Ye receives National Science Foundation CAREER Award
2023-08-21
Jinwei Ye, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "CAREER: Towards Polarimetric Visual Understanding."
In this project, Ye will study how the way surfaces reflect polarized light can be used to help recognize objects more effectively.
Ye will address the following two questions: (1) How does the polarization of light change after interacting with various types of surfaces? (2) What can polarized light tell us about the kinds of objects that it has interacted with?
Addressing these questions can lead to significant improvements in machine vision systems by strengthening their capability to do geometric ...
Intermittent fasting improves Alzheimer’s pathology
2023-08-21
One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is disruption to the body’s circadian rhythm, the internal biological clock that regulates many of our physiological processes. Nearly 80% of people with Alzheimer’s experience these issues, including difficulty sleeping and worsening cognitive function at night. However, there are no existing treatments for Alzheimer’s that target this aspect of the disease.
A new study from researchers at University of California San Diego School ...
New “bandit” algorithm uses light for better bets
2023-08-21
How does a gambler maximize winnings from a row of slot machines? This is the inspiration for the "multi-armed bandit problem," a common task in reinforcement learning in which "agents" make choices to earn rewards. Recently, an international research team led by Hiroaki Shinkawa at the University of Tokyo developed an extended photonic reinforcement learning scheme that moves from the static bandit problem towards a more challenging dynamic environment. This study was published July 25 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The success of ...
For men with erectile dysfunction, penile implants are usually covered by insurance – but not always
2023-08-21
August 21, 2022 – Implantable penile prostheses (IPPs) are an established treatment option for erectile dysfunction (ED), and are covered by insurance in about 80% of cases, reports a paper in the September issue of Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
However, some employer-sponsored insurance plans specifically exclude this guideline-recommended treatment option for ED, according to the new research by Dr. Mohit Khera, MD, MBA, MPH, of Baylor College ...
Adversities permanently change our brains
2023-08-21
Neuroscientists at Radboudumc show that adversities permanently change the functioning of the brain. Furthermore, an aberrant reaction of the brain to adversities is related to anxiety symptoms. This may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Your brain is shaped by the things you experience. That sounds logical, but can you really measure that? And what can you do with it? Neuroscientists at Radboud university medical center investigated the influence of adversities in life on patterns in the brain. They found remarkable associations that may have predictive value for the development of psychiatric disorders.
Special ...
MSU hires Judd Herzer for new mobility director role
2023-08-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Michigan State University today named Judd Herzer as the director of MSU Mobility to help amplify and focus the university’s vast research activities in the smart-vehicle landscape. Satish Udpa, University Distinguished Professor in the College of Engineering at MSU and co-founder of MSU Mobility, has been fulfilling the duties of this newly created role in an interim capacity while the university looked for the ideal candidate.
Mobility is among MSU’s principal areas of research and innovation, and MSU Mobility and its ...
Antil receives funding for workshop on digital twins
2023-08-21
Harbir Antil, Director, Center for Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, and Professor, Mathematical Sciences, received funding for: "Mathematics for Digital Twins (MATH-DT)."
This award will provide support for a workshop titled "Mathematical Opportunities in Digital Twins" to be held on Dec. 11-13, 2023, at George Mason University's campus in Arlington, VA.
The workshop will bring together key experts working in many aspects of mathematics, key application fields, and industry with the goal of determining ...
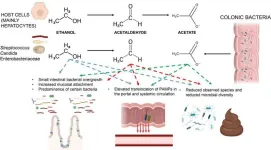
Understanding mechanisms of alcohol-associated bowel disease
2023-08-21
Alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for gastrointestinal diseases, including cancer. Alcohol can damage the gastrointestinal tract in several ways. It can promote an impairment of several intestinal barrier functions, leading to leaky gut and dysbiosis. Ethanol metabolism can also produce toxic substances such as acetaldehyde and acetate, further damaging the gut and potentially promoting cancer. Ethanol and its metabolites enhance DNA damage response and dysregulate the epithelial proliferation/differentiation program, thereby increasing the risk of cancer development.
In a new paper published in eGastroenterology, ...
SARS-CoV-2: The grasping fingers of the viral N protein
2023-08-21
#FRANKFURT. Immediately after the infection of a cell in the throat or lungs, the SARS-CoV-2 virus works very hard to replicate, using the human cell’s metabolic pathways to produce its proteins and make sure that its genetic material (the RNA genome) is copied. The RNA genome is then packaged very compactly into new virus particles that are released from the cell to infect more cells.
