Positive body image linked to better life satisfaction
2023-09-05
Having more positive body image is strongly associated with better psychological wellbeing and life satisfaction, according to a new study led by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) in England.
Published in the journal Body Image, the research is one of the largest studies ever conducted on the topic of body image, involving 56,968 participants in 65 nations.
The research was focused on ‘body appreciation’, defined as “accepting, holding favourable opinions toward, and respecting the body, while also rejecting media-promoted appearance ...
AADOCR announces MIND the Future Class of 2023-2024
2023-09-05
Alexandria, VA -- The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) is pleased to announce the program participants (mentees) for the fourth cohort of the AADOCR Mentoring an Inclusive Network for a Diverse Workforce of the Future (AADOCR MIND the Future):
Shaun Abrams
NIH/NIDCR, Bethesda, MD
Craniofacial development, anomalies, stem cell biology
Jean Calvo
University of California, San Francisco
Pediatric dentistry, dental education, patient safety, individuals with special needs
Louise M. Dornelas-Figueira
University of Florida, Gainesville
Oral ...
Disparities in who dwells behind crumbling US levees
2023-09-05
American Geophysical Union
5 September 2023
Release 23-33
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/disparities-in-who-dwells-behind-us-levees/
Key points:
Tens of millions of people live in areas protected by at least one levee in the United States
Nationally, members of historically disadvantaged or underserved groups are more likely to be overrepresented in communities living behind levees
People of Hispanic descent are most likely to be overrepresented behind levees, with ~40% overrepresentation ...
Chris Allen named chief financial officer of Keck Medicine of USC
2023-09-05
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has named Chris Allen chief financial officer (CFO), effective Aug. 31. He previously served as interim CFO of Keck Medicine and CFO of Keck Medical Center of USC.
In this role, Allen will continue to oversee Keck Medicine’s strategic financial plans, financial and governmental reporting, budgeting, funds flow, revenue cycle and material management. He will also lead the assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation of the health system’s financial ...
Mason researchers studying zoonotic transmission pathways
2023-09-05
Taylor M. Anderson, Assistant Professor, Geography and Geoinformation Science, and Amira Roess, Professor, Global Health and Epidemiology, are studying zoonotic transmission pathways.
Specifically, the researchers received funding for the project: "Investigating zoonotic transmission pathways to better understand and predict the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in urban and suburban landscapes: a case study of the white-tailed deer."
They aim to investigate unknown transmission pathways at the human-wildlife interface in urban ...
Resistant starch supplement reduces liver triglycerides in people with fatty liver disease
2023-09-05
Resistant starch is a nondigestible fiber that ferments in the large intestine, and consumption of it has previously been shown to have a positive effect on metabolism in animal studies. Now, a 4-month randomized controlled trial in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) indicates that daily intake of resistant starch can alter gut bacteria composition and lower liver triglycerides and liver enzymes associated with liver injury and inflammation. This research appears in the journal Cell Metabolism on September 5.
NAFLD, caused by a buildup of fat in the liver, affects about 30% of the population worldwide. It can lead ...
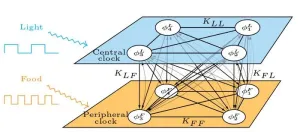
Synchronizing your internal clocks may help mitigate jet lag, effects of aging
2023-09-05
WASHINGTON, Sept. 5, 2023 -- Traveling to faraway places is a great way to seek out new experiences, but jet lag can be an unpleasant side effect. Adjusting to a new time zone is often accompanied by fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and a host of other problems that can turn an otherwise exciting adventure into a miserable trip.
Jet lag is caused by a difference between the circadian system — the body’s internal clock — and the surrounding environment. Around the turn of the century, scientists began to recognize that the body has multiple internal clocks, calibrated in different ways, and that jet lag-like symptoms can result when these ...
Trends in preterm infant mortality by race, socioeconomic status
2023-09-05
About The Study: This study found that between 1995 and 2020, U.S. preterm infant mortality improved among all categories of prematurity. Inequalities in preterm infant mortality based on maternal race and ethnicity have remained constant while socioeconomic disparities have widened over time.
Authors: Tim Venkatesan, M.A. (Cantab), M.B., B.Chir., D.T.M.&H., of the UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health in London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3487)
Editor’s ...
