Breast cancer patients with higher BMI more likely to experience heart damage during chemotherapy
2023-08-02
Breast cancer survival rates have improved considerably in the last few decades in Colombia, but factors that increase the likelihood of patients experiencing cardiovascular side effects, like cardiotoxicity, are not well-known or well-treated. A recent study in the North-East region of Colombia found 11.94% of patients with a high BMI being treated for breast cancer at a regional center experienced heart damage, or cardiotoxicity, during chemotherapy. The study will be presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Latin America 2023 Together with Asociación Costarricense ...
Study presents workaround for randomized experiments
2023-08-02
AUSTIN, Texas – A new statistical tool can help researchers get meaningful results when a randomized experiment, considered the gold standard, is not possible.
Randomized experiments split participants into groups by chance, with one undergoing an intervention and the other not. But in real-world situations, they can’t always be done. Companies might not want to use the method, or such experiments might be against the law.
Developed by a researcher at The University of Texas at Austin, the new tool called two-step synthetic control adapts an existing research workaround, known as the synthetic control method.
The ...
Cal Poly study analyzes nearshore California marine heatwaves and cold spells amid changing climate conditions
2023-08-02
The first-ever study to look at drivers of both marine heatwaves and cold spells in the shallow nearshore along the California Current —coordinated by California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo (Cal Poly) and the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, William & Mary — found that certain environmental conditions and the state of the ocean can lead to an enhanced risk for ocean temperature extremes.
The findings were recently published in Nature Scientific Reports in an article titled “Effects of basin-scale climate modes and upwelling on nearshore marine heatwaves and cold spells in the California Current.”
Extreme ...
Mimicking the body’s own defenses to destroy enveloped viruses
2023-08-02
Just as bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance, viruses can also evade drug treatments. Developing therapies against these microbes is difficult because viruses often mutate or hide themselves within cells. But by mimicking the way the immune system naturally deals with invaders, researchers reporting in ACS Infectious Diseases have developed a “peptoid” antiviral therapy that effectively inactivates three viruses in lab tests. The approach disrupts the microbes by targeting certain ...
Novel molecules fight viruses by bursting their bubble-like membranes
2023-08-02
Antiviral therapies are notoriously difficult to develop, as viruses can quickly mutate to become resistant to drugs. But what if a new generation of antivirals ignores the fast-mutating proteins on the surface of viruses and instead disrupts their protective layers?
“We found an Achilles heel of many viruses: their bubble-like membranes. Exploiting this vulnerability and disrupting the membrane is a promising mechanism of action for developing new antivirals,” said Kent Kirshenbaum, professor of chemistry at NYU and the study’s senior author.
In a new study ...
More than 2,600 health care organizations recognized for commitment to high-quality cardiovascular care
2023-08-02
DALLAS, August 2, 2023 — The American Heart Association, a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives, has recognized 2,671 health care and emergency response organizations — nearly 145 more than in 2022 — for their commitment to improving health outcomes for cardiovascular patients through evidence-based efficient and coordinated care.
The American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines® and Mission: Lifeline® are hospital-based quality improvement recognition programs that use the latest evidence-based scientific guidelines to save lives and hasten health care recovery ...
Stalking a silent killer
2023-08-02
With a survival rate in the single digits, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is highly lethal. In fact, by the time PDAC is clinically diagnosed, it is already considered incurable via surgery or other means in up to 90% of patients.
Yangzom D. Bhutia, D.V.M., Ph.D., from the Department of Cell Biology and Biochemistry at the Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center (TTUHSC) School of Medicine, has for years focused her research on PDAC. To bolster her efforts, the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health recently awarded Bhutia a five-year, $1.76 million grant (“SLC6A14 as a unique ...
Many people feel their jobs are pointless
2023-08-02
A sociological study by the University of Zurich confirms that a considerable proportion of employees perceive their work as socially useless. Employees in financial, sales and management occupations are more likely to conclude that their jobs are of little use to society.
In recent years, research showed that many professionals consider their work to be socially useless. Various explanations have been proposed for the phenomenon. The much-discussed “bullshit jobs theory” by the American anthropologist David Graeber, for example, states that some jobs are objectively useless and that this occurs more frequently ...
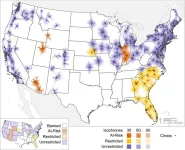
Abortion facility access means long drives for 41.8% of women
2023-08-02
SPOKANE, Wash. – One year after the Dobbs decision, 41.8% of U.S. women of reproductive age have to drive 30 minutes or more to reach an abortion care facility, according to a study of data as of June 2, 2023. Researchers predicted that number would rise to 53.5% if other state bills under consideration are passed.
