Stanford Medicine-led study finds genetic factor fends off Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
2023-08-30
About one in every five people carries a version of a gene that, although largely unsung, appears to confer protection against both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues have learned. These lucky people may someday benefit all the more from a vaccine that could slow or stall the progression of these two most common neurodegenerative conditions.
An analysis of medical and genetic data from hundreds of thousands of people of diverse ancestries from several continents has revealed ...
First-time fathers seem to experience a steeper decline in relationship satisfaction in the first two years post-partum than second-time fathers
2023-08-30
First-time fathers seem to experience a steeper decline in relationship satisfaction in the first two years post-partum than second-time fathers, who appear to recover lost relationship satisfaction by the time their second child is 14 months old, according to a study published August 30, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Judith T. Mack and Lena Brunke from Technische Universität Dresden, Germany, and colleagues.
Having a strong primary relationship can help couples more successfully weather potentially-challenging transitions like the birth of a child. Most research on ...
Detailed analysis of two Late Bronze Age urn burials uncovers animal bones and jewelry amidst the cremated remains of a woman and child, and reveals insights into prehistoric funerary rites
2023-08-30
Detailed analysis of two Late Bronze Age urn burials uncovers animal bones and jewelry amidst the cremated remains of a woman and child, and reveals insights into prehistoric funerary rites
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0289140
Article Title: More than urns: A multi-method pipeline for analyzing cremation burials
Author Countries: Austria, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Belgium
Funding: This study was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) in the framework of the project ‘Unlocking the secrets ...
Antibody shows promise for preventing organ rejection after transplantation
2023-08-30
DURHAM, N.C. – A man-made antibody successfully prevented organ rejection when tested in primates that had undergone a kidney transplant, Duke Health researchers report.
The finding clears the way for the new monoclonal antibody to move forward in human clinical trials. Results of the study appear online Aug. 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“Current medications to prevent organ rejection are good overall, but they have a lot of side effects,” said lead author Imran J. Anwar, M.D., a surgical research fellow ...
New blood test detects a key indicator of Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-30
DURHAM, N.C. – Researchers have developed a blood test that detects Parkinson’s disease, potentially establishing a way to help diagnose the condition before nervous system damage worsens.
A new blood-based diagnostic test would be a major advancement for Parkinson’s disease, which afflicts 10 million people worldwide and is the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Led by a team of Duke Health neuroscientists, the study appears Aug. 30 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
“Currently, Parkinson’s disease is diagnosed largely based on clinical symptoms after significant neurological damage has ...
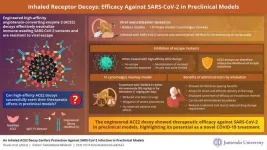
Inhaled receptor decoy therapy for COVID-19 in preclinical models
2023-08-30
The surface protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), known as the spike protein, is critical for infecting host cells. The spike protein facilitates the infection process by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors on the surface of airway epithelial cells, initiating the virus entry into the cells. By engineering an ACE2 receptor to increase the affinity to the spike protein, researchers demonstrated a novel method to neutralize the virus effectively. The engineered ACE2 (3N39v4-Fc) acts as a decoy by binding to the viral spike protein, thus preventing the binding of viruses to the ACE2 receptor on the cell surface. ...
Pedal power pays off: Mountain biking benefits outweigh risks
2023-08-30
New Curtin research into injuries sustained by trail users has found mountain biking is not the dangerous, injury-plagued sport reserved for thrill-seekers that it is often perceived to be and that the health benefits outweigh the risks.
Researchers analysed data from dozens of studies across the world, including Australia, encompassing 220,935 injured mountain bikers and 17,757 injured hikers. The study aimed to pinpoint the injury types and affected body areas in order to gain insights into the medical treatment of such cases.
Lead author PhD candidate Paul Braybrook, from Curtin’s School of Nursing, said mountain bikers were primarily injured on their upper limbs, ...
Bat study reveals how the brain is wired for collective behavior
2023-08-30
The same neurons that help bats navigate through space may also help them navigate collective social environments, finds a new study published today in the journal Nature.
Many mammals — including bats and humans — are believed to navigate with the help of a brain structure called the hippocampus, which encodes a mental “map” of familiar surroundings. For example, as you walk around your neighborhood or commute to work, individual “place” neurons in the hippocampus fire to indicate where you are.
In the new study, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, used wireless neural ...
