Are you breaking your body clock?
2023-08-17
Researchers are using mathematical models to better understand the effects of disruptions like daylight savings time, working night shifts, jet lag or even late-night phone scrolling on the body’s circadian rhythms.
The University of Waterloo and the University of Oxford researchers have developed a new model to help scientists better understand the resilience of the brain’s master clock: the cluster of neurons in the brain that coordinates the body’s other internal rhythms. They also hope to suggest ...
HKUMed & CityU researchers jointly generate human neural stem cells with powerful therapeutic potential for the treatment of spinal cord injury, paving the way for new therapeutic opportunities
2023-08-17
A joint research team from LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed) and City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has generated human neural stem cells with powerful therapeutic potential for the treatment of spinal cord injury that paves the way for new therapeutic opportunities. The new findings are now published in the leading multidisciplinary science journal, Advanced Science [link to publication].
Background
Traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) commonly caused by a car accident, fall, or sport-related accident results in the progressive loss of neurons involved in motor and sensory functions at and around ...
Nauseous territory: outfoxing predators using baits that make them barf
2023-08-17
Introduced foxes, dogs, cats, rats, and other predators kill millions of native animals every year, but what if they were conditioned to associate this prey with food that made them ill?
A team of international researchers have shown the potential to do just that, burying baits containing capsules of levamisole, a chemical that induces nausea and vomiting when consumed by predators.
In a world first experiment conducted in south-eastern Australia, where introduced red foxes are responsible for countless wildlife deaths, the Australian National University (ANU) and University of South Australia scientists laid baits of fried deboned chicken, with some containing ...
Accelerating discovery in artificial intelligence for science
2023-08-17
What if artificial intelligence (AI) could be used to spur discovery in areas such as biotechnology, drug discovery and fluid dynamics? Using geometric graphs and innovative methodologies, AI can solve fundamental problems in basic natural science. The possibilities are endless in this relatively new field known as AI for science.
Dr. Shuiwang Ji, a professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Texas A&M University, recently received a National Science Foundation grant to ...
Sylvester Surgeon-scientist awarded center’s first Department of Defense grant to study pancreatic cancer
2023-08-17
MIAMI, FLORIDA (Aug. 17, 2023) – Researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have been awarded a grant from the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD)’s Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program to target chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer.
The $800,000, three-year grant is the first DoD award to Sylvester to study pancreatic cancer, a disease characterized by extreme resistance to chemotherapy and other treatments and dismal survival rates.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is the most common and aggressive ...
Novel treatment based on gene editing safely and effectively removes HIV-like virus from genomes of non-human primates
2023-08-17
(Philadelphia, PA) – A single injection of a novel CRISPR gene-editing treatment safely and efficiently removes SIV – a virus related to the AIDS-causing agent HIV – from the genomes of non-human primates, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University now report. The groundbreaking work complements previous experiments as the basis for the first-ever clinical trial of an HIV gene-editing technology in human patients, which was authorized by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022.
The preclinical study, published online ...
Urban great tits have paler plumage than their forest-living relatives
2023-08-17
As urban areas expand, animals increasingly find themselves living in towns and cities. While some animals may benefit from milder temperatures and fewer natural predators in urban settings, they also have to cope with pollutants and changes in their diet. Previous research has shown that animals in cities are “duller” in terms of yellow-orange-red colour tones compared to their non-urban counterparts. However, previous studies have only focused on single geographic locations.
“We used feather samples collected from great tits in cities and forests across Europe. Different methods all confirmed that urban great tits ...
Our plastic waste can be used as raw material for detergents, thanks to an improved catalytic method
2023-08-17
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — We’ve managed to accumulate so much plastic trash that it’s daunting to think about what could be done with the tons upon tons of nonbiodegradable waste. And as much as we are trying to scale back our dependence on single-use plastics, we continue to add to the global plastic trash hoard. Events like the COVID-19 pandemic only served to expand their use for personal protective equipment and disposable and take-away packaging.
But, for researchers at UC Santa Barbara, one person’s single-use packaging ...
Why killer bacteria affect some people more severely
2023-08-17
Group A streptococci are fairly common bacteria that can cause, among other things, strep throat or impetigo. However, if the bacteria become invasive, the situation can become very dangerous. In this case, the name sometimes changes to murder bacteria or flesh-eating bacteria and can give rise to life-threatening conditions such as blood poisoning and septic shock, or soft tissue infections that may make an amputation necessary.
