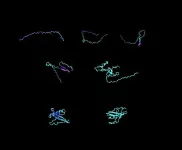
Male crested macaques more likely to respond to offspring screams recruiting support
2023-08-29
When infants are involved in agonistic conflicts, male crested macaques (Macaca nigra) are more likely to respond to screams from their own offspring. This is the conclusion of a recent study led by behavioural ecologist Professor Anja Widdig from Leipzig University and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig as part of the Macaca Nigra Project (MNP). The researchers studied the behaviour of crested macaques in the Tangkoko Nature Reserve on Sulawesi, Indonesia, over a 24-month period (2008 to 2010). A special issue of the “International ...
CDI study of fevers in children during COVID-19 raises further questions
2023-08-29
An uptick in fevers detected among children at more than two dozen hospitals in North America during COVID-19 highlights the question whether there are normally more autoinflammatory disorders such as recurrent fevers among children going overlooked in non-pandemic times, according to a new study by researchers including a CDI physician-scientist.
The paper “Increase in pediatric recurrent fever evaluations during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in North America” was published by Frontiers in Pediatrics on Aug. 3, and includes Sivia Lapidus, M.D., pediatric rheumatologist, Joseph M. Sanzari Children’s ...
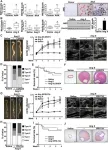
Study sheds light on why breast cancer survivors don’t take their medications, and what can be done about it
2023-08-29
For roughly 80% of breast cancer survivors, treatment doesn’t end with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Instead, for the next five to 10 years, doctors recommend that they take medication to block sex hormones, which can fuel tumor growth and spark recurrence.
The drugs, no doubt, are life-saving: they’ve been shown to cut risk of cancer recurrence by as much as half in patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors (HR+)—the most common form of breast cancer. Yet despite their promised benefits, 40% of patients stop taking them early and a third take them less frequently than directed.
New CU ...
Neural network helps design brand new proteins
2023-08-29
WASHINGTON, August 29, 2023 – With their intricate arrangements and dynamic functionalities, proteins perform a plethora of biological tasks by employing unique arrangements of simple building blocks where geometry is key. Translating this nearly limitless library of arrangements into their respective functions could let researchers design custom proteins for specific uses.
In Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, Markus Buehler of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology combined attention neural networks, often referred to as transformers, with graph neural ...
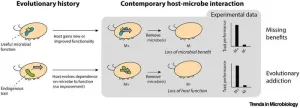
Some hosts have an “evolutionary addiction” to their microbiome
2023-08-29
We’ve long known that hosts malfunction without their microbiome—whether they are missing key microbial species or are completely microbe free. This malfunctioning is usually explained by the need for microbes to perform unique and beneficial functions, but evolutionary ecologist Tobin Hammer of the University of California, Irvine, is questioning that narrative.
In a peer-reviewed opinion article publishing August 29 in the journal Trends in Microbiology, Hammer argues that, in some cases, microbes might not actually be helping their hosts; instead, microbe-free hosts might malfunction because they have evolved an addiction to their microbes. ...
A lightweight wearable device helps users navigate with a tap on the wrist
2023-08-29
Scientists at Rice University in Houston, Texas have developed a fabric-based wearable device that “taps” a user’s wrist with pressurized air, silently helping them navigate to their destination. The study, published August 29 in the journal Device, demonstrated that users correctly interpreted which direction the device was telling them to go an average of 87% of the time. Since the wearable embeds most of its control system within the fabric itself, using air instead of electronics, it can be built lighter and more compact than existing designs.
“We envision this device will be used by individuals who need or desire information to be transmitted ...
Long-term maternal and child outcomes following postnatal SSRI treatment
2023-08-29
About The Study: The results of this study of 61,000 mother-child dyads suggest that postnatal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment was associated with a reduced risk of postnatal depression–associated maternal mental health problems and child externalizing behaviors across early childhood years. These findings suggest that postnatal SSRI treatment may bring benefits in the long term to women with postnatal depression and their offspring.
Authors: Chaoyu Liu, M.D., Ph.D., of King’s College in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Cannabis use disorder and reasons for use in a state where recreational cannabis use is legal
2023-08-29
About The Study: In this study of primary care patients in a state with legal recreational cannabis use, cannabis use disorder (CUD) was common among patients who used cannabis. Moderate to severe CUD was more prevalent among patients who reported any nonmedical use. These results underscore the importance of assessing patient cannabis use and CUD symptoms in medical settings.
Authors: Gwen T. Lapham, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.S.W., of the Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
#MedEd: How doctors use social media to advance medicine
2023-08-29
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 11:00 A.M. EDT ON TUESDAY, AUGUST 29, 2023
Social media’s effects on propagating misinformation among the lay public are widely debated, but a new paper from JAMA suggests physicians using social media are revolutionizing medical education.