One viral protein, called the nucleocapsid protein (N), is particularly important for rapid and efficient replication. ...
Climate win-win: study quantifies benefits of enhanced weathering
2023-08-21
Applying ground-up silicate rock to Midwestern farm fields can capture significant amounts of carbon dioxide and prevent it from accumulating in the atmosphere, according to a new study that successfully quantified those climate benefits for the first time.
Working with Eion Corp., researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the Leverhulme Centre for Climate Change Mitigation (LC3M) developed a new method to calculate the CO2-reduction potential of basalt rock amendments applied to cropland soil, a process known as enhanced weathering.
Traditional row-crop agriculture releases sizable amounts of soil-derived carbon to the atmosphere as CO2, a greenhouse gas ...
Late mortality after COVID-19 infection in veterans vs risk-matched comparators
2023-08-21
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that COVID-19 was not associated with any clinically significant excess mortality among those who survived at least 180 days compared with closely risk-matched comparators, despite having worse 2-year total mortality. This finding has individual level and health system planning implications and should be reassuring to persons who have survived COVID-19 for at least 180 days.
Authors: Theodore J. Iwashyna, M.D., Ph.D., of the Ann Arbor VA in Ann Arbor, Michigan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Screen time at age 1 and communication, problem-solving developmental delay at ages 2 and 4
2023-08-21
About The Study: In this study including 7,097 mother-child pairs, greater screen time for children at age 1 was associated with developmental delays in communication and problem-solving at ages 2 and 4. These findings suggest that domains of developmental delay should be considered separately in future discussions on screen time and child development.
Authors: Taku Obara, Ph.D., of Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
International pediatric COVID-19 severity over the course of the pandemic
2023-08-21
About The Study: This study including 31,000 hospitalized children with SARS-CoV-2 infection suggested that while intensive care unit admission decreased over the course of the pandemic in all age groups, ventilatory and oxygen support did not decrease over time in children younger than age 5. These findings highlight the importance of considering different pediatric age groups when assessing disease severity in COVID-19.
Authors: Kirsty Short, Ph.D., of the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.3117)
Editor’s ...
Websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone Tests
2023-08-21
About The Study: In this study including content analysis of 27 websites across multiple countries, most websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) tests included false and misleading claims which might lead consumers to purchase an AMH test in the belief that it can reliably predict fertility potential and age of menopause. Depending on the test result, this may in turn lead to misplaced anxiety or reassurance about one’s fertility and modifications to subsequent conception or contraceptive plans and behavior.
Authors: Tessa Copp, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the ...
Artificial intelligence beyond the clinic
2023-08-21
With the advent of ChatGPT4, the use of artificial intelligence in medicine has absorbed the public’s attention, dominated news headlines, and sparked vigorous debates about the promise and peril of medical AI.
But the potential of AI reaches far beyond the frontlines of medicine.
AI is already changing the way scientists discover and design drugs. It is predicting how molecules interact and proteins fold with never-before-seen speed and accuracy. One day, AI may even be used routinely to safeguard the function of nuclear reactors.
These are but a few of the exciting applications of AI in the natural sciences, ...
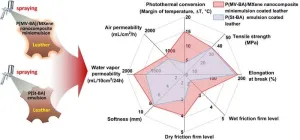
Bio-based waterborne poly(vanillin-butyl acrylate)/mxene coatings for leather with desired warmth retention and antibacterial properties
2023-08-21
A study published in the journal of Engineering reveals a remarkable development in the field of green coating materials for leather. Researchers have successfully synthesized a solvent-free, bio-based antibacterial agent and aromatic monomer called methacrylated vanillin (MV). This innovative compound not only imparts antibacterial properties to leather coatings but also serves as an eco-friendly alternative to the petroleum-based carcinogen styrene (St).
In this research article, titled "Bio-based ...
Genetic study shows that common medication used to prevent heart attacks may be ineffective for majority of British South Asians
2023-08-21
Clopidogrel is a commonly prescribed medication used to prevent further heart attacks after an initial event. It needs to be activated in the body to be effective. Studies of European populations show that 30% of individuals have genetic variants that reduce or prevent activation through the production of an enzyme called CYP2C19. People of South Asian ancestry have high rates of cardiovascular disease, but previous studies have not looked for these variants in UK South Asian populations or linked these variants with risk of recurrent heart attacks if prescribed clopidogrel in South Asian ancestry ...