Emergency department pediatric readiness and disparities in mortality based on race and ethnicity
2023-09-05
About The Study: In this study of 633,000 children treated in 586 emergency departments across 11 states, mortality of Black children was greater than that of white children at all quartile levels of readiness among those with acute medical emergencies but not traumatic injuries. Increased readiness was associated with decreased mortality overall, and it decreased most for Black children with acute medical emergencies.
Authors: Peter C. Jenkins, M.D., M.Sc., of the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, is the corresponding ...
Cardiac arrest survival at EMS agencies in catchment areas with primarily Black and Hispanic populations
2023-09-05
About The Study: Risk-standardized survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were 1.9% lower at emergency medical service (EMS) agencies working in Black and Hispanic catchment areas than in white catchment areas in this study including 764 EMS agencies. This difference was not explained by EMS response times, rates of EMS termination of resuscitation, or first responder rates of initiating cardiopulmonary resuscitation or applying an automated external defibrillator. These findings suggest there is a need for further assessment of these discrepancies.
Authors: Paul S. Chan, M.D., M.Sc., Saint Luke’s Hospital ...
Eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement compared with expert clinical diagnosis of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In a study of children ages 16 to 30 months assessed for autism in six specialty clinics, eye-tracking–based measurement of social visual engagement was predictive of autism diagnoses by clinical experts. Further evaluation of this test’s role in early diagnosis and assessment of autism in routine specialty clinic practice is warranted.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.13295)
Editor’s ...
Measurements of social visual engagement to aid early diagnosis and assessment of autism
2023-09-05
About The Study: In two diagnostic studies of 1,089 children younger than age 3, objective eye-tracking–based measurements of social visual engagement quantified diagnostic status as well as individual levels of social disability, verbal ability, and nonverbal ability in autism. These findings suggest that objective measurements of social visual engagement can be used to aid in autism diagnosis and assessment.
Authors: Warren Jones, Ph.D., of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Measuring children’s looking behavior yields new tool to help diagnose autism earlier, research shows
2023-09-05
ATLANTA (September 5, 2023) – Results of clinical studies published simultaneously today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) and in JAMA Network Open demonstrate that measuring children’s looking behavior predicts expert clinical diagnosis of autism in children between ages 16 to 30 months tested with a high degree of accuracy. According to researchers from Marcus Autism Center, a subsidiary of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, this new tool can help clinicians diagnose autism earlier while also providing objective measurements of each child’s strengths and vulnerabilities, to help jumpstart effective support for child ...
Linking two solar technologies is a win-win for efficiency and stability
2023-09-05
While conventional silicon-based solar cells have had an unmistakable impact on the buildout of renewable energy resources around the world, additional performance improvements have become increasingly difficult to make as the devices approach their practical efficiency limits. This constraint has prompted scientists to seek out new technologies that can be combined with silicon cells to unlock higher efficiencies.
Solar cells made with crystals called perovskites are one such technology that have rapidly emerged as an appealing low-cost add-on, but perovskite cells are notoriously susceptible to voltage-induced ...
Why are male kidneys more vulnerable to disease than female kidneys? USC Stem Cell-led mouse study points to testosterone
2023-09-05
Female kidneys are known to be more resilient to disease and injury, but males need not despair. A new USC Stem Cell-led study published in Developmental Cell describes not only how sex hormones drive differences in male and female mouse kidneys, but also how lowering testosterone can “feminize” this organ and improve its resilience.
“By exploring how differences emerge in male and female kidneys during development, we can better understand how to address sex-related health disparities for patients with kidney ...
Racial and socioeconomic differences still determine survival rates of premature babies in the US
2023-09-05
The US continues to face stark inequalities in preterm birth and mortality rates between mothers of differing socioeconomic status and race, finds a new report led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in JAMA Paediatrics, examined data from the US National Centre for Health Statistics Birth Infant/Death Dataset, of over 12 million preterm infant births over the course of 25 years, between 1995 and 2020.
Preterm birth is defined as any infant born before 37 weeks and is the leading cause of infant death ...
3D-printed ‘living material’ could clean up contaminated water
2023-09-05
Researchers at the University of California San Diego have developed a new type of material that could offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution to clean pollutants from water.
Dubbed an “engineered living material,” it is a 3D-printed structure made of a seaweed-based polymer combined with bacteria that have been genetically engineered to produce an enzyme that transforms various organic pollutants into benign molecules. The bacteria were also engineered to self-destruct in the presence ...
