University of Tennessee extension wins “Employer of the Year” from international organization
2023-08-11
Ask just about any person in the University of Tennessee Extension family what they like about their job, and they might mention the impact they have in their communities and the people they help. Long thought of as a career where you can realize a calling for service, an international organization now confirms what many employees have believed for some time – that UT Extension is a great place to work.
The International Association of Administrative Professionals (IAAP) has named UT Extension as its 2023 Employer of the Year. This ...
Interdisciplinary team studies decomposition effects on soil
2023-08-11
Forensic researchers at the University of Tennessee Knoxville’s famous Anthropological Research Facility, popularly known as the “Body Farm,” have made headlines for decades in their discoveries of what happens to human bodies after death. Now, a multidisciplinary team—engineers, soil scientists, and biologists—digs in with them for a deeper look at what happens to the soil underneath a decomposing body. Their study, “Soil Elemental Changes During Human Decomposition,” published in June 2023 by PLOS One, could benefit investigators searching for human remains in remote or hard-to access-vegetated areas.
“This ...
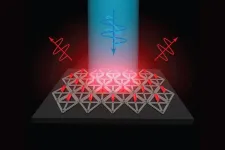
Arrays of quantum rods could enhance TVs or virtual reality devices
2023-08-11
Cambridge, MA – Flat screen TVs that incorporate quantum dots are now commercially available, but it has been more difficult to create arrays of their elongated cousins, quantum rods, for commercial devices. Quantum rods can control both the polarization and color of light, to generate 3D images for virtual reality devices.
Using scaffolds made of folded DNA, MIT engineers have come up with a new way to precisely assemble arrays of quantum rods. By depositing quantum rods onto a DNA scaffold in a highly controlled way, the researchers can regulate their orientation, which is a key factor in determining the polarization of light emitted by the array. This makes it easier ...
Artificial intelligence designs advanced materials
2023-08-11
In a world where annual economic losses from corrosion surpass 2.5 trillion US Dollars, the quest for corrosion-resistant alloys and protective coatings is unbroken. Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly pivotal role in designing new alloys. Yet, the predictive power of AI models in foreseeing corrosion behaviour and suggesting optimal alloy formulas has remained elusive. Scientists of the Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung (MPIE) have now developed a machine learning model that enhances the predictive accuracy by up to 15% compared to existing frameworks. This model uncovers new, but realistic corrosion-resistant alloy compositions. ...
Even treated wastewater affects our rivers
2023-08-11
Effluents from wastewater treatment plants have a dual effect: Some species disappear, while others benefit. Especially certain insect orders, such as stonefly and caddisfly larvae, are decimated. Certain worms and crustaceans, by contrast, can increase in number. A team from Goethe University Frankfurt led by Daniel Enns and Dr. Jonas Jourdan has corroborated this in a comprehensive study, which has now been published in the journal Water Research. They examined 170 wastewater treatment plants in Hesse in relation to species composition.
Wastewater treatment plants are ...
Study: Infant formula safety checks can be improved with stratified sampling
2023-08-11
URBANA, Ill. – Producers of infant formula employ comprehensive food safety systems, including product testing to ensure those systems are working. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign finds that some testing methods are more powerful at catching contaminants than others.
Spacing out samples over time in a stratified sampling pattern is better at catching risky pathogens like Cronobacter than randomly sampling from the product as it is being produced, the researchers found. Furthermore, while taking more samples of product generally increases the chance to catch the pathogen, there is a point after which it ...
UTEP launches new research partnerships with Chihuahua universities
2023-08-11
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 11, 2023) – How are our region’s pecan farms affected by drought? Is there a better way to address domestic violence in Ciudad Juárez? These are a few of the big questions scientists are asking as they prepare to embark on a new cross-border research collaboration.
Created by The University of Texas at El Paso, the U.S.-Mexico Faculty Collaboration Fellowship program will support research projects with higher education institutions in the State of Chihuahua to spur studies on issues ...
Behind the rind: new genomic insights into watermelon evolution, quality, and resilience
2023-08-11
Watermelon is a globally significant agricultural product, both in terms of the total amount produced and the total economic value generated.
Scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute have constructed a comprehensive "super-pangenome" for watermelon and its wild relatives, uncovering beneficial genes lost during domestication that could improve disease resistance and fruit quality of this vital fruit crop.
"We aimed to delve deeper into the genetic variations that make watermelons so diverse and unique," stated ...
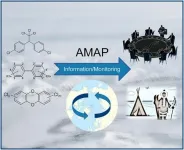
Arctic monitoring program plays vital role in global pollution reduction efforts
2023-08-11
Historically, the Arctic was considered a pristine region, but scientific research spanning the last three decades has revealed the harsh reality of long-range transported pollutants reaching the Arctic from different corners of the world. In response to this alarming discovery, AMAP was created with the mission to monitor pollution and its effects on the Arctic environment and human health.
In a new article published on 26 July 2023, in the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Arctic Knowledge Ltd, presents the initiation and implementation of a systematic scientific and political cooperation in the Arctic related to environmental ...
University of Chicago scientists invent smallest known way to guide light
2023-08-11
Directing light from place to the place is the backbone of our modern world. Beneath the oceans and across continents, fiber optic cables carry light that encodes everything from YouTube videos to banking transmissions—all inside strands about the size of a hair.
University of Chicago Prof. Jiwoong Park, however, wondered what would happen if you made even thinner and flatter strands—in effect, so thin that they’re actually 2D instead of 3D. What would happen to the light?
Through a series of innovative experiments, he and his team found ...
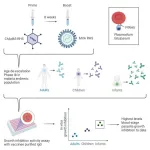
Malaria vaccine candidate appears safe and produces promising immune response in a cohort of Tanzanian infants
2023-08-11
An experimental malaria vaccine appears safe and promotes an immune response in African infants, one of the groups most vulnerable to severe malaria disease. There is currently only one malaria vaccine, “RTS,S” that is approved by the World Health Organization and offers partial disease protection. However, in the results of the early-stage phase Ib trial conducted in Tanzania and published on August 11th in the journal Med, researchers find that targeting RH5 – a protein that the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum uses to invade red blood cells – can generate a promising immune response ...
A roadmap to help AI technologies speak African languages
2023-08-11
From text-generating ChatGPT to voice-activated Siri, artificial intelligence-powered tools are designed to aid our everyday life — as long as you speak a language they support. These technologies are out of reach for billions of people who don’t use English, French, Spanish or other mainstream languages, but researchers in Africa are looking to change that. In a study published August 11 in the journal Patterns, scientists draw a roadmap to develop better AI-driven tools for African languages.
“It doesn’t ...
Synthetic extracellular matrix supports endometrial organoids
2023-08-11
Scientists have developed a synthetic extracellular matrix (ECM) that can support the growth of a mini endometrium in a dish for at least two weeks. The endometrium—the mucosal lining of the uterus—has been historically hard to model in the lab, which has limited scientists’ ability to study its role in healthy and diseased states like endometriosis. The matrix, described on August 11 in the journal Med, allows cells to interact in an environment that recapitulates human physiology which could help researchers better simulate the healthy and pathological response to menstrual cycles.
“With this matrix, we can begin to extrapolate and utilize ...
Using the body’s “invisible scalpel” to remove brain cancer
2023-08-11
LA JOLLA (August 11, 2023)—Glioblastoma, the most common and deadly form of brain cancer, grows rapidly to invade and destroy healthy brain tissue. The tumor sends out cancerous tendrils into the brain that make surgical tumor removal extremely difficult or impossible.
Now, Salk scientists have found the immunotherapy treatment anti-CTLA-4 leads to considerably greater survival of mice with glioblastoma. Furthermore, they discovered that this therapy was dependent on immune cells called CD4+ T cells infiltrating the brain and triggering the tumor-destructive activities of other immune cells ...
Playing football may increase the risk for Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-11
(Boston)—Identification of risk factors for Parkinson’s disease (PD) is essential for early diagnosis. Dating back to the 1920s, Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism—an umbrella term that refers to motor symptoms found in Parkinson’s disease and also other conditions—have long been described in boxers. Repetitive head impacts from tackle football can also have long-term neurological consequences like chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). But research on the association between participation in tackle football and PD is limited.
In the largest study to describe the association between participation ...
Perceptions of safety of daily cannabis vs tobacco smoking and secondhand smoke exposure
2023-08-11
About The Study: This survey study of 5,035 adults found that adults increasingly perceived daily smoking and secondhand exposure to cannabis smoke as safer than tobacco smoke from 2017 to 2021. Given that these views do not reflect the existing science on cannabis and tobacco smoke, the findings may have important implications for public health and policy as the legalization and use of cannabis increase.
Authors: Beth Cohen, M.D., M.A.S., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.28691)
Editor’s ...
Gestational age and birth outcomes in term singleton pregnancies conceived with infertility treatment
2023-08-11
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that, in pregnancies conceived with infertility treatment, delivery at 39 weeks provided the lowest perinatal risk when comparing risk of delivery at this week of gestation versus the subsequent week of gestation.