La Jolla, Calif. (August 29, 2023) — Ever wonder what your doctor is doing on social media? A new study published in JAMA led by John W. Ayers, Ph.D., from the Qualcomm Institute within the University of California San Diego, finds some physicians are harnessing the reach ...
Underutilized antidepressant treatment for postnatal depression associated with improved child outcomes at age five
2023-08-29
New research led by the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has found that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment for postnatal depression is associated with improvements in child behaviour up to five years after childbirth.
Up to 15% of women experience postnatal depression which has been shown to be associated with poor outcomes for mothers’ and their children. Researchers at King’s IoPPN, in collaboration with the University of Oslo, analysed data from ...
Broken by bison, aspen saplings having a tough time in northern Yellowstone
2023-08-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. – In northern Yellowstone National Park, saplings of quaking aspen, an ecologically important tree in the American West, are being broken by a historically large bison herd, affecting the comeback of aspen from decades of over-browsing by elk.
Findings of the research led by Luke Painter of Oregon State University were published today in Ecology and Evolution.
The study comes five years after Painter, who teaches ecology and conservation in the OSU College of Agricultural Sciences, published a paper in Ecosphere showing that wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone had been a catalyst for aspen recovery both outside and ...
Partners from more than 100 countries collaborate as LOINC® issues 1,945 new concepts in semiannual release
2023-08-29
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semiannual content update with 1,945 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations exchange medical data. The release contains newly created content based on requests submitted by stakeholders from more than 100 countries.
LOINC version 2.75 is available for download from the LOINC website and via the LOINC Terminology Service using HL7® FHIR®. The updated version includes new, edited and newly mapped concepts ...
New study will examine impact of lifestyle physical activity on cognition for older adults
2023-08-29
Jason Yang has been awarded nearly $400,000 from the National Institute on Aging to explore the role of lifestyle physical activity (light movements, walking) in cognition among insufficiently active older adults with higher risks for Alzheimer’s or related dementias. The exercise science assistant professor will use the two-year R21 grant to help determine if frequent and regular engagement in lifestyle physical activity over time may benefit cognitive function for this population.
A ...
More sleep could reduce impulsive behavior in children
2023-08-29
Sleep is a critical part of a child’s overall health, but it can also be an important factor in the way they behave.
According to a new study from the Youth Development Institute at University of Georgia, getting enough sleep can help children combat the effects of stressful environments.
“Stressful environments are shown to make adolescents seek immediate rewards rather than delayed rewards, but there are also adolescents who are in stressful environments who are not impulsive,” said lead author Linhao Zhang, a fourth-year doctoral student in UGA’s College of Family and Consumer Sciences. “We looked at what explains that link and what makes some people ...
New study sheds light on the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in abdominal aortic aneurysm
2023-08-29
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), a common degenerative vascular disease, particularly afflicts men over the age of 60, with up to 8% affected. Characterized by the abnormal dilation of the abdominal aorta, AAA risks a potentially fatal rupture. Despite increasing research efforts, effective pharmaceutical strategies to curb aneurysm growth remain elusive.
In a study published in the journal of Genes & Diseases, researchers from Sant Pau Hospital Research Institute and Biomedical Research Institute Sant Pau scrutinized the Wnt signaling pathway's deregulation in human abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). This ...
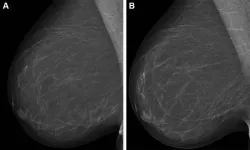
Combining AI models improves breast cancer risk assessment
2023-08-29
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Combining artificial intelligence (AI) systems for short- and long-term breast cancer risk results in an improved cancer risk assessment, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Most breast cancer screening programs take a one-size-fits-all approach and follow the same protocols when it comes to determining a woman’s lifetime risk of developing breast cancer. Using mammography-based deep learning models may improve the accuracy of breast cancer risk assessment and can also lead to earlier ...
Anionic nanogel delivers effective anti-obesity drug to mouse livers
2023-08-29
An anti-obesity drug can be delivered selectively to the liver using a nanogel-based carrier, according to a study. Synthetic thyroid hormone mimics are promising treatments for metabolic diseases including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and inflammatory liver disease; however, the molecules are not highly bioavailable or potent, which are necessary to see significant weight loss. S. Thayumanavan and colleagues designed a nanogel-based carrier with anionic moieties on the surface ...
Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) selects Symplectic Elements to enable comprehensive research management
2023-08-29
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Australia’s Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) has chosen Symplectic Elements from Digital Science’s flagship products to advance awareness of its world-class research.
ANSTO is the home to some of Australia’s most significant national infrastructure for research. Thousands of scientists from industry and academia benefit from gaining access to ANSTO’s ...
