Air pollution has decreased across the US, but new Yale research finds health burdens remain unequal among racial groups
2023-09-01
New Haven, Conn. — Health benefits that have resulted from reductions in fine particulate air pollution aren’t distributed equally among populations in the U.S., a new Yale-led study finds. Racial and ethnic minorities — and Black people in particular — still experience disproportionately high rates of cardiovascular disease-related deaths caused by exposure to fine particulate matter, according to the research.
The findings were published Aug. 31 in Nature Human Behavior.
Fine particulate matter, also known as PM2.5, consists of particles or droplets smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, or ...
Precarious employment conditions can increase risk of early death
2023-09-01
People without a secure job contract can reduce their risk of premature death by 20 per cent if they gain permanent employment, a study from Karolinska Institutet published in The Journal of Epidemiology and Community reports. According to the researchers, the results indicate that job security on the Swedish labour market needs to improve.
Precarious employment is a term that is used to describe jobs with short contracts (e.g. temping), low wages and a lack of influence and rights, all of which lead to a working life without predictability and security.
In the present study, the researchers have examined how this affects the risk of death.
“This is ...
Alaska scientists heading to Greenland for glacier research, museum project
2023-09-01
University of Alaska Fairbanks scientists will make several trips to Greenland over two years to study how meltwater and the ocean affect glacial ice loss.
The four-year research project, funded by a $565,000 National Science Foundation grant, will create a traveling museum exhibit about the drivers of Arctic climate change. The exhibit will appear first at the University of Alaska Museum of the North, likely in 2026.
Ice loss from the polar ice sheets is the largest anticipated contributor to global mean-sea-level rise in the coming century. Scientists need to better understand glacier behavior to improve predictions of sea-level rise.
At the study’s conclusion, ...
Native American patients were sicker and more likely to die during the COVID-19 pandemic, UNM researchers find
2023-09-01
When the COVID-19 pandemic swept into New Mexico in the spring of 2020, seriously ill patients from all over the state were brought to The University of New Mexico Hospital in Albuquerque, where many wound up in intensive care, breathing with the help of ventilators.
Early on, researchers from the UNM Center for Global Health launched a study of hospitalized patients to gauge the severity of symptoms from the infection, gathering data on 475 patients from April 2020 through December 2021.
In paper published this week in PNAS Nexus, ...
New research explains “Atlantification” of the Arctic Ocean
2023-09-01
New research by an international team of scientists explains what’s behind a stalled trend in Arctic Ocean sea ice loss since 2007. The findings indicate that stronger declines in sea ice will occur when an atmospheric feature known as the Arctic dipole reverses itself in its recurring cycle.
The many environmental responses to the Arctic dipole are described in a paper published online today in the journal Science. This analysis helps explain how North Atlantic water influences Arctic Ocean climate. Scientists call it Atlantification.
The research is led by professor Igor Polyakov of the University of Alaska Fairbanks College of ...
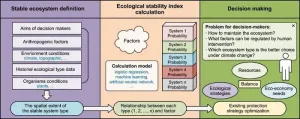
Landscape-based methodology reveals ecological stability in the Qingzang plateau
2023-09-01
In a groundbreaking study published in Volume 17 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a landscape-oriented framework to assess ecological stability in China's Qingzang Plateau (QP). The QP demonstrated a medium-high stability level with minimal changes in recent years. Ecological stability involves understanding changes in ecosystem components over time, with two major concepts explored: systems close to equilibrium and non-equilibrium behavior. Despite lacking a consensus on the definition of "ecological stability", stability indices ...
Research explores why daughters in Chinese families of son preference fail to break from sustained exploitation
2023-09-01
New research from Lancaster University Management School (LUMS) unveils the extent of sustained exploitation within many Chinese families that have a clear preference for sons over daughters – and why daughters can stay ‘trapped’ in this situation throughout their lives.
The new study explores Chinese families that have a strong preference for sons, where daughters are expected to make substantial financial or labour contributions to their parents before and after marriage– often to subsidise the schooling and living ...
Adding immune modulator to targeted therapy does not improve survival in difficult-to-treat thyroid cancer
2023-09-01
Results of a multicenter phase II clinical trial led by the University of Chicago Medicine Comprehensive Cancer Center show that adding an immunomodulatory agent to treatment with the targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) cediranib did not make a difference in outcomes for treating patients with an advanced form of thyroid cancer that develops from thyroid follicular cells called differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
The findings were published in Annals of Oncology on May 13, 2023.
Most patients with DTC receive successful treatment. But a small group develops cancer that recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, making it hard to treat with traditional methods like ...