IHT Group to manufacture, sell hog-cooling technology developed at Purdue
2023-08-30
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. and WINNIPEG, Manitoba – IHT Group, a division of Decisive Dividend Corp. (TSXV: DE) based in Winnipeg, Manitoba, is bringing patented cooling pad technology for hogs to the North American market in spring 2024.
The pads are 2-foot-by-4-foot aluminum tread plates on top of copper pipes that circulate water. Sensors in the pads determine if the hog is too hot and circulate new water to keep the pad cool. The technology was designed by researchers in Purdue University’s Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering and Department of Animal Sciences.
Heat harms hogs
Record heat across North America ...
T-cells infiltrate brain, cause respiratory distress in condition affecting the immunocompromised
2023-08-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When an immunocompromised person’s system begins to recover and produce more white blood cells, it’s usually a good thing – unless they develop a potentially deadly inflammatory condition. New research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has found that the pulmonary distress often associated with the condition is caused not by damage to the lungs, but by newly populated T-cells infiltrating the brain.
Knowing this mechanism of action can help researchers and ...
The International Society of Microbiota will host a symposium dedicated to clinicians on probiotics and microbiota supplements applications in diseases
2023-08-30
Venice, Italy – The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) is pleased to announce the upcoming symposium on probiotics and microbiota supplements. The symposium will take place on October 17, 2023, in Venice, Italy, one day prior to the 10th World Congress on Targeting Microbiota 2023.
About ISM 2023 Symposium:
The symposium will focus on the strain specificity of probiotics and microbiota supplements and their clinical applications for disease management. It will also elaborate on the use and mode of action of postbiotics and metabolites like the SCFA butyrate.
Speakers will present the latest research on the use of probiotics to treat a variety ...
American Meteorological Society announces 2024 weather, water, and climate honorees
2023-08-30
[Boston, MA, USA—August 30, 2023] Each year, the American Meteorological Society recognizes outstanding individuals and organizations in the weather, water, and climate community through its Awards and Honors program. The organization is proud to announce its 2024 recipients, who will receive their award or honor at the 104th AMS Annual Meeting in Baltimore, Maryland, 28 January–1 February, 2024.
“Working across a wide range of sciences and services, the members of our community are vital to upholding safety and quality of life in the United States and across ...
Do driverless cars feel safe? New study shows gradual introduction needed to build comfort among all road users
2023-08-30
While self-driving vehicles (SDVs) are being hailed as a solution for safer, more efficient roads, new research suggests British Columbians are not quite ready to embrace self-driving cars wholeheartedly – and will need a period of gradual transition before adoption.
The study, conducted by the Research on Active Transportation Lab (REACT) at the University of British Columbia, reveals mixed perceptions of automated vehicles, particularly their effects on pedestrian comfort and safety.
Do self-driving cars feel safe?
Four out of 10 participants (41 per cent) thought that pedestrians faced reduced safety and comfort levels ...
MD Anderson research highlights for August 30, 2023
2023-08-30
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a novel computational tool to detect single base pair DNA changes in single-cell sequencing data, a potential target to treat hypertension caused by drugs commonly used in organ transplants, further insights into the steps involved in ...
Study finds high blood and urinary metal levels among exclusive marijuana users
2023-08-30
Research conducted at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health detected significant levels of metals in the blood and urine among marijuana users, concluding that marijuana may be an important and under-recognized source of lead and cadmium exposure. This is among the first studies to report biomarker metal levels among marijuana users and most likely the largest study to date, that links self-reported marijuana use to internal measures of metal exposure, rather than just ...
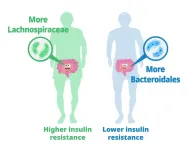
Bacteria treatment reduces insulin resistance, protects against diabetes
2023-08-30
Researchers led by Hiroshi Ohno at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) in Japan have discovered a type of gut bacteria that might help improve insulin resistance, and thus protect against the development of obesity and type-2 diabetes. The study, published August 30 in the scientific journal Nature, involved genetic and metabolic analysis of human fecal microbiomes and then corroborating experiments in obese mice.
Insulin is a hormone released by the pancreas in response to blood sugar. Normally, it helps get the sugar ...
Researchers identify stem cells in the thymus for the first time
2023-08-30
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 30 August 2023
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Cells
Researchers identify stem cells in the thymus for the first time
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified stem cells in the human thymus for the first time. These cells represent a potential new target to understand immune diseases and cancer and how to boost the immune system.
The thymus is a gland located in the front part of the chest, the place where thymocytes (the cells in the thymus) mature into T ...
