Editorial: Turning the tide on obesity?
2023-08-03
In an Editorial, Cynthia Bulik and Andrew Hardaway highlight the recent advances in medical treatments for obesity and weight loss. “With the emergence of new, highly effective weight-loss drugs, might the ‘fat decades’ become a closed chapter in the history of public health?” ask the authors. The “obesity epidemic” is a global health concern, with more than a billion people affected by obesity and many more overweight. Although various environmental, biological, and behavioral factors have been implicated in obesity, few consistently effective treatments exist for the disease. Recently, however, new weight-loss ...
Compensation for damages can and should address social and cultural impacts
2023-08-03
In this Policy Forum, Robin Gregory and colleagues highlight how a suite of methodological approaches can be used to bring less tangible social and cultural losses that marginalized groups incur into the formal compensation assessment framework. “Though the issues and approaches we describe are applicable in many contexts,” the authors write, “we illustrate them … with a focus on Indigenous communities, for whom the neglect of social and cultural losses in assessments of compensation ...
Adult tropical trees of the same species grow farther apart than factors like seed dispersal limits can explain
2023-08-03
Tropical trees distance themselves from members of their own species more than they do other species, a new study shows. What’s more, trees of the same species exist at distances farther apart than would be expected by chance or the limits of seed dispersal. The results reveal pervasive within-species spatial repulsion in adult trees, providing new insights into the ecological dynamics that stabilize species diversity and enable the exceptionally high diversity of tropical forests. Tropical forests host an unusually high diversity of tree species. For example, some tropical forests contain more than 250 tree species per hectare. However, how hundreds of species coexist on relatively small ...
A gut hormone for controlling appetite doubles as an immune regulator for the fungal microbiome
2023-08-03
Peptide YY (PYY), a hormone produced by gut endocrine cells that was already known to control appetite, also plays an important role in maintaining the balance of fungi in the digestive system of mammals, according to new research from the University of Chicago.
In a study published this week in Science, researchers found that specialized immune cells in the small intestine called Paneth cells express a form of PYY that prevents the fungus Candida albicans from turning into its more virulent form. PYY was already known to be produced by endocrine cells in the gut as a hormone that signals satiety, or when an animal has had enough to eat. The new research shows that it also ...
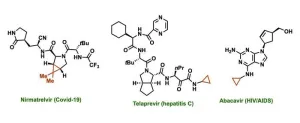
New, simple and accessible method creates potency-increasing structure in drugs
2023-08-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Chemical structures called cyclopropanes can increase the potency and fine-tune the properties of many drugs, but traditional methods to create this structure only work with certain molecules and require highly reactive—potentially explosive—ingredients. Now, a team of researchers from Penn State has identified and demonstrated a safe, efficient and practical way to create cyclopropanes on a wide variety of molecules using a previously undescribed chemical process. With additional development, the new method—described ...
Study finds a surprising new role for a major immune regulator
2023-08-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A signaling protein known as STING is a critical player in the human immune system, detecting signs of danger within cells and then activating a variety of defense mechanisms.
STING is primarily on the lookout for DNA, which can indicate either a foreign invader such as a virus or damage to the host tissue or cell. When STING detects that danger signal, it can turn on at least three different pathways — one leading to interferon production, one to non-canonical autophagy (involved in recycling cell components and clearing pathogens), and a third to formation of the inflammasome, a complex of proteins that activates ...
Winter storms over Labrador Sea influence Gulf Stream system
2023-08-03
The Gulf Stream, which brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to Europe and keeps the climate mild, is only part of a larger system of oceanic currents called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC for short. It runs through the Atlantic like a giant climate machine: as warm water from the tropics is transported northwards at the surface, the current reverses in the North Atlantic – the water cools, becomes heavier and flows south at depth.
Where exactly these sinking processes take place is the subject of current research, and recent measurement programmes have located them to the east of Greenland. ...
Doctors, medical professionals, and artificial intelligence: Innocent bystanders or vicious culprits? – a hot topic of the AI & Medicine 2024 World Congress in Paris, France
2023-08-03
Paris, France – August 3, 2023 – The First International Congress on Artificial Intelligence and Medicine, AI & Medicine 2024, is set to take place on April 11-12, 2024, in Paris, France. Building on the success of IA & Néphrologie 2023, the conference aims to bridge the gap between cutting-edge technology and health care.
AI & Medicine 2024 aims to inform medical professionals about the capabilities of advanced machine learning techniques, and simultaneously raise awareness within the tech industry regarding the unique challenges and requirements of the healthcare sector. The congress will offer a platform to discuss the current applications of AI in diagnostics, ...
A spinout’s biggest competitor may be the parent company, not other entrepreneurs
2023-08-03
Spinouts, or new ventures started by employees leaving a parent firm, often outperform other types of new firms. But a new study published in Strategic Management Journal finds that when parent firms identify and implement ideas internally, they outperform spinouts. For example, if employees at Microsoft leave the parent and start their own spinout in the competing industry, the spinout potentially needs to compete against a new establishment formed by Microsoft in the same industry.
New ventures by former employees often have an edge over competitors because of the knowledge transfer from their ...
FSU researcher finds potential new tool for early identification of dementia risk
2023-08-03
Research at the Florida State University College of Medicine has identified a potential low-cost method for predicting if a person is at risk of developing dementia.
By analyzing data from nearly 13,000 subjects who participated in a long-term aging study, researchers found that an interviewer’s rating of a cognitively healthy person’s memory successfully predicted the likelihood of developing dementia over a 15-year period. Their findings will be published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
“Our findings show that interviewers ...
Current takes a surprising path in quantum material
2023-08-03
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell researchers used magnetic imaging to obtain the first direct visualization of how electrons flow in a special type of insulator, and by doing so they discovered that the transport current moves through the interior of the material, rather than at the edges, as scientists had long assumed.
The finding provides new insights into the electron behavior in so-called quantum anomalous Hall insulators and should help settle a decades-long debate about how current flows in more general quantum Hall insulators. These insights will inform the development of topological materials for next-generation quantum devices.
The team’s paper, “Direct ...
Professor Deborah Laufer discusses barriers to cervical cancer screening in Uruguay – BGI Insights
2023-08-03
The recently released BGI Genomics 2023 Global State of Cervical Cancer Awareness Report highlights the level of knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to cervical cancer screening and the human papillomavirus (HPV) on a global scale.
Dr. Deborah Laufer, a gynecologist and Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine in the University of Montevideo, offers her insights on this report's findings and the steps needed to improve cervical cancer awareness in Uruguay.
Q: 40% of respondents worldwide did not choose HPV as the key cause of cervical cancer. 37% in Uruguay did not mention it either. ...
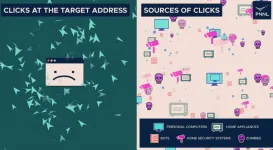
Researchers strengthen defenses against common cyberattack
2023-08-03
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scientists have developed a better way to recognize a common internet attack, improving detection by 90 percent compared to current methods.
The new technique developed by computer scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory works by keeping a watchful eye over ever-changing traffic patterns on the internet. The findings were presented on August 2 by PNNL scientist Omer Subasi at the IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience, where the manuscript was recognized as the best research paper presented at the meeting.
The ...
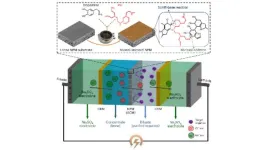
Mussel-inspired membrane can boost sustainability and add value to industrial wastewater treatment
2023-08-03
Engineers have developed a new kind of membrane that separates chemicals within wastewater so effectively that they can be reused, presenting a new opportunity for industries to improve sustainability, while extracting valuable by-products and chemicals from wastewater.
Created for use in wastewater treatment, the thin-film composite nanoporous membrane known as a TFC NPM, exhibits an ‘unprecedented’ capability to separate salts and other chemical components from water, and could lead to more sustainable treatment and management of water in a range of industries.
A research ...
CAR-T immune therapy attacks ovarian cancer in mice with a single dose
2023-08-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — CAR-T immune therapies could be effective against solid tumors if the right targets are identified, a new study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers suggests. The researchers successfully deployed CAR-T in a mouse model of ovarian cancer, a type of aggressive, solid-tumor cancer that has eluded such therapies until now.
“Even with an advanced stage tumor model, even with a single dose, we saw strong anti-tumor effects,” said Diana Rose Ranoa, ...
GABA receptors in brain could be targets to treat depression and its cognitive symptoms
2023-08-03
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Depression is a complex condition correlated with multiple differences in brain function and mechanisms. A new paper spanning known data about the neurotransmitter GABA and its principal receptors showcases evidence of the receptors’ importance in depression and potential as therapeutic targets.
Based on evidence from research on the receptors’ function in the brain and the drugs that can activate or inhibit them, the authors propose possible mechanisms by which GABA-modulating treatments could ...
New clinical trial to assess canine cancer treatment
2023-08-03
DENVER/Aug. 3, 2023 – A newly funded study will evaluate the potential of a cancer drug to control tumor growth and improve outcomes for dogs with histiocytic sarcoma, an aggressive and typically fatal canine cancer.
The multi-center clinical trial is being conducted at Michigan State University, University of Florida, University of Wisconsin and Virginia Tech, and funded by the Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America through Morris Animal Foundation's Donor-Inspired Study program. Histiocytic sarcoma was ...
How sensory neurons impact the gut
2023-08-03
LA JOLLA, CA—Gastrointestinal and digestive issues impact roughly 3 million people across the United States alone, and that number is growing. A new study from Scripps Research scientists shows how sensory neurons control our gastrointestinal tracts—critical information that could shape our understanding of related diseases and disorders.
The study, published in the journal Cell on Aug. 3rd, 2023, used a combination of human clinical data and animal models to reveal that the receptor PIEZO2 controls gastrointestinal transit through the stomach, small intestine, and colon by sensing the presence of food and slowing the rate of gut motility accordingly. These ...
Study finds hallmarks of T cell exhaustion within hours of tumor exposure
2023-08-03
Immune system T cells that should be able to kill cancer cells become dysfunctional or “exhausted” within hours of encountering a tumor, according to a study reported Aug. 3 in Nature Immunology.
The surprising findings have implications for cancer immunotherapies that aim to harness the tumor-killing power of T cells, and they challenge existing ideas about how T cells become exhausted, said Mary Philip, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Medicine in the Division of Hematology and Oncology ...
New research casts doubt on role of fungus in driving pancreatic cancer
2023-08-03
DURHAM, N.C. – Four years ago, a report that a common species of fungus might fuel pancreatic cancer offered a promising new view of the deadly disease.
But in working to validate the finding, Duke Health researchers have found no such association. In a study appearing online Aug. 3 in the journal Nature, the Duke researchers conducted a multi-pronged analysis of data from the earlier study and found no link between the pancreatic microbiome and the development of pancreatic cancer.
“We were intrigued by the original finding, as were ...
Dopamine controls movement, not just rewards
2023-08-03
Dopamine: It’s not just for rewards anymore.
In a new Northwestern University-led study, researchers identified and recorded from three genetic subtypes of dopamine neurons in the midbrain region of a mouse model.
Although there is a long-standing, common assumption that most — if not all — dopamine neurons solely respond to rewards or reward-predicting cues, the researchers instead discovered that one genetic subtype fires when the body moves. And, even more surprisingly, these neurons curiously do not respond to rewards at all.
Not only ...
Study uncovers epigenetic source of resistance to targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
2023-08-03
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes promote tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer
Publication: Cancer Cell
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Senior and Lead Authors: Cigall Kadoch, PhD; Claudia Gentile, PhD; Akshay Sankar
Study Summary:
When lung cancers driven by mutations in the EGFR gene become resistant to osimertinib or other targeted therapies, epigenetic changes, rather than genetic changes, are often to blame. In a new study in Cancer Cell, researchers at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Yale Cancer Center show that the main source of these changes are ...
Past climate warming driven by hydrothermal vents
2023-08-03
About 55 million years ago, the Atlantic Ocean was born. Until then, Europe and America were connected. As the continents began to move apart, the Earth’s crust between them ruptured, releasing large volumes of magma. This rift volcanism has led to the formation of large igneous provinces (LIPs) in several places around the world. One such LIP was formed between Greenland and Europe and now lies several kilometres below the ocean surface. An international drilling campaign led by Christian Berndt from the GEOMAR ...
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of the Ring Nebula
2023-08-03
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has recorded breath-taking new images of the iconic Ring Nebula, also known as Messier 57.
The images, released today by an international team of astronomers led by Professor Mike Barlow (UCL, UK) and Dr Nick Cox (ACRI-ST, France), with Professor Albert Zijlstra of The University of Manchester, showcase the nebula's intricate and ethereal beauty in unprecedented detail, providing scientists and the public with a mesmerizing view of this celestial wonder.
For many sky enthusiasts, the Ring Nebula is a well-known object that is visible all summer long and is located in the constellation ...
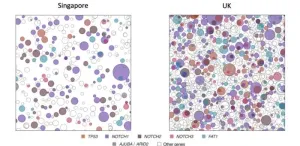
Wellcome Sanger Institute: Skin cancer-related mutations higher in the UK than Singapore
2023-08-03
SKIN CANCER-RELATED MUTATIONS HIGHER IN THE UK THAN SINGAPORE
A new study has shown how, on average, people in the UK have facial skin that is far more DNA damaged from the sun than people in Singapore, explaining the far higher risk of developing the most common skin cancers in the UK.
This study looked at keratinocyte cancers - basal and squamous cell carcinomas - rather than melanoma, a rarer and sometimes fatal form of skin cancer, finding Northern European skin types in the UK were less able to protect themselves from UV damage.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and their collaborators at ...
[1] ... [1748]
[1749]
[1750]
[1751]
[1752]
[1753]
[1754]
[1755]
1756
[1757]
[1758]
[1759]
[1760]
[1761]
[1762]
[1763]
[1764]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.