of a patient’s blood.
Assistant Professor of Biomolecular Engineering Daniel Kim and his lab are developing more accurate and powerful liquid biopsy technologies that take advantage of signals from RNA “dark matter,” an understudied ...
Largest genetic study of epilepsy to date provides new insights on why epilepsy develops and potential treatments
2023-08-31
Thursday, 31 August 2023: The largest genetic study of its kind, coordinated by the International League Against Epilepsy, including scientists from FutureNeuro at RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, has discovered specific changes in our DNA that increase the risk of developing epilepsy.
The research, published today in Nature Genetics, greatly advances our knowledge of why epilepsy develops and may inform the development of new treatments for the condition.
Epilepsy, a common brain disorder of which there are many different types, is known to have genetic component and to sometimes run in families. Here, researchers compared the DNA from diverse groups of almost ...
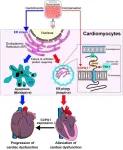
Intracellular recycling: the key to surviving potent anti-cancer drugs
2023-08-31
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) determine how cardiomyocytes protect themselves against anti-cancer medication
Tokyo, Japan – A cell contains many specialized subunits, called organelles, that carry out important tasks such as energy generation, protein synthesis, and calcium outflux. But what happens when something goes wrong with one of the organelles?
In a study recently published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: CardioOncology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) have ...
Growing triple-decker hybrid crystals for lasers
2023-08-31
By controlling the arrangement of multiple inorganic and organic layers within crystals using a novel technique, researchers at Duke University and Purdue University have shown they can control the energy levels of electrons and holes (positive charge carriers) within a class of materials called perovskites. This tuning influences the materials’ optoelectronic properties and their ability to emit light of specific energies, demonstrated by their ability to function as a source of lasers.
Appearing online August 31 in the journal Nature Chemistry, the research is the result of a close collaboration between several ...
Positive framing of genomics met with scepticism in some communities
2023-08-31
August 31, 2023 - New research published today in Human Genetics and Genomics Advances reveals the difference between ‘what we say’ and ‘what people hear’ when engaging underrepresented communities around genomics and healthcare.
Genomics datasets, which underpin the ability to interpret all genetic tests, are known to consist of DNA from predominately white, Northern European populations. As genomics becomes an increasingly important part of everyday healthcare*, barriers to diverse participation must be overcome so that everyone can benefit from genomic medicine, not just the privileged few.
The research ...
People who are in good shape take fewer mental-health related medication
2023-08-31
“We find that people who are in better shape fill fewer prescriptions for anxiety and depression medications,” says Linda Ernstsen, the senior author of the article and an associate professor from the Department of Public Health and Nursing at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU).
The research group based its work on the Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT). Since 1984, 250,000 Trøndelag residents have voluntarily contributed their health data to this comprehensive ...
Breathe! The shape-shifting ball that supports mental health
2023-08-31
A soft ball that ‘personifies’ breath, expanding and contracting in synchronicity with a person’s inhalations and exhalations, has been invented by a PhD student at the University of Bath in the UK. The ball is designed to support mental health, giving users a tangible representation of their breath to keep them focused and to help them regulate their emotions.
Alexz Farrall, the student in the Department of Computer Science who invented the device, said: "By giving breath physical form, the ball enhances self-awareness and engagement, fostering positive mental health outcomes."
Generally, ...
Out with the old, in with the new: Agile mentorship to support future scientists
2023-08-31
INDIANAPOLIS – Mentorship has existed throughout history. Socrates mentored Plato, who, in turn, mentored Aristotle. Humphry Davy, the chemist who was the first to isolate potassium, sodium and at least five other elements, mentored Michael Faraday, inventor of the world’s first electric generator. Sigmund Freud mentored Carl Jung. Science teacher Elizabeth Mommaerts mentored Sally Ride. Maya Angelou mentored Oprah Winfrey. The list of knowledge bearers and knowledge seekers who have connected meaningfully goes ...
CityU researchers develop ultra-sensitive photoacoustic microscopy for wide biomedical application potential
2023-08-31
Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy is an up-and-coming biomedical imaging technique for studying a broad range of diseases, such as cancer, diabetes and stroke. But its insufficient sensitivity has been a longstanding obstacle for its wider application. Recently, a research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) developed a multi-spectral, super-low-dose photoacoustic microscopy system with a significant improvement in the system sensitivity limit, enabling new biomedical applications and clinical translation in the future.
Photoacoustic ...
Henry Ford Health Hospitals earn full reaccreditation from National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers
2023-08-31
DETROIT – All five of Henry Ford Health’s acute care hospitals have earned a full three-year reaccreditation by the National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers (NAPBC), a quality program administered by the American College of Surgeons. With Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, Henry Ford Jackson Hospital, Henry Ford Macomb Hospital, Henry Ford West Bloomfield Hospital and Henry Ford Wyandotte Hospital earning full reaccreditation, Henry Ford has the highest number of Commission on Cancer and NAPBC-accredited hospitals of any health system in Michigan.
“The NAPBC accreditation is reflective of our unwavering commitment ...
Is digital media use a risk factor for psychosis in young adults?