Invasive streptococcal infections have increased in recent decades. The reason for this is not fully understood.
The outcome of infections can ...
Risk of cancer death after exposure to low-dose ionising radiation underestimated
2023-08-17
Prolonged exposure to low-dose ionising radiation is associated with a higher risk of death from cancer than previously thought, suggests research tracking the deaths of workers in the nuclear industry, published in The BMJ today.
The findings should inform current rules on workplace protection from low-dose radiation, say the researchers.
To date, estimates of the effects of radiation on the risk of dying from cancer have been based primarily on studies of survivors of atomic bombs dropped on Japan at the ...
Smartphone app may support drinkers who overindulge to drink less heavily
2023-08-17
Access to a smartphone alcohol intervention app helped university students to cut down their overall alcohol consumption and the number of days they drank heavily, suggests a study published in The BMJ today.
Unhealthy drinking is the biggest risk factor to health for 15 to 49-year olds, and unhealthy use of alcohol is especially prevalent among adult students, prompting the authors to design a smartphone app to encourage healthier drinking among this group.
The authors tested the app in 1770 university students who had screened positive for ...
THE LANCET: Levonorgestrel emergency contraceptive pill is more effective when taken with an anti-inflammatory medication, study suggests
2023-08-17
*Please see end of press release for a link to the embargoed content*
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
A randomised controlled trial of 860 women requesting emergency contraception found 95% of pregnancies were prevented following combined treatment with levonorgestrel and the anti-inflammatory medication piroxicam, compared to 63% of pregnancies being prevented when levonorgestrel was taken alone.
This is the first randomised trial where piroxicam has been studied for its contraceptive action in humans.
The authors say, if these results can be reproduced in future studies, co-treatment with piroxicam and levonorgestrel ...
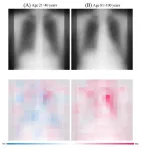
How old are you, really? AI can tell your true age by looking at your chest
2023-08-17
Osaka, Japan - What if “looking your age” refers not to your face, but to your chest? Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have developed an advanced artificial intelligence (AI) model that utilizes chest radiographs to accurately estimate a patient’s chronological age. More importantly, when there is a disparity, it can signal a correlation with chronic disease. These findings mark a leap in medical imaging, paving the way for improved early disease detection and intervention. The results are set to be published in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
The research team, led by graduate student ...
Global genomic collaboration provides diagnoses and informs care for infants with epilepsy
2023-08-17
Epilepsy in infants ranges in severity and can leave caregivers with questions about their child’s health. While genetic testing to help determine the cause of epilepsy is possible, comprehensive testing does not always happen routinely and it can take a long time, leaving families waiting for answers.
Published in The Lancet Neurology, this international study sequenced the genomes of 100 infants with unexplained seizures, along with their parents, from four countries (England, USA, Canada and Australia) to better understand the potential strengths of early, broad genome sequencing (a process ...
The BMJ’s editor-in-chief urges royal colleges to improve transparency on payments from industry and patient groups
2023-08-17
The BMJ’s editor in chief is urging the Academy of Medical Royal Colleges and its members to establish a standard for declaring payments they receive from industry and patient groups in the wake of a recent investigation by The BMJ into such payments.
The investigation, published by The BMJ in July,* found that royal colleges, responsible for doctors’ and some other healthcare professionals’ education and training, had received more than £9m in payments from drug and medical device companies since 2015 but that they didn’t always disclose these payments publicly in their annual reports.
In an open letter to the institutions ...
Fresh evidence of ChatGPT’s political bias revealed by comprehensive new study
2023-08-17
Fresh evidence of ChatGPT’s political bias revealed by comprehensive new study
The artificial intelligence platform ChatGPT shows a significant and systemic left-wing bias, according to a new study by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
The team of researchers in the UK and Brazil developed a rigorous new method to check for political bias.
Published today in the journal Public Choice, the findings show that ChatGPT’s responses favour the Democrats in the US, the Labour Party in the UK, and in Brazil President Lula da Silva of the Workers’ Party.
Concerns ...
The modern sea spider had started to diversify by the Jurassic, study finds
2023-08-17
An extremely rare collection of 160-million-year-old sea spider fossils from Southern France are closely related to living species, unlike older fossils of their kind.
These fossils are very important to understand the evolution of sea spiders. They show that the diversity of sea spiders that still exist today had already started to form by the Jurassic.