The study estimated longer drives as well, finding that 29.3% of women didn’t have access to a facility within a 60-minute drive and 23.6% lacked access even within a 90-minute drive. Those figures would jump to 45.6% ...
Unhappy family or trauma in youth leads to poor health in old age
2023-08-02
Adverse childhood experiences have impacts deep into old age, especially for those who experienced violence, and include both physical and cognitive impairments.
It’s known that a difficult childhood can lead to a host of health issues as a young or midlife adult, but now, for the first time, researchers at UC San Franciso have linked adverse experiences early in life to lifelong health consequences.
They found that older U.S. adults with a history of stressful or traumatic experiences as children were more likely to experience both physical and cognitive impairments in their senior years. Stressful childhood experiences could include exposure to ...
Extroverts more likely to resist vaccines, study shows
2023-08-02
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 2, 2023) – Which types of personalities were more hesitant about COVID-19 vaccination during the pandemic’s peak? Extroverts — according to a new study on more than 40,000 Canadians.
“We expected that people who were especially high in extroversion would be more likely to get the vaccine,” said Melissa Baker, Ph.D., lead author and assistant professor at The University of Texas at El Paso. “We figured those people would want to get back out in the world and socialize, right? It’s actually the opposite.”
The findings, ...
UTokyo researchers imagine future see-through objects
2023-08-02
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science(IIS), The University of Tokyo, conducts a wide range of research, including physics, chemistry and biology. In this context, DLX Design Lab carries out activities aimed at fusing science, technology, and design. One of these activities is the Treasure Hunting Project, which aims to inform the general public about the value and potential of scientific research. As part of this project, in 2022-2023, DLX Design Lab produced a video introducing future ...
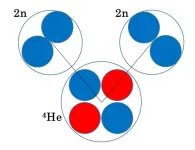
Correlation between neutron pairs observed in helium-8 nuclei
2023-08-02
Atomic nuclei consist of nucleons such as protons and neutrons, which are bound together by nuclear force or strong interaction. This force allows protons and neutrons to form bound states; however, when only two neutrons are involved, the attractive force is slightly insufficient to create such a state. This prompts the question: would four neutrons be adequate? This question has captivated atom physicists, who have actively sought to unlock this mystery in both the theoretical and experimental realms.
With ...
Training on LSA lifeboat operation using Mixed Reality
2023-08-02
Research Background
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has identified the human element as one of the key attributes for the safety of life at sea and a contributing factor to most of the casualties in the shipping sector. The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty which requires signatory flag states to ensure that ships flagged by them comply with minimum safety standards in construction, equipment and operation. As part of the SOLAS code, there is the requirement that all personnel on vessels at sea must undertake Standards of Training, ...
Humble feijoa to help prevent type 2 diabetes?
2023-08-02
Can the humble feijoa help the world tackle type 2 diabetes? University of Auckland scientists are investigating.
With more than 200,000 people in New Zealand living with type 2 diabetes, prevention is key to tackling this important health issue. Could a solution be found growing in New Zealand backyards?
The feijoa study, named FERDINAND, is a six-month weight-loss and maintenance programme, during which adults with raised blood sugar will be given about a gram of whole-fruit feijoa powder (or a placebo) each ...
Irregular sleep patterns associated with harmful gut bacteria
2023-08-02
New research has found irregular sleep patterns are associated with harmful bacteria in your gut.
The study, published today in The European Journal of Nutrition, by researchers from King’s College London and ZOE, the personalised nutrition company, is the first to find multiple associations between social jet lag – the shift in your internal body clock when your sleeping patterns change between workdays and free days - and diet quality, diet habits, inflammation and gut microbiome composition in a single cohort.
Previous research has shown that working shifts disrupts the body clock and can increase risk ...
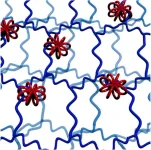
Multicyclic molecular wheels with polymer potential
2023-08-02
Molecules that act as connected wheels can hold long molecular chains together to modify the properties of soft polymers.
Rotaxanes are interlocked molecular structures with a linear ‘axle’ molecule penetrating one or more cyclic ‘wheel’ molecules. Bulky groups at the end of the axle prevent the wheels from coming off. Now, researchers at Hokkaido University have taken the previous achievements of this technology a step further, making macro-rotaxanes that have multicyclic wheels interlocked with several high-molecular-weight axles. They report their innovation in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Rotaxanes, initially regarded as ...