Tracking species range shifts in a changing climate
2023-08-21
As our planet undergoes significant transformations due to climate change, habitats are being altered, appearing, disappearing, or changing in quality. Understanding the impact of these changes on the geographic distributions of species is of great significance. The shrinking ranges of protected organisms and the expanding ranges of noxious species, such as pests and pathogens, highlight the urgent need to monitor range movements precisely. However, this task poses challenges as the available observation time is often short compared to the pace of underlying population processes, making it difficult to distinguish between directional shifts and random fluctuations.
Addressing ...
Formerly depressed patients continue to focus on negative
2023-08-21
People who have recovered from a major depressive episode, when compared with individuals who have never experienced one, tend to spend more time processing negative information and less time processing positive information, putting them at risk for a relapse, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our findings suggest that people who have a history of depression spend more time processing negative information, such as sad faces, than positive information, such as happy faces, and that this difference is greater compared to healthy people with no history,” said lead author Alainna Wen, PhD, ...
Natural language processing to extract social risk factors influencing health
2023-08-21
INDIANAPOLIS – Social risk factors such as financial instability and housing insecurity are increasingly recognized as influencing health. But unlike diagnosis codes, prescription information, lab or other test reports, social risk factors do not adhere to standardized, controlled terminology in a patient’s electronic medical record, making this information difficult to extract from the clinical notes where they typically are found.
A new study has found that a natural language processing (NLP) system developed by Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health informaticians showed excellent performance when ported ...
To close the gap at the top, start with the bottom
2023-08-21
Ames, IA — Twenty years ago, the National Football League adopted the Rooney Rule. It attempted to address racial disparity in top positions by requiring teams to interview at least one person of color for every head coach opening.
But newly published research suggests the gap will persist unless it’s closed at the bottom. The NFL has a hierarchal labor pool, explains Andreas Schwab, co-author and associate professor of entrepreneurship at Iowa State University. Under the head coach are two coordinators who oversee defense and offense. These coordinators supervise position-specific coaches who may have their own assistant coaches.
“To become ...
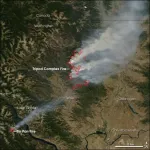
REBURN: A new tool to model wildfires in the Pacific Northwest and beyond
2023-08-21
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For Immediate Release
August 21, 2023
In 2006, the Tripod Complex Fire burned more than 175,000 acres in north-central Washington. The fire, which was within the Okanogan-Wenatchee National Forest, was more than three times the size of Seattle. Yet while considered severe at the time, even larger wildfires in 2014, 2015 and 2021 have since dwarfed Tripod.
Past research shows that large and severe wildfires like these were much rarer in the western U.S. and Canada prior to the late ...
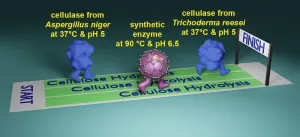
Chemists build synthetic catalysts to break down biomass like super enzymes
2023-08-21
AMES, Iowa – Yan Zhao gestured toward the trees outside his campus window on a rainy afternoon.
The professor of chemistry at Iowa State University is developing new synthetic catalysts to break down cellulose, the plant fibers that make those trees tall and strong.
“Cellulose is built to last – a tree doesn’t just disappear after rain,” Zhao said. “Cellulose is a huge challenge to break down.”
Zhao thinks he has an idea and a technology that can get the job done, making plant biomass a practical source of sugars that can be converted to many applications, including ...
Understanding the neurological mechanisms behind Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-21
Nearly one million people in the United States are living with Parkinson’s disease, making it the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Current medical treatments for Parkinson’s are focused on helping people manage symptoms. But the underlying mechanisms of the neurological disorder remain poorly understood.
Tamily Weissman, associate professor of biology and department chair, is working to change that. Parkinson’s symptoms occur because of a drop in dopamine levels when ...
Space travel depletes red blood cells and bone, but bone marrow fat may come to the rescue
2023-08-21
A study of 14 astronauts suggests that while space travel depletes red blood cells and bone, the body can eventually replenish them back on Earth with the help of fat stored in the bone marrow. The study, published in Nature Communications, has important implications for health in space and on Earth.
“We found that astronauts had significantly less fat in their bone marrow about a month after returning to Earth,” said senior study author Dr. Guy Trudel, a rehabilitation physician and researcher at The Ottawa Hospital and professor at the University of Ottawa. ...
[1] ... [1726]
[1727]
[1728]
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
1734
[1735]
[1736]
[1737]
[1738]
[1739]
[1740]
[1741]
[1742]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.