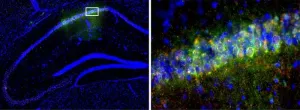
This disease can be caused by a food allergy and prevent children from eating. A new study may show how to treat it
2023-07-31
A new study from Tulane University has identified a new treatment for a chronic immune system disease that can prevent children from eating.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is triggered by food allergies or airborne allergens which causes a type of white blood cell, eosinophils, to build up in the lining of the esophagus. This causes the esophagus to shorten and the esophageal wall to thicken, making swallowing difficult and causing food to get stuck in the throat.
The disease occurs in an estimated 1 in 2,000 adults but more frequently affects children (1 in 1,500) where symptoms can be harder to diagnose and pose greater risks as difficulty feeding can lead to malnutrition, weight loss and ...
Oxycodone prescriptions after delivery not linked to longer-term opioid use compared to codeine prescriptions
2023-07-31
Postpartum prescriptions for oxycodone were not associated with increased risk of longer-term opioid use compared to codeine prescriptions, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221351.
Over the last 10 years, there has been a shift to fewer codeine prescriptions and an increase in prescriptions for stronger opioids, such as hydrocodone, hydromorphone and oxycodone for patients postpartum.
“This occurred in part ...
Novel vaccine may hold key to prevent or reduce the impact of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-07-30
Research Highlights:
A novel vaccine that targets a protein involved in Alzheimer’s disease helped eliminate toxic cells in mice with the condition.
After vaccination, the mice had fewer amyloid plaques and less inflammation in brain tissue and showed improvement in behavior and awareness.
Embargoed until 12 p.m. CT/1 p.m. ET, Sunday, July 30, 2023
BOSTON, July 30, 2023 — A novel vaccine that targets inflamed brain cells associated with Alzheimer’s disease may hold the key to potentially preventing or modifying the course of the disease, according to preliminary research presented at the American Heart Association’s Basic Cardiovascular Sciences Scientific ...
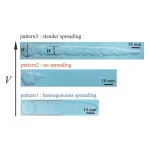
To spread or slide? Scientists uncover how foams are spread on surfaces
2023-07-29
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have uncovered the physics behind how foams are spread on surfaces. Balls of foam placed on a flat substrate were scraped across with a plate and observed. They identified different patterns which strongly depend on the scraping speed, governed by competing physical phenomena. Their findings apply to all kinds of soft materials that need to be spread evenly on surfaces, from mayonnaise on bread to insulation on walls.
Whether ...
How to save the NHS – an expert prescription
2023-07-29
Whether it’s setting up a Bank of England-type body to run it or fining patients for missing appointments, healthcare leaders, policymakers and practitioners past and present have a wealth of ideas about how they would change the NHS for the better.
Professor Dinesh Bhugra, a psychiatrist and former president of the British Medical Association and the Royal College of Psychologists, asked 14 peers, physicians and patients’ representatives for their prescription for the NHS.
The interviews are reproduced in Professor Bhugra’s new book, Conversations about the NHS. Thought-provoking and in some cases, controversial, ideas include:
Setting ...
Unlocking a mystery of fetal development
2023-07-28
As with many toxins, exposure to the toxic metal cadmium during pregnancy can adversely impact fetal development. Now, researchers at the Rutgers School of Public Health think they’re beginning to understand how the metal inflicts its damage: by disrupting placental hormones that regulate pregnancy physiology.
Unlike other toxins, relatively little cadmium crosses the placenta to directly impact the fetus. Instead, the placenta concentrates cadmium in its tissue at rates of up to six times that found in umbilical cord serum.
“We already know a lot about cadmium and its detrimental impacts on fetal health, such ...
How breast milk boosts the brain
2023-07-28
A new study by scientists at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging (HNRCA) at Tufts University suggests that a micronutrient in human breast milk provides significant benefit to the developing brains of newborns, a finding that further illuminates the link between nutrition and brain health and could help improve infant formulas used in circumstances when breastfeeding isn’t possible.
The study, published July 11 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), also paves the way to study what role this micronutrient might play in the brain as ...
New study findings underscore the importance of timely newborn screenings in early care for cystic fibrosis
2023-07-28
Aurora, Colo. (July 28, 2023) – The Journal of Pediatrics has published a manuscript by Stacey Martiniano, MD, pulmonary specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado and associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado. Dr. Martiniano was primary author on the study titled, Late Diagnosis in the Era of Universal Newborn Screening Negatively Effects Short- and Long-Term Growth and Health Outcomes in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. The manuscript’s senior author was Susanna McColley, MD, professor of pediatrics in pulmonary and sleep medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg ...
Royal Society of Chemistry honors Hong with fellow selection
2023-07-28
The Royal Society of Chemistry has named Yi Hong, a distinguished university professor of bioengineering at The University of Texas at Arlington, as a fellow.