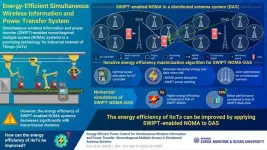
KMOU scientists develop an energy-efficient wireless power and information transfer system
2023-09-05
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoTs) refers to a technology that combines wireless sensors, controllers, and mobile communication technologies to make every aspect of industrial production processes intelligent and efficient. Since IIoTs can involve several small battery-driven devices and sensors, there is a growing need to develop a robust network for data transmission and power transfer to monitor the IIoT environment.
In this regard, wireless power transfer is a promising technology. It utilizes radio frequency signals to power small devices that consume minimal power. Recently, simultaneous wireless information ...
ERC starting grants: 400 bright minds awarded over €628 million
2023-09-05
This funding, part of the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, will be invested in scientific projects spanning all disciplines of research. For example, a geochemist in the Netherlands will study Venus’ atmosphere to better understand habitability beyond Earth; a computer scientist in Germany seeks to make virtual reality more inclusive to physically disabled people; a geneticist in the UK aims to analyse parasites that cause malaria; and a researcher in Israel is set to investigate how algorithms are used at work to supervise employees.
ERC President Professor Maria Leptin said: “It is part of our mission to give early-career talent the independence to pursue ambitious ...
Dr. Niels Schröter wins ERC Starting Grant
2023-09-05
This is the first ERC Starting Grant to be hosted at the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics. ChiralTopMat aims to provide the direct experimental observation of chiral spin-hedgehogs in structurally chiral crystals and to explore ways to control their properties for applications in magnetic memory devices. Moreover, another focus will be to test the stability of topological Berry curvature monopoles against strong electronic interactions that Schröter’s group recently discovered in a chiral topological semimetal, a material that combines structural ...
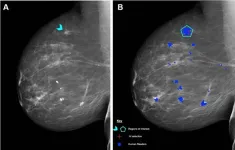
AI performs comparably to human readers of mammograms
2023-09-05
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using a standardized assessment, researchers in the UK compared the performance of a commercially available artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm with human readers of screening mammograms. Results of their findings were published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Mammographic screening does not detect every breast cancer. False-positive interpretations can result in women without cancer undergoing unnecessary imaging and biopsy. To improve the sensitivity and specificity of ...
Perspective: Building megaprojects on time and under-budget
2023-09-05
A Perspective sheds light on why megaprojects take so long and cost so much—and what can be done to prevent the problem. Why did Boston’s “Big Dig” building project go 19 billion dollars over budget and take 9 years longer than anticipated? Globally, between $6 trillion and $9 trillion is spent on megaprojects every year, including everything from space telescopes to wind farms. In the United States, the recently passed $1 trillion infrastructure bill means a new era of megaprojects is at hand. In a Perspective, Guru Madhavan and colleagues review the causes behind ballooning costs and extended timelines for such megaprojects. Problems include premature ...
Can an artificial nose detect food spoilage?
2023-09-05
Researchers have developed an energy-efficient computing-based chip with smell-sensing units that can detect food spoilage and provides real-time conditions continuously throughout the spoilage process. The system is described in a study published in Advanced Science.
Other electronic noses, or artificial olfactory systems (AOSs), have been developed in the past, but they have numerous limitations, including high energy consumption, time delays, and data loss.
The AOS developed in this study requires little energy and integrates sensing and computing units on the same chip. It detects food spoilage by employing thin zinc oxide ...
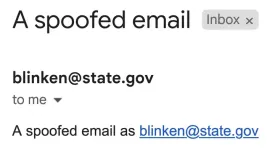
Scammers can abuse security flaws in email forwarding to impersonate high-profile domains
2023-09-05
Sending an email with a forged address is easier than previously thought, due to flaws in the process that allows email forwarding, according to a research team led by computer scientists at the University of California San Diego.
The issues researchers uncovered have a broad impact, affecting the integrity of email sent from tens of thousands of domains, including those representing organizations in the U.S. government–such as the majority of U.S. cabinet email domains, including state.gov, ...
Experts propose new global definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome
2023-09-05
Sept. 5, 2023 – In a new report posted online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, a global consensus conference of 32 critical care experts with broad international representation and from diverse backgrounds has proposed a new definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In addition to the experts, critical care societies from around the world provided input, once they received feedback from their members. The report, which builds on the 2012 Berlin Definition of ARDS, will be published Jan. 1, 2024 in the American Thoracic Society’s AJRCCM.
ARDS is a life-threatening illness in which the lungs ...
[1] ... [1710]
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
[1716]
[1717]
1718
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
[1725]
[1726]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.