Molecule reduces inflammation in Alzheimer’s models
2023-08-29
Though drug developers have achieved some progress in treating Alzheimer’s disease with medicines that reduce amyloid-beta protein, other problems of the disease including inflammation, continue unchecked. In a new study, scientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT describe a candidate drug that in human cell cultures and Alzheimer’s mouse models reduced inflammation and improved memory.
The target of the new “A11” molecule is a genetic transcription factor called PU.1. Prior research has shown that amid Alzheimer’s disease, PU.1 ...
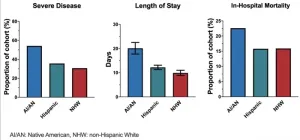
Disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on American Indians
2023-08-29
A study of COVID-19 patients at a New Mexico hospital finds that the virus hit American Indian patients particularly hard—even though Native American patients had fewer other illnesses or conditions than non-native patients. Douglas Perkins and colleagues analyzed data on 475 patients with COVID-19 infections from the University of New Mexico Hospital. The sample was 30.7% Native American, 47% Hispanic, and 18.5% non-Hispanic White. At admission, Native American patients were younger, more likely to need ...
Novel SwRI-developed antenna array wins 2023 R&D 100 Award
2023-08-29
SAN ANTONIO — August 29, 2023 —Novel Southwest Research Institute-developed direction-finding technology has won a prestigious R&D 100 Award. R&D World Magazine has recognized SwRI’s Wideband Conformal Continuous-Slot Antenna Array as one of the 100 most significant innovations for 2023.
“Southwest Research Institute strives to uncover innovative solutions to complex problems,” said SwRI President and CEO Adam L. Hamilton, P.E. “I am very proud of the work SwRI does and pleased to know this technology, which will provide significant support to naval operations, has been recognized as one of the most important innovations ...
Texas Biomed partners with Scancell to test novel COVID vaccine
2023-08-29
SAN ANTONIO (Aug. 29, 2023) – A DNA-based vaccine is very effective at protecting against COVID-19, according to a joint preclinical study by Scancell Ltd and Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) recently published in the Journal of Biotechnology and Biomedicine.
Unlike the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines that use messenger RNA (mRNA) to cue the immune system to produce antibodies, this vaccine platform uses sections of viral DNA to achieve a similar result.
“There is always a need to develop new, or improve on existing vaccines to ensure we have effective tools to counter emerging variants,” says Texas Biomed Innovation ...
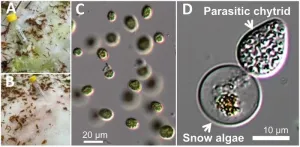
Chytrid fungi revealed to be parasitic species that infects snow algae
2023-08-29
The microbial communities found in glacier and snowpack ecosystems are an essential part of cold weather environments. Chytrids, a group of fungi that include well-known frog pathogens, are often found in abundance in these ecosystems, but culturing these organisms and learning more about their lifecycle, including their relationship to the snow algae found in these environments, has proven challenging.
In a recently published paper, researchers revealed that they were able to analyze chytrid DNA from two alpine snowpack sites in Japan using single-spore PCR.
The paper was published in Frontiers in Microbiology on June 20.
“We have captured the chytrids ...
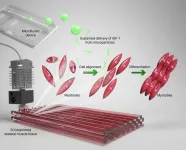
New and improved bioink to enhance 3D bioprinted skeletal muscle constructs
2023-08-29
(LOS ANGELES) – August 29, 2023 - An advancement in 3D bioprinting of native-like skeletal muscle tissues has been made by scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI). The key to the TIBI scientists’ approach lies in their specially formulated bioink, which contains microparticles engineered for sustained delivery of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). As was shown in their recent paper in Macromolecular Bioscience, sustained delivery of IGF-1 enhances the formation of mature skeletal muscle tissue from muscle precursor cells and facilitates their structural alignment. This increases the efficiency of the regenerative process ...
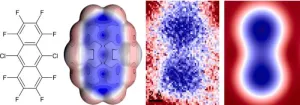
Scientists continue to push the boundaries of imaging techniques and reveal the mysterious world of molecules
2023-08-29
Scientists from the IOCB Prague, the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, and Palacký University Olomouc, have once again successfully uncovered the mysteries of the world of molecules and atoms. They have experimentally confirmed the correctness of a decades-old theory that assumed a non-uniform distribution of electron density in aromatic molecules. This phenomenon significantly affects the physicochemical properties of molecules and their interactions. This research expands the possibilities for designing new nanomaterials and is the theme of a paper that has just been published in Nature Communications.
The ...
[1] ... [1717]
[1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
1725
[1726]
[1727]
[1728]
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.