Scientist who expands chemists’ tools joins The Wertheim UF Scripps Institute
2023-07-31
JUPITER, Fla. — A new scientist joining The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology invents creative and efficient ways to build complex, potentially useful molecules, studying their activity so that compounds found in nature may eventually become useful products, such as medications.
Synthetic chemist and associate professor Masayuki Wasa, Ph.D., joins the institute from Boston College, where he was an assistant professor of chemistry. Synthetic chemists specialize in assembling larger molecules from smaller parts, like a child assembling a Lego spaceship from a basket of oddly shaped pieces.
But the work is far from child’s ...
Thomas J. Herzog, MD takes office as The GOG Foundation, Inc. President
2023-07-31
At the NRG Oncology Summer Meeting on Thursday, July 20, 2023, at approximately 5:44pm EDT, Larry J. Copeland, MD passed the presidential gavel to Thomas J. Herzog, MD at The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) Board of Directors meeting.
Dr. Herzog brings a comprehensive background in clinical trials, the integral business aspects and acumen to this important position. A practicing gynecologic oncologist and member of the Board of Directors of GOG-F, he has served as the Treasurer of GOG-F from 2014-2023 and prior ...
ACP issues updated guidance for colorectal cancer screening of asymptomatic adults
2023-07-31
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 31 July 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf ...
Why you shouldn’t declaw tigers or other big cats
2023-07-31
Declawing house cats to keep them from scratching people and furniture is controversial – and even banned in some countries and areas in the U.S. – but the practice is not limited to house cats. In a new study, researchers looked at the effects of declawing on larger cat species and found that declawing disproportionately impacts their muscular capabilities as compared to their smaller brethren.
While it is illegal in the U.S. to surgically modify an exotic animal, declawing is still done on large cats like lions and tigers, often in an effort to allow cubs to more safely ...
Cutting-edge cancer research lab opens operations at Pepper Place
2023-07-31
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Birmingham’s Pepper Place has a striking new addition to its teeming farmers’ market and noted food offerings — a multimillion-dollar cancer research laboratory.
The lab is IN8bio’s new research and development facility in the Martin Biscuit Building at Pepper Place. This R&D space has about 6,000 square feet of wet lab space and around 4,000 square feet for offices, conferences and break areas. IN8bio is a biotechnology company focused on developing novel cellular therapies for cancer, with deep roots in cutting-edge cancer research developed at ...
New UArizona study links brain waves directly to memory
2023-07-31
Neurons produce rhythmic patterns of electrical activity in the brain. One of the unsettled questions in the field of neuroscience is what primarily drives these rhythmic signals, called oscillations. University of Arizona researchers have found that simply remembering events can trigger them, even more so than when people are experiencing the actual event.
The researchers, whose findings are published in the journal Neuron, specifically focused on what are known as theta oscillations, which emerge in the brain's hippocampus region during activities like exploration, navigation and sleep. The hippocampus plays ...
New chemical process makes it easier to craft amino acids that don’t exist in nature
2023-07-31
Every protein in your body is made up of the same 20 building blocks called amino acids. But just because nature is stuck with a limited toolkit doesn’t mean humans can’t expand it.
A study published in Science on July 27 by a team including Pitt chemists describes a powerful new way to create “unnatural” amino acids, which could find use in protein-based therapies and open up novel branches of organic chemistry.
“This is a completely new transformation: new to nature and new to chemistry,” ...
Social media marketing most effective when it prompts consumers to start posting
2023-07-31
Social media is a critical marketing tool to help raise awareness when firms launch new products. The platforms can help inform consumers about product characteristics and benefits relative to competitors’ products.
New research from the University of Notre Dame analyzes data from the motion picture industry, which often relies on social media promotion, in an effort to understand how marketers could better promote other new products.
“The Ripple Effect of Firm-Generated Content on New Movie Releases,” forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing Research ...
Study shows new stroke surgery eligibility criteria may dramatically increase lifesaving stroke surgery rates, with nationwide implications
2023-07-31
Study Shows New Stroke Surgery Eligibility Criteria May Dramatically Increase Lifesaving Stroke Surgery Rates, with Nationwide Implications
SAN DIEGO—A recent study presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting noted that U.S. rates of endovascular thrombectomy, a lifesaving stroke treatment, are projected to increase dramatically based on new criteria.
In the study, endovascular thrombectomy was shown to improve clinical outcomes in patients with large ischemic strokes. This change has the ...
Lignin separation method could make renewable material profitable
2023-07-31
RICHLAND, Wash. – A novel method to extract lