Websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone Tests
2023-08-21
About The Study: In this study including content analysis of 27 websites across multiple countries, most websites selling direct-to-consumer Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) tests included false and misleading claims which might lead consumers to purchase an AMH test in the belief that it can reliably predict fertility potential and age of menopause. Depending on the test result, this may in turn lead to misplaced anxiety or reassurance about one’s fertility and modifications to subsequent conception or contraceptive plans and behavior.
Authors: Tessa Copp, Ph.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the ...
Artificial intelligence beyond the clinic
2023-08-21
With the advent of ChatGPT4, the use of artificial intelligence in medicine has absorbed the public’s attention, dominated news headlines, and sparked vigorous debates about the promise and peril of medical AI.
But the potential of AI reaches far beyond the frontlines of medicine.
AI is already changing the way scientists discover and design drugs. It is predicting how molecules interact and proteins fold with never-before-seen speed and accuracy. One day, AI may even be used routinely to safeguard the function of nuclear reactors.
These are but a few of the exciting applications of AI in the natural sciences, ...
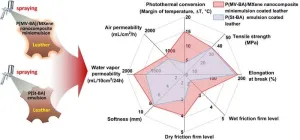
Bio-based waterborne poly(vanillin-butyl acrylate)/mxene coatings for leather with desired warmth retention and antibacterial properties
2023-08-21
A study published in the journal of Engineering reveals a remarkable development in the field of green coating materials for leather. Researchers have successfully synthesized a solvent-free, bio-based antibacterial agent and aromatic monomer called methacrylated vanillin (MV). This innovative compound not only imparts antibacterial properties to leather coatings but also serves as an eco-friendly alternative to the petroleum-based carcinogen styrene (St).
In this research article, titled "Bio-based ...
Genetic study shows that common medication used to prevent heart attacks may be ineffective for majority of British South Asians
2023-08-21
Clopidogrel is a commonly prescribed medication used to prevent further heart attacks after an initial event. It needs to be activated in the body to be effective. Studies of European populations show that 30% of individuals have genetic variants that reduce or prevent activation through the production of an enzyme called CYP2C19. People of South Asian ancestry have high rates of cardiovascular disease, but previous studies have not looked for these variants in UK South Asian populations or linked these variants with risk of recurrent heart attacks if prescribed clopidogrel in South Asian ancestry ...
Tracking species range shifts in a changing climate
2023-08-21
As our planet undergoes significant transformations due to climate change, habitats are being altered, appearing, disappearing, or changing in quality. Understanding the impact of these changes on the geographic distributions of species is of great significance. The shrinking ranges of protected organisms and the expanding ranges of noxious species, such as pests and pathogens, highlight the urgent need to monitor range movements precisely. However, this task poses challenges as the available observation time is often short compared to the pace of underlying population processes, making it difficult to distinguish between directional shifts and random fluctuations.
Addressing ...
Formerly depressed patients continue to focus on negative
2023-08-21
People who have recovered from a major depressive episode, when compared with individuals who have never experienced one, tend to spend more time processing negative information and less time processing positive information, putting them at risk for a relapse, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our findings suggest that people who have a history of depression spend more time processing negative information, such as sad faces, than positive information, such as happy faces, and that this difference is greater compared to healthy people with no history,” said lead author Alainna Wen, PhD, ...
Natural language processing to extract social risk factors influencing health
2023-08-21
INDIANAPOLIS – Social risk factors such as financial instability and housing insecurity are increasingly recognized as influencing health. But unlike diagnosis codes, prescription information, lab or other test reports, social risk factors do not adhere to standardized, controlled terminology in a patient’s electronic medical record, making this information difficult to extract from the clinical notes where they typically are found.
A new study has found that a natural language processing (NLP) system developed by Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health informaticians showed excellent performance when ported ...
To close the gap at the top, start with the bottom
2023-08-21
Ames, IA — Twenty years ago, the National Football League adopted the Rooney Rule. It attempted to address racial disparity in top positions by requiring teams to interview at least one person of color for every head coach opening.
But newly published research suggests the gap will persist unless it’s closed at the bottom. The NFL has a hierarchal labor pool, explains Andreas Schwab, co-author and associate professor of entrepreneurship at Iowa State University. Under the head coach are two coordinators who oversee defense and offense. These coordinators supervise position-specific coaches who may have their own assistant coaches.
“To become ...
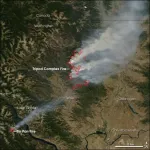
REBURN: A new tool to model wildfires in the Pacific Northwest and beyond
2023-08-21
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For Immediate Release
August 21, 2023
In 2006, the Tripod Complex Fire burned more than 175,000 acres in north-central Washington. The fire, which was within the Okanogan-Wenatchee National Forest, was more than three times the size of Seattle. Yet while considered severe at the time, even larger wildfires in 2014, 2015 and 2021 have since dwarfed Tripod.