2023-08-31
On average, young adults in Canada spend several hours on their smartphones every day. Many jump from TikTok to Netflix to Instagram, putting their phone down only to pick up a video game controller. A growing body of research is looking into the potential dangers of digital media overuse, as well as potential benefits of moderate digital media use, from a mental health standpoint.
A recent McGill University study of 425 Quebecers between the ages of 18 and 25 has found that young adults who have more frequent psychotic experiences also tend to spend more time using digital media. Interestingly, the study, which surveyed the participants ...
Why men, wealthy people and maritime residents are more likely to develop skin cancer
2023-08-31
A new study led by McGill University examines why people living in Atlantic regions are more at-risk for developing melanoma than other Canadians, providing lessons on skin cancer prevention for the whole country.
Rates of melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer, have been rising globally, including in Canada. Current estimates indicate that up to 1 in 3 Canadians will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. While some Atlantic provinces such as Prince Edward Island (PEI) and Nova Scotia have the highest incidence rate of melanoma in the country, neighbouring provinces like New Brunswick ...
The search for the super potato
2023-08-31
As climate change continues to pose severe challenges to ensuring sustainable food supplies around the world, scientists from McGill University are looking for ways to improve the resilience and nutritional quality of potatoes. Professor Martina Strömvik and her team have created a potato super pangenome to identify genetic traits that can help produce the next super spud.
“Our super pangenome sheds light on the potato’s genetic diversity and what kinds of genetic traits could potentially be bred into our modern-day crop to make it better,” ...
Better paths yield better AI
2023-08-31
Deep Learning (DL) performs classification tasks using a series of layers. To effectively execute these tasks, local decisions are performed progressively along the layers. But can we perform an all-encompassing decision by choosing the most influential path to the output rather than performing these decisions locally?
In an article published today in Scientific Reports, researchers from Bar-Ilan University in Israel answer this question with a resounding "yes". Pre-existing deep architectures have been improved by updating the most influential paths to the output.
"One can ...
Children’s books are still Whiter, and more male, than US society
2023-08-31
A new paper in the Quarterly Journal of Economics, published by Oxford University Press, finds that children’s books in the United States continue to underrepresent ethnic minorities. In addition, it finds that male characters are overrepresented in such stories and children are often presented with lighter skin tones for no apparent editorial reason.
Education teaches children about the world, its people, and their place in it. Much of this happens through the books society presents to children ...
New insight for stabilizing halide perovskite via thiocyanate substitution
2023-08-31
α-FAPbI3, a promising solar cell material with a cubic perovskite structure that is metastable at room temperature, can be stabilized by introducing a pseudo-halide ion like thiocyanate (SCN–) into its structure, demonstrated by Tokyo Tech researchers in a new study. Their finding provides new insights into the stabilization of the α-phase via grain boundary and pseudo-halide engineering.
The light we receive every day from the Sun, if harnessed efficiently, can help us tackle the ongoing global energy crisis as well as our concern with climate change. Materials with good photophysical properties, i.e., light absorption, ...
Scientists develop finger sweat test to detect antipsychotic drugs in patients
2023-08-31
Antipsychotic drugs treat incredibly vulnerable patients. Maintaining a treatment regimen is difficult for many patients, but not taking the medication is associated with a higher risk of poor health outcomes. These drugs are also very powerful with strong side-effects, and blood tests are often used to calibrate a patient’s dosage and confirm that they are taking the recommended dose.
However, blood tests are invasive and potentially uncomfortable. Scientists have now discovered a way to test the levels of common antipsychotic drugs in the sweat ...
Acting fast when an epidemic hits
2023-08-31
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo and Dalhousie University have developed a method for forecasting the short-term progression of an epidemic using extremely limited amounts of data.
Their model, the Sparsity and Delay Embedding-based Forecasting model, or SPADE4, uses machine learning to predict the progression of an epidemic using only limited infection data. SPADE4 was tested on both simulated epidemics and real data from the fifth wave of the Covid-19 pandemic in Canada and successfully predicted the epidemics’ progressions with 95 per cent confidence.
“Covid taught us that we really need to come up with methods ...
Tracking the ol' mutation trail
2023-08-31
Kyoto, Japan -- From the early stages of cell mutations starting in puberty to their manifestations as breast cancer in later years, the entire process has remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, a team of researchers at Kyoto University has revealed the mechanism by which breast cancer is formed in the cells of the mammalian epithelium, whose main function is to secrete milk.
According to the team's first analysis, approximately 20 mutations accumulate annually in each epithelial cell until menopause. After menopause, however, the mutation rate significantlydecreases.
"Additionally, our results suggest ...
When the gig is up; gig workers don’t always trust their boss and that might be a good thing
2023-08-31
DURHAM, N.H. — As the so-called ‘gig economy’ continues to grow, so do questions about how this type of non-traditional work compares to full time work arrangements and how these new relationships differ and impact performance and commitment. Researchers from the University of New Hampshire took a closer look at gig workers – which include freelancers, independent contractors and temporary workers – and examined relationships between workers and their managers and found that one trait, trust, could be a double-edged sword.
“Millions of workers are now considered gig workers, offering them more flexibility ...
[1] ... [1716]
[1717]
[1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
1724
[1725]
[1726]
[1727]
[1728]
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.