Linking infectious and narcology care is effective in suppressing HIV in people who inject drugs in Russia
2023-09-01
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center found that providing pragmatic support, specifically rapid access to antiretroviral therapy, pharmacotherapy for opioid use disorder, and strengths-based case management, improved treatment outcomes for people with HIV who inject drugs in St. Petersburg, Russia. Published in The Lancet HIV, researchers from the Linking Infectious and Narcology Care – Part II (LINC-II) trial highlight that the odds of achieving viral load suppression at 12 months are 3 times higher for participants randomized to the intervention group.
Russia ...
Study could help explain why certain brain tumors don’t respond well to immunotherapy
2023-09-01
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center sheds new light on why tumors that have spread to the brain from other parts of the body respond to immunotherapy while glioblastoma, an aggressive cancer that originates in the brain, does not.
In people with tumors that originated in other parts of the body but spread to the brain, treatment with a type of immunotherapy called immune checkpoint blockade appears to elicit a significant increase in both active and exhausted T cells — signs that the T cells have been triggered to fight the cancer. The ...
Red blood cells exposed to oxygen deficiency protect against myocardial infarction
2023-09-01
Red blood cells exposed to oxygen deficiency protect against myocardial infarction, according to a new KI study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation. The study also shows that the protective effect is enhanced by a nitrate-rich vegetable diet.
Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all of the body’s cells and carbon dioxide back to the lungs. A new study, conducted at Karolinska Institutet in collaboration with Karolinska University Hospital, now shows that red blood cells have an intrinsic function of protecting against ...
UMC Utrecht investigates the link between RSV infection and chronic respiratory tract disease
2023-09-01
UMC Utrecht will lead an international consortium that will try to answer a key question that’s in the mind of many pediatricians, infectiologists, pulmonologists and other health professionals: “Why are children that had an RSV infection in early childhood at increased risk of developing asthma later in life?” The project - which will run for five years - is funded by a HORIZON HLTH 2023 grant from the European Commission of € 7 million.
Chronic respiratory tract diseases such as asthma and COPD ...
Study shows making cities greener doesn’t just capture carbon – it reduces it
2023-09-01
Dozens of European cities could reach net zero carbon emissions over the next 10 years by incorporating nature into their infrastructure, according to a new study.
Published recently in the journal, Nature Climate Change, the analysis shows the ways cities can orchestrate a wide range of green solutions like parks, streetscaping and roof gardens to not only capture carbon emissions, but help reduce them.
The study was undertaken by researchers from Sweden, the U.S. and China. It recommends the most effective approaches for natural carbon sequestration in 54 cities in the EU. And it shows how blending these steps with other climate ...
Researchers find Antarctic ice shelves thinner than previously thought
2023-09-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio – As global ice dams begin to weaken due to warming temperatures, a new study suggests that prior attempts to evaluate the mass of the huge floating ice shelves that line the Antarctic ice sheet may have overestimated their thickness.
The research, recently published in the Journal of Glaciology, is the first large-scale study of its kind to compare ice shelf thickness data from ice-penetrating radar measurements to thickness data estimated from contemporary surface elevation measurements.
By juxtaposing vast datasets of 20 of the 300 ...
Di-isononyl phthalate disrupts pregnancy in mice, study finds
2023-09-01
We are constantly exposed to phthalates in our environment through plastic products such as storage containers, medical devices, packages, fabrics, and toys. Specifically, di-isononyl phthalate is inevitably becoming a part of our lives. Unfortunately, the impact of DiNP on the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy is largely unknown. In a new study, researchers used mice to understand how DiNP affects pregnancy.
“Although we finally recognize that environmental chemicals impact women's health, most studies have focused on men’s reproductive health and very few studies have looked at how these chemicals affect women,” said Jodi Flaws (EIRH co-leader/MME), ...
Health System Program Improved Equity in Allocation of Scarce Medication
2023-09-01
A program designed to ensure fairness and that people living in the most disadvantaged U.S. neighborhoods would be offered a scarce, potentially life-saving medication proved feasible in a large health system. The approach can improve equity in receipt of the drug by people disproportionately affected by disease, according to a new analysis published today in JAMA Health Forum by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC scientist-clinicians.
However, the study revealed that more work needs to be done in building trust with and improving the ability to contact Black patients to ensure they ultimately receive scarce medications and other health care resources ...
Weighted lottery to equitably allocate scarce supply of COVID-19 monoclonal antibody
2023-09-01
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that a weighted lottery to allocate scarce resources is feasible and may result in more drug allocation to individuals who reside in disadvantaged neighborhoods and who identify as Black; however, Black individuals allocated the drug may be less likely to accept allocation and receive it.