AI-supported mammography screening is found to be safe
2023-08-02
Mammography screening supported by artificial intelligence (AI) is a safe alternative to today’s conventional double reading by radiologists and can reduce heavy workloads for doctors. This has now been shown in an interim analysis of a prospective, randomised controlled trial, which addressed the clinical safety of using AI in mammography screening. The trial, led by researchers from Lund University in Sweden, has been published in The Lancet Oncology.
Each year around one million women in Sweden are called to mammography screening. Each screening examination is reviewed by two breast radiologists to ensure a high sensitivity, so called double reading. ...
Decades of research have left knowledge gaps about cells that regulate the immune system: Purdue and NIH
2023-08-02
Decades of research have left knowledge gaps about cells that regulate the immune system: Purdue and NIH
Four decades of research have produced a vast pool of knowledge about regulatory T cells, a subset of our immune cells. Even so, scientists at Purdue University and the National Institutes of Health have identified 14 understudied T-reg proteins that merit increased attention for the molecular roles they play in disease onset.
“Our lab studies the exact molecular mechanism underlying autoimmunity, infection and cancer,” said Majid Kazemian, associate professor of biochemistry in the College of Agriculture ...
Reducing the risks of nuclear war—the role of health professionals
2023-08-02
About The Editorial: In this editorial, JAMA and JAMA Network journals join journals worldwide to call on health professionals to warn the public about the major danger to health and essential life support systems posed by the threat of nuclear war and urge action to prevent use of nuclear weapons.
Authors: Chris Zielinski, of the University of Winchester, U.K., and World Association of Medical Editors, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Early-stage cancer diagnoses decreased sharply in the U.S. during first year of COVID-19 pandemic; underserved greatly affected
2023-08-02
ATLANTA, August 1, 2023 – A new study from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) found monthly adult cancer diagnoses decreased by half in April 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The largest decrease was for stage I cancers, resulting in a higher proportion of late-stage diagnoses. The study is the most comprehensive research to date about the effects of the first year of the pandemic on cancer diagnoses and stage in the nation. The paper was published today in the ...
Results of large pragmatic trial will help guide treatment of malignant bowel obstruction in patients with advanced cancer
2023-08-02
Findings from the first-ever prospective trial including a randomized pathway comparing surgery to non-surgical treatment of malignant bowel obstruction (MBO) provide important evidence to help inform clinical decision-making in managing this frequent complication in patients with advanced cancer.
Results include data on clinical outcomes and patient quality of life and are being reported in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
The S1316 study, a hybrid design trial that included a randomized component, was led by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute ...
THE LANCET ONCOLOGY: First randomised trial finds AI-supported mammography screening is safe and almost halved radiologist workload
2023-08-02
Peer-reviewed / Randomised trial / People
Planned interim safety analysis of the first randomised trial investigating the use of AI in a national breast cancer screening programme underscores the potential of AI to make mammography screening more accurate and efficient.
Interim findings from a cohort of over 80,000 women in Sweden reveal AI-supported screening detected 20% more cancers compared with the routine double reading of mammograms by two breast radiologists.
The use of AI did not increase false positives (when a mammogram ...
Royal Ontario Museum researchers identify oldest known species of swimming jellyfish
2023-08-02
Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) announces the oldest swimming jellyfish in the fossil record with the newly named Burgessomedusa phasmiformis. These findings are announced in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Jellyfish belong to medusozoans, or animals producing medusae, and include today’s box jellies, hydroids, stalked jellyfish and true jellyfish. Medusozoans are part of one of the oldest groups of animals to have existed, called Cnidaria, a group which also includes ...
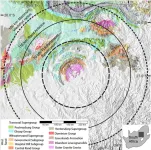
Earth’s most ancient impact craters are disappearing
2023-08-01
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/earths-most-ancient-impact-craters-are-disappearing/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Matthew S. Huber, University of the Western Cape, mhuber@uwc.ac.za (UTC+2 hours)
WASHINGTON — Earth’s oldest craters could give scientists critical information about the structure of the early Earth and the composition of bodies in the solar system as well as help to interpret crater records on other ...
[1] ... [1753]
[1754]
[1755]
[1756]
[1757]
[1758]
[1759]
[1760]
1761
[1762]
[1763]
[1764]
[1765]
[1766]
[1767]
[1768]
[1769]
... [8815]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.