Hong said he was honored by the selection.
“Chemistry is amazing because it helps to create many new biomedical materials for human health and life saving,” Hong said. “This recognition encourages me not only to invent more creative biomaterials through chemical design for disease treatment, but also to be a role model to our next generation of scientists and engineers ...
Astronomers shed new light on formation of mysterious fast radio bursts
2023-07-28
More than 15 years after the discovery of fast radio bursts (FRBs) – millisecond-long, deep-space cosmic explosions of electromagnetic radiation – astronomers worldwide have been combing the universe to uncover clues about how and why they form.
Nearly all FRBs identified have originated in deep space outside our Milky Way galaxy. That is until April 2020, when the first Galactic FRB, named FRB 20200428, was detected. This FRB was produced by a magnetar (SGR J1935+2154), a dense, city-sized neutron star with an incredibly powerful magnetic field.
This groundbreaking discovery led some to believe that FRBs identified at cosmological distances outside ...
Texas Tech physicist lands NSF grant
2023-07-28
Myoung-Hwan Kim, an assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Texas Tech University, has been awarded a National Science Foundation grant in the field of materials research (DMR) related to quantum information science (QIS).
An emerging field of research, QIS involves studying the transmission of information through quantum mechanics principles. Kim’s research will examine the influence of magnetism and topology on quantum particles delivering information. Kin’s award is one of two Texas Tech recently received from the NSF for QIS research. The other was awarded to Lu Wei, an assistant professor in the Department of Computer ...
Study looks at Achilles' heel of insulin pump technology
2023-07-28
Since the insulin pump started widespread use in the early 1980s, it’s become the option of choice for type 1 diabetes patients to manage their glucose levels in a way that doesn’t require testing their blood sugar and injecting insulin multiple times daily.
But now, a first-of-its kind study is looking at the issue of patients “running out of real estate” due to pump sites becoming fibrotic, irritated and less effective at delivering insulin. The UW Medicine-led study was published July 14 in the journal Diabetes Care, a publication of the American Diabetes Association.
“No ...
New study finding underscore the importance of timely newborn screenings in early care for cystic fibrosis
2023-07-28
Aurora, Colo. (July 28, 2023) – The Journal of Pediatrics has published a manuscript by Stacey Martiniano, MD, pulmonary specialist at Children’s Hospital Colorado and associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado. Dr. Martiniano was primary author on the study titled, Late Diagnosis in the Era of Universal Newborn Screening Negatively Effects Short- and Long-Term Growth and Health Outcomes in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. The manuscript’s senior author was Susanna McColley, MD, professor of pediatrics in pulmonary and sleep medicine at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital ...
New study finds the prealbumin gene alone is insufficient for diagnosis of heart failure
2023-07-28
BOSTON - A new multi-center study led by doctors at Boston Medical Center and Columbia University found that having a genetic variant in the prealbumin gene alone is not sufficient for diagnosis of transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy in older Black patients. Published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, researchers discovered that a blood test that measures the transthyretin or prealbumin protein might also be helpful in diagnosing transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy and could be used to trigger more definitive imaging testing.
Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR‐CM) is an underdiagnosed cause of congestive heart failure among patients 60+ years of age. ...
A wearable ultrasound scanner could detect breast cancer earlier
2023-07-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When breast cancer is diagnosed in the earliest stages, the survival rate is nearly 100 percent. However, for tumors detected in later stages, that rate drops to around 25 percent.
In hopes of improving the overall survival rate for breast cancer patients, MIT researchers have designed a wearable ultrasound device that could allow people to detect tumors when they are still in early stages. In particular, it could be valuable for patients at high risk of developing breast cancer in between ...
Mutation accessibility fuels influenza evolution
2023-07-28
(Memphis, Tenn.—July 28, 2023) The influenza (flu) virus is constantly undergoing a process of evolution and adaptation through acquiring new mutations. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have added a new layer of understanding to explain why and how flu viruses change. The “survival of the accessible” model provides a complementary view to the more widely recognized “survival of the fittest” way of evolving. The work was published today in Science Advances.
Viruses undergo a rapid evolutionary flux due to constant genetic mutations. This rapid flux is why people get a flu shot ...
Billions in conservation spending fail to improve wild fish stocks in Columbia Basin
2023-07-28
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Four decades of conservation spending totaling more than $9 billion in inflation-adjusted tax dollars has failed to improve stocks of wild salmon and steelhead in the Columbia River Basin, according to Oregon State University research.
The study led by William Jaeger of the OSU College of Agricultural Sciences is based on an analysis of 50 years of data suggesting that while hatchery-reared salmon numbers have increased, there is no evidence of a net increase in wild, naturally spawning salmon and steelhead.