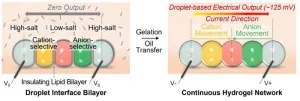
New ‘droplet battery’ could pave the way for miniature bio-integrated devices
2023-08-30
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 16:00 BST / 11:00 ET WEDNESDAY 30 AUGUST 2023
Researchers have developed a miniature battery that could be used to power tiny devices integrated into human tissues.
The design uses an ionic gradient across a chain of droplets – inspired by how electric eels generate electricity.
The device was able to regulate the biological activity of human neurons.
This could open the way to the development of tiny bio-integrated devices, with a range of applications in biology and medicine.
University of Oxford researchers have made a significant step towards realising miniature ...
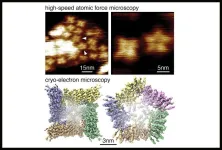
Study finds how some ion channels form structures permitting drug delivery
2023-08-30
A member of an important class of ion channel proteins can transiently rearrange itself into a larger structure with dramatically altered properties, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The discovery is a significant advance in cell biology, likely solves a long-standing mystery about an unusual feature of some ion channels and has implications for the development of drugs targeting these proteins and for drug delivery.
Ion channels are ubiquitous in the cell membranes of higher organisms. ...
Discoveries on memory mechanisms could unlock new therapies for Alzheimer’s and other brain diseases
2023-08-30
AURORA, Colo. (Aug. 30, 2023) – Scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have made a `paradigm shifting’ discovery on the mechanisms required for learning and memory that could lead to new therapies for Alzheimer’s disease and potentially Down syndrome.
The study was published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
For over 30 years, researchers believed that LTP or long-term potentiation, which is crucial for learning and memory, required enzymatic actions by an enzyme known as CaMKII.
But a team of researchers led by Ulli ...
Newly engineered versions of bacterial enzyme reveal how antibiotics could be more potent
2023-08-30
Modern medicine depends on antibiotics to treat infections by disabling targets inside bacterial cells. Once inside these cells, antibiotics bind to certain sites on specific enzyme targets to stop bacterial growth. Randomly occurring changes (mutations) in the genes for these targets occur naturally, in some cases making the target harder for the antibiotic to attach to, and that bacterial version resistant to treatment.
For this reason, the more antibiotics have been used over time, the greater the chances that bacterial populations will evolve to have mutants resistant to existing antibiotics, and the more urgent the call for new approaches ...
World’s coastal wetlands and coral reef islands are hanging by a thread, new study shows
2023-08-30
Coastal wetlands and coral reef islands will struggle to grow fast enough to keep pace with rising sea levels driven by climate change, according to a new study published in Nature. The study was conducted by an international team that includes a Tulane University researcher. The findings show that the future of marshes and other low-lying coastal areas depend heavily on whether global warming can be limited to less than 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) as formulated by the Paris Agreement.
A key finding of the paper is that coastal marshes, mangroves, ...
A simpler way to connect quantum computers
2023-08-30
Researchers have a new way to connect quantum devices over long distances, a necessary step toward allowing the technology to play a role in future communications systems.
While today’s classical data signals can get amplified across a city or an ocean, quantum signals cannot. They must be repeated in intervals — that is, stopped, copied and passed on by specialized machines called quantum repeaters. Many experts believe these quantum repeaters will play a key role in future communication networks, allowing enhanced security and enabling connections between remote quantum computers.
The Princeton study, published Aug. ...
Parental incarceration increases cardiovascular risk in young adults
2023-08-30
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of racial disparities in mortality between Black and white people in the United States. New research from the University of Chicago Medicine suggests that parental incarceration may be contributing to these health gaps.
According to the new study, people who experienced a parent or parental figure’s incarceration anytime before the age of 18 had higher levels of hypertension and coronary disease biomarkers than people whose parents were not incarcerated. These results indicate that mass incarceration may have transgenerational health consequences.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are difficult ...
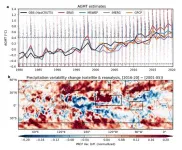
Unveiling global warming’s impact on daily precipitation with deep learning
2023-08-30
A collaborative international research team led by Professor Yoo-Geun Ham from Chonnam National University and Professor Seung-Ki Min from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has made a discovery on the impact of global warming on global daily precipitation. Using a deep learning approach, they have unveiled a significant change in the characteristics of global daily precipitation for the first time. Their research findings were published on August 30 in the online version of Nature, the ...
[1] ... [1718]
[1719]
[1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
[1725]
1726
[1727]
[1728]
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
[1734]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.