Past research shows that large and severe wildfires like these were much rarer in the western U.S. and Canada prior to the late ...
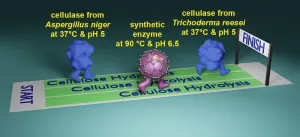
Chemists build synthetic catalysts to break down biomass like super enzymes
2023-08-21
AMES, Iowa – Yan Zhao gestured toward the trees outside his campus window on a rainy afternoon.
The professor of chemistry at Iowa State University is developing new synthetic catalysts to break down cellulose, the plant fibers that make those trees tall and strong.
“Cellulose is built to last – a tree doesn’t just disappear after rain,” Zhao said. “Cellulose is a huge challenge to break down.”
Zhao thinks he has an idea and a technology that can get the job done, making plant biomass a practical source of sugars that can be converted to many applications, including ...
Understanding the neurological mechanisms behind Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-21
Nearly one million people in the United States are living with Parkinson’s disease, making it the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Current medical treatments for Parkinson’s are focused on helping people manage symptoms. But the underlying mechanisms of the neurological disorder remain poorly understood.
Tamily Weissman, associate professor of biology and department chair, is working to change that. Parkinson’s symptoms occur because of a drop in dopamine levels when ...
Space travel depletes red blood cells and bone, but bone marrow fat may come to the rescue
2023-08-21
A study of 14 astronauts suggests that while space travel depletes red blood cells and bone, the body can eventually replenish them back on Earth with the help of fat stored in the bone marrow. The study, published in Nature Communications, has important implications for health in space and on Earth.
“We found that astronauts had significantly less fat in their bone marrow about a month after returning to Earth,” said senior study author Dr. Guy Trudel, a rehabilitation physician and researcher at The Ottawa Hospital and professor at the University of Ottawa. ...
COVID-19 may trigger new-onset high blood pressure
2023-08-21
Research Highlights:
An analysis of more than 45,000 people infected with SARS-CoV-2 found a significant association between the virus and the development of persistent high blood pressure among those with no prior history of high blood pressure.
In addition, people with COVID-19 infection and no history of high blood pressure were significantly more likely to develop persistent high blood pressure compared to people with the influenza virus.
People with COVID-19 who are over age 40, men, Black adults or those with preexisting ...
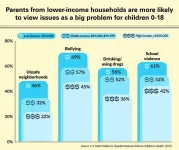
Overuse of social media and devices top parent concerns as kids head back to school
2023-08-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – As children head back to school, two issues have climbed higher on their parents’ list of concerns: the role of social media and the internet in kids’ lives.
Over half of parents also rate mental health issues as leading health concerns for children and teens, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
Overall, emotional health and technology use dominated this year’s top 10 list of parent concerns about health-related issues for kids in the U.S.– surpassing childhood obesity, which parents rated the number one children’s health issue ...
Citizen scientists reveal how the common wasp spreads across UK
2023-08-21
The Big Wasp Survey, a citizen science project involving thousands of volunteers throughout the UK, has yielded important genetic insights into the common wasp, reports a study led by UCL researchers.
Using data and samples of Vespula vulgaris (a species of yellowjacket wasp known as the Common Wasp) collected by amateur ‘citizen scientists’, the researchers conducted the first large-scale genetic analysis of the insect across its native range.
The insights, published in Insect Molecular Biology, revealed a single population of the wasp across Britain, while the insect’s genetics were more differentiated across the Irish Sea in Northern Ireland. The researchers ...
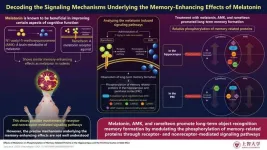
Melatonin and its derivatives enhance long-term object recognition memory
2023-08-21
Multiple studies have demonstrated the memory-enhancing effects of melatonin and its derivatives in animal models. It is also known that the formation of both short- and long-term memories require the phosphorylation of certain memory-related proteins. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying melatonin-induced memory enhancement have remained elusive. Now, medical researchers from Sophia University, Japan, have made important findings that contribute significantly to the elucidation of the underlying mechanisms in a recent article that was made available online on 10 May 2023 and published in Volume 34 Issue 9 of NeuroReport on 7 June 2023.
Regarding the premise of the study, ...
Recreational nitrous oxide use is no laughing matter
2023-08-21
Nitrous oxide is a popular recreational drug, especially among young people, that can cause serious and sometimes permanent neurological defects. A new review in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) aims to help clinicians recognize signs of nitrous oxide toxicity https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230196.
Also known as “laughing gas,” nitrous oxide is an anesthetic sometimes used in pediatric and dental procedures. Inexpensive and easily obtainable online, it is increasingly used for a quick high. In the 2021 Global Drug Survey, 10% of all respondents, and 15% of Canadian respondents, indicated having used the drug in the ...