Findings were published today in PLOS One.
Jaeger, a professor of applied economics, notes that ...
Imaging shows how solar-powered microbes turn CO2 into bioplastic
2023-07-28
ITHACA, N.Y. - When considering ways to sustainably generate environmentally friendly products, bacteria might not immediately spring to mind.
However, in recent years scientists have created microbe-semiconductor biohybrids that merge the biosynthetic power of living systems with the ability of semiconductors to harvest light. These microorganisms use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide into value-added chemical products, such as bioplastics and biofuels. But how that energy transport occurs in such a tiny, complex ...
Novel Raman technique breaks through 50 years of frustration
2023-07-28
Raman spectroscopy — a chemical analysis method that shines monochromatic light onto a sample and records the scattered light that emerges — has caused frustration among biomedical researchers for more than half a century. Due to the heat generated by the light, live proteins are nearly destroyed during the optical measurements, leading to diminishing and non-reproducible results. As of recently, however, those frustrations may now be a thing of the past.
A group of researchers with the Institute for Quantum Sciences and Engineering at Texas A&M ...
Unique Mexican black and pinto bean varieties are high in healthy compounds
2023-07-28
URBANA, Ill. – Common beans are important food sources with high nutritional content. Bean seeds also contain phenolic compounds, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that promote health. A study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and CIATEJ in Guadalajara, Mexico, explored the composition of seed coat extracts from black and pinto bean varieties unique to the Chiapas region of Southern Mexico.
“These beans are preserved among Mayan communities and grown by indigenous farmers. They are heirlooms from past generations and are important because of their cultural significance and contribution to biodiversity,” explained ...
Circadian clock gene helps mice form memories better during the day
2023-07-28
A gene that plays a key role in regulating how bodies change across the 24-hour day also influences memory formation, allowing mice to consolidate memories better during the day than at night. Researchers at Penn State tested the memory of mice during the day and at night, then identified genes whose activity fluctuated in a memory-related region of the brain in parallel with memory performance. Experiments showed that the gene, Period 1, which is known to be involved in the body’s circadian clock, is crucial for improved daytime memory performance.
The research demonstrates a link between the circadian system and memory formation ...
Neonatal stem cells from the heart could treat Crohn’s disease
2023-07-28
Research from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that direct injection of neonatal mesenchymal stem cells, derived from heart tissue discarded during surgery, reduces intestinal inflammation and promotes wound healing in a mouse model of Crohn’s disease-like ileitis, an illness marked by chronic intestinal inflammation and progressive tissue damage.
The study, published in the journal Advanced Therapeutics, offers a promising new and alternative treatment approach that avoids the pitfalls of current Crohn’s disease medications, including diminishing effectiveness, ...
China, Indonesia, and Vietnam lead global growth for coming decade in new Harvard Growth Lab projections
2023-07-28
Cambridge, MA – China, India, Indonesia, Uganda, and Vietnam are projected to be among the fastest-growing economies for the coming decade, according to researchers at the Growth Lab at Harvard University. The new growth projections presented in The Atlas of Economic Complexity include the first detailed look at 2021 trade data, which reveal continued disruptions from the uneven economic recovery to the global pandemic. China is expected to be the fastest-growing economy per capita, although its growth rate is smaller than gains seen over the past decade.
Growth over the coming decade is projected to take off in three growth poles, East Asia, Eastern ...
Researchers tickle rats to identify part of the brain critical for laughter and playfulness
2023-07-28
To study play behaviors in animals, scientists must be able to authentically simulate play-conducive environments in the laboratory. Animals like rats are less inclined to play if they are anxious or restrained, and there is minimal data on the brain activity of rats that are free to play. After getting rats comfortable with a human playmate, tickling them under controlled conditions, then measuring the rats’ squeaks and brain activity, a research team reports on July 27 in the journal Neuron that a structure in rat brains called the periaqueductal gray is essential for play and laughter.
“We know that vocalizations such as laughter are very ...
Scientists discover secret of virgin birth, and switch on the ability in female flies
2023-07-28
Scientists have pinpointed a genetic cause for virgin birth for the first time, and once switched on the ability is passed down through generations of females.
For the first time, scientists have managed to induce virgin birth in an animal that usually reproduces sexually: the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.
Once induced in this fruit fly, this ability is passed on through the generations: the offspring can reproduce either sexually if there are males around, or by virgin birth if there aren’t.
For most animals, reproduction is sexual - it involves a female’s egg being fertilised by a male’s sperm. ...
[1] ... [1760]
[1761]
[1762]
[1763]
[1764]
[1765]
[1766]
[1767]
1768
[1769]
[1770]
[1771]
[1772]
[1773]
[1774]
[1775]
[1776]
... [8817]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.