Authors: Erin K. McCreary, Pharm.D., of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Telehealth vs in-clinic medication abortion services
2023-09-01
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that telehealth medication abortion services (tele-MAB) facilitates abortion care access for those further from brick-and mortar abortion facilities and, thus, may mitigate the impacts of travel logistics and costs. Additionally, tele-MAB may better meet the needs of those with prior abortion experience, perhaps due to greater familiarity with the abortion process.
Authors: Anna E. Fiastro, M.P.H., M.E.M., Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.31900)
Editor’s ...
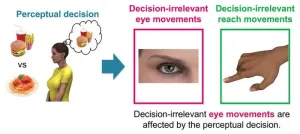
The eyes are a window into the deciding mind
2023-09-01
Researchers worldwide are seeking visible indicators of what is going on inside our minds as we think about issues and take decisions. They are searching for the ability to probe the invisible workings of the mind by monitoring subtle signals from the body. New insights from experiments at Tohoku University have revealed a link between eye movements and certain types of decision-making. Kazumichi Matsumiya and Shota Furukawa at the university's Graduate School of Information Sciences reported their findings in the journal Communications Biology.
"Our work has revealed that eye movements that are not ...
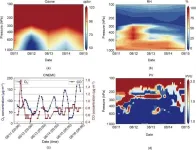
Three types of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation influence precipitation over the Yangtze river valley in various ways
2023-09-01
The Yangtze River Valley (YRV) is one of the most densely populated and economically developed regions in China. Summer precipitation over this region shows considerable intraseasonal variability with a period of 10–90 days, which can induce extreme precipitation events and lead to massive economic losses and human casualties.
The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO) is the intraseasonal variability active in the tropical Indian Ocean and western Pacific region. Over the last three decades, scientists have studied the influence of the BSISO, because it is an essential predictability source in extended-range forecasts.
A new study published in Atmospheric ...
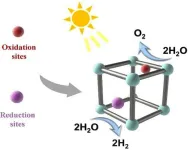
Roadmap drafted for research into metallic ‘sponges’ for clean hydrogen
2023-09-01
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) could deliver a major efficiency boost to the photocatalytic production of clean hydrogen. Chemical engineers have drafted a comprehensive overview of the state of their field and a plan for where it needs to focus.
Clean hydrogen production remains an energy-intensive and therefore costly proposition, inhibiting the battle against global warming. Metal organic frameworks—in effect tiny molecular ‘sponges’—look set to radically improve the efficiency of photocatalytic production of hydrogen due to their unique structural ...
Radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes receives $3.5 million from NIH
2023-09-01
The National Institutes of Health has provided $3.5 million for a large-scale clinical trial testing a radical new approach to managing type 2 diabetes that, in an earlier study, put almost 70% of participants in remission without weight loss or medication.
The approach was developed by UVA Health’s Daniel J. Cox, PhD. It is built on the notion that educating people about how to make wise dietary and exercise choices can allow them to control their blood sugar and possibly even alter the course of the disease.
“Instead of focusing on reducing weight with diets ...
Breakthrough in atmospheric analysis: Chinese satellite delivers high spatial resolution ozone profiles
2023-09-01
A breakthrough in satellite observations has allowed scientists to obtain high spatial resolution ozone profiles, enhancing our understanding of ozone distribution and its impact on the atmosphere. The research, conducted by the research team led by Cheng Liu and Fei Zhao at the University of Science and Technology of China, utilized data from the Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument (EMI) on the Gaofen-5 satellite, the first Chinese ultraviolet-visible hyperspectral spectrometer.
Ozone plays a crucial role in the atmosphere, and understanding its vertical distribution is key to comprehending its horizontal and vertical transport, as well as its physical and chemical ...
Flowering for naught: 120 years with nothing to show
2023-09-01
A long-lived monocarpic species of bamboo, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, only flowers once every 120 years before it dies. The upcoming flowering event for this species does not bode well for its continued long-term survival, as most flowers are not producing viable seeds.
Flowering for some plants is a yearly occurrence, for others, it is a once-in-a-lifetime event. A widespread species of bamboo in Japan, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, takes this one-time flowering event and pushes it to the extreme: they flower once every 120 years before dying to make way for the next ...
TTUHSC secures National Academy of Inventors membership
2023-09-01
Since its inception in 2009 with 13 founding institutions, the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has grown to more than 4,600 individual members worldwide from more than 300 U.S. and international colleges and universities, government agencies and non-profit research institutes. That growth continued recently when the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) added its name to the NAI membership roster.
Lance R. McMahon, Ph.D., TTUHSC senior vice president for research and innovation, said the university’s new NAI membership and the appointment of several faculty members as senior members ...
[1] ... [1709]
[1710]
[1711]
[1712]
[1713]
[1714]
[1715]
[1716]
1717
[1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
[1725]
... [8832]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.