Lead author Dr Romain Sabroux from the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, said: “Sea spiders (Pycnogonida), are a group of marine animals that is overall very poorly studied.
“However, ...
MD Anderson receives nearly $4.9 million in CPRIT funding for cancer prevention programs and recruitment
2023-08-17
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center was awarded four grants totaling nearly $4.9 million from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) to support the expansion of physical activity programs for survivors, the dissemination of targeted tobacco cessation programs and the recruitment of a first-time, tenure-track faculty member.
MD Anderson’s Active Living After Cancer (ALAC) program received continued funding from CPRIT via two grants totaling $2,448,643 to ...
Real-time parking info now available through UTA Parking Finder app
2023-08-17
The University of Texas at Arlington has launched a new digital parking platform this fall that gives users real-time knowledge of available parking spaces, electric vehicle charging locations and garage/lot percentage occupancy.
The UTA Parking Finder is currently live and enables students, employees and visitors to make informed parking decisions in real time. Additional parking lot parking sensors will be added during the next three years until approximately 85% of all parking space on campus is covered.
The North Central Texas Council of Governments and Modii, a provider of modern mobility solutions, ...
Researchers unveil a new, economical approach for producing green hydrogen
2023-08-17
Researchers at the University of Colorado have developed a new and efficient way to produce green hydrogen or green syngas, a precursor to liquid fuels. The findings could open the door for more sustainable energy use in industries like transportation, steelmaking and ammonia production.
The new study, published Aug. 16 in the journal Joule, focuses on the production of hydrogen or syngas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide that can be converted into fuels like gasoline, diesel and kerosene. The CU Boulder team lays the groundwork for what could be the first commercially viable method ...
Brown-led research provides unprecedented look at what influences sea ice motion in the Arctic
2023-08-16
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study led by researchers at Brown offers fresh insights into the forces above and beneath the ocean surface that influence how sea ice moves and disperses in the Arctic Ocean, which is warming at over twice the rate of the global average.
The in-depth analysis reveals how local tidal currents strongly affect the movement of the ice along its journey and provides an unprecedented look at how the makeup of the seafloor is causing some of the most abrupt changes.
Data from the study can be applied to improve complex computer simulations used for forecasting Arctic sea ...
ORNL's Bryan Maldonado to receive 2023 HENAAC Most Promising Engineer Award
2023-08-16
Bryan Maldonado, a dynamic systems and controls researcher at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been recognized by the 2023 Hispanic Engineer National Achievements Awards Conference, or HENAAC, with the Most Promising Engineer Award.
Given by Great Minds in STEM, or GMiS, the award highlights engineers who have made significant contributions to raising science, technology, engineering and math education awareness in underserved communities. Maldonado will receive ...
Several vaccines associated with reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease in adults 65 and older
2023-08-16
Prior vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria, with or without pertussis (Tdap/Td); herpes zoster (HZ), better known as shingles; and pneumococcus are all associated with a reduced risk for developing Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research from UTHealth Houston.
A pre-press version of a study was published online recently in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. It was led by co-first authors Kristofer Harris, program manager in the Department of Neurology with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston; Yaobin Ling, graduate research assistant ...
The Global Flourishing Study launches open access of sample research data with the Center for Open Science
2023-08-16
Charlottesville, VA – The first sample dataset from the Global Flourishing Study (GFS) initiative is now available to researchers, with the project’s initial full dataset scheduled for release in the coming months through the Center for Open Science (COS).
The GFS, a partnership among Gallup, COS, and researchers at Baylor University and Harvard University, is a $43.4 million, five-year study of 200,000 individuals in 22 countries. The GFS data will be an open-access resource for researchers, journalists, policymakers, and ...
State-of-the-art UMass Lowell aerospace center seeded by $5.5M grant
2023-08-16
Drawing on UMass Lowell’s expertise in spacecraft design and track record of successful missions, the university has secured $5.5 million in state funding to launch a research center where scientists, industry leaders and startups can build and test miniature satellites and components essential to spaceflight.
The initiative, known as the Massachusetts Alliance for Space and Technology and Sciences, or MASTS, is anchored by a two-year, $5.5 million grant from the state via the Massachusetts ...
[1] ... [1731]
[1732]
[1733]
[1734]
[1735]
[1736]
[1737]
[1738]
1739
[1740]
[1741]
[1742]
[1743]
[1744]
[1745]
[1746]
[1747]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.