Authors: Ira Hamilton, M.D., of the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Cincinnati, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.28335)
Editor’s ...
Football participation and Parkinson disease among men
2023-08-11
About The Study: In this study, 729 participants with a history of playing organized football had higher odds of having a reported parkinsonism or Parkinson disease diagnosis compared with participants in other organized sports. Longer duration of play and higher level of football play were associated with higher odds of a reported diagnosis.
Authors: Michael L. Alosco, Ph.D., of the Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.28644)
Editor’s ...
Association of caregiver depression risk with patient outcomes in Parkinson disease
2023-08-11
About The Study: Patients with Parkinson disease who had caregivers at higher risk of depression were more likely to have worse quality of life and higher emergency department use than patients who had caregivers not at higher risk of depression. Additional caregiving resources and interventions to reduce caregiver depression symptoms could potentially improve patient outcomes.
Authors: Nabila Dahodwala, M.D., M.S., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.27485)
Editor’s ...
De-code of the crop
2023-08-11
A research group led by Kyoto University's Graduate School of Agriculture has deciphered buckwheat's high-precision chromosomal-level genome sequence, a key step toward unraveling the evolution of the buckwheat genome and the origins of the cultivated crop.
By altering specific genes using a method independent of common genome-editing techniques,
the researchers successfully developed a self-fertile buckwheat variety as well as a new type of the crop with a sticky, mochi-like texture. This breeding method may contribute to a more diverse range of orphan crops than what is possible with existing genome editing technologies.
With the world's population predicted to reach ...
More than 2 million additional Americans faced food insufficiency following drawdown of pandemic-related SNAP benefits, Penn Medicine study finds
2023-08-11
PHILADELPHIA— The recent discontinuation of pandemic-related food assistance benefits, known as the Supplemental Food Assistance Program (SNAP) Emergency Allotments, led to a substantial increase in food insufficiency in the United States, according to a new study led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The primary goal of SNAP, which distributes cash-like benefits to low-income families to buy food, is to combat food insecurity, which affects 10 percent of U.S. households. The findings were published in JAMA Health Forum today.
Comparing trends in food insufficiency ...
COVID-19 vaccination and boosting during pregnancy benefits pregnant people and newborns
2023-08-11
WHAT:
Receiving a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine or booster during pregnancy can benefit pregnant people and their newborn infants, according to findings recently published in Vaccine. The paper describes results from the Multisite Observational Maternal and Infant Study for COVID-19 (MOMI-VAX), which was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The MOMI-VAX study launched in June 2021 when data on COVID-19 vaccination in pregnant people were sparse. Researchers hoped to understand the ...
Evolving elegance: TU Dresden scientists connect beauty and safeguarding in ammonoid shells
2023-08-11
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusk animals that are now an iconic fossil group often collected by amateurs. Over 350 million years of evolution, ammonoids developed increasingly elaborate shells with fractal-like geometry. For nearly 200 years, scientists have debated the reason why these animals show a trend of increasing complexity in their shell structures. Dr. Robert Lemanis and Dr. Igor Zlotnikov from the B CUBE – Center for Molecular Bioengineering at TU Dresden created mechanical simulations of theoretical and computed tomography-based models to unveil a potential explanation: the intricate architecture of these shells may have been nature's ingenious ...
Researchers “film” novel catalyst at work
2023-08-11
A novel catalysis scheme enables chemical reactions that were previously virtually impossible. The method developed at the University of Bonn is also environmentally friendly and does not require rare and precious metals. The researchers recorded the exact course of the catalysis in a kind of high-speed film. They did this using special lasers that can make processes visible that last only fractions of a billionth of a second. The results allow them to further optimize the catalyst. They have been published in the international edition of the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie.
Let’s say you are playing mini ...
Mosquito hearing could be targeted by insecticides
2023-08-11
Specific receptors in the ears of mosquitoes have been revealed to modulate their hearing, finds a new study led by researchers at UCL and University of Oldenburg. Scientists say, this discovery could help develop new insecticides and control the spread of harmful diseases, such as malaria.
The ability of male mosquitoes to hear female mosquitoes is a crucial requirement for their reproduction. As a result, the finding could help develop novel insecticides or mating disruptors to prevent mosquito-borne diseases like malaria, dengue, and yellow fever
In the study, published in Nature Communications, ...
[1] ... [1740]
[1741]
[1742]
[1743]
[1744]
[1745]
[1746]
[1747]
1748
[1749]
[1750]
[1751]
[1752]
[1753]
[1754]
[1755]
[1756]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.