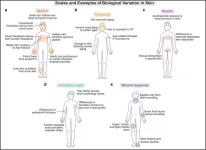
Time is right to develop a consensus Human Skin Cell Atlas, according to leading dermatology experts
2023-08-21
Philadelphia, August 21, 2023 – As a single organ, our skin is able to perform a broad repertoire of vital functions. Dermatology experts call for a reference guide to single-cell composition of normal human skin, which is still lacking. A grassroots movement to establish a Human Skin Cell Atlas is taking shape, as reported in a review in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier. A global team of experts has outlined a roadmap as a first step towards creating a comprehensive and inclusive reference work on this important topic.
Our skin performs vital functions, such as protecting us from external threats ...
Plans for UK’s first menopause education programme launched by UCL academics
2023-08-21
Experts at UCL have teamed up with leading women’s health charities to design a new education and support programme for women across the country experiencing menopause.
The National Menopause Education and Support Programme will be led by Professor Joyce Harper (UCL EGA Institute for Women’s Health), Dr Shema Tariq (UCL Institute for Global Health) and Dr Nicky Keay (UCL Division of Medicine). It is in partnership with two charities, Wellbeing of Women and Sophia Forum. The programme also has the support of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists and British Menopause ...
Scientists elaborated the design and application prospect of China’s Tiangong space station
2023-08-20
As a manned spacecraft operating in orbit for a long time, a space station embodies a country’s scientific and technological strength comprehensively. China’s manned space project was approved in 1992 with a 3-step strategic plan, and building a space station is the final goal of this plan. In September 2010, China’s manned space station project was officially established. After 11 years of unremitting efforts, on 2021 April 29, the Tianhe core module was successfully launched into orbit by the carrier rocket ...
COVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases in children
2023-08-20
Research at a Glance:
A Murdoch Children’s Research Institute-led review has found COVID-19 vaccines are effective against severe cases of the disease in children and adolescents. However, with most children now having caught the SARS-CoV-2 virus and building up a natural immunity, the additional benefit of vaccination in healthy children is minimal
The review explored the challenges and considerations around COVID-19 vaccination of children, especially in low- and middle-income countries, in the context of high levels of community transmission and infection-derived ...
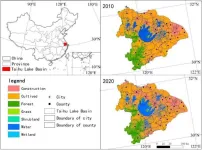
An aid to ecological management and decision-making ES supply and demand dynamics
2023-08-19
Ecosystem services (ESs) provide a variety of services and benefits for human well-being, but the supply-demand mechanism of ecosystem services under different spatio-temporal scales is unclear. The Taihu Lake Basin (TLB) is a microcosm of degraded and unsustainable ecosystem services. Rapid industrialization and urbanization poses a great threat to the environment and ecology. Therefore, it is urgent to assess the changes in supply and demand for TLB ecosystem services from a spatio-temporal and multi-stakeholder perspective, and ...
Remote learning during pandemic aids medical students with disabilities
2023-08-18
Medical students who reported a disability to their school increased by more than 25% during the COVID-19 pandemic, a study shows.
The proportion of students reporting attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or chronic health and/or psychological disabilities has increased between 2015 and 2021.
Despite the increase in medical students reporting these conditions, the requests for more inclusive preclinical testing accommodations, like extra time for test completion or a less distracting environment, decreased during the pandemic between 2019 and 2021.
According to authors of the new research letter in JAMA Network Open, the remote curriculum delivery during the pandemic may have allowed ...
DOE funds Gulf Coast-focused direct air capture hub feasibility study
2023-08-18
The U.S. Department of Energy has awarded an LSU-led consortium a $4.9 million grant to support the first phase of the Pelican Gulf Coast Carbon Removal project. The Pelican Consortium, which includes Shell and the University of Houston, will evaluate the feasibility of building a direct air capture (DAC) hub in Louisiana. DAC technologies capture carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere. The captured carbon dioxide can then be used to manufacture products or be permanently stored in deep geological formations.
The project will leverage existing regional infrastructure in one of the highest emitting areas in the Gulf Coast, benefit the local energy workforce, and support ...
DOE announces $70 million in research training opportunities for students and faculty from historically underrepresented institutions
2023-08-18
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $70 million in funding to support research by historically underrepresented groups in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) and to diversify leadership in the physical sciences. The funding, through DOE’s Reaching a New Energy Sciences Workforce (RENEW) initiative, will support internships, training programs, and mentor opportunities at 65 different institutions, including 40 higher-learning institutions that serve minority populations. Ensuring America’s best and brightest students have pathways to STEM fields will be key to leading the world’s energy transition ...
[1] ... [1739]
[1740]
[1741]
[1742]
[1743]
[1744]
[1745]
[1746]
1747
[1748]
[1749]
[1750]
[1751]
[1752]
[1753]
[1754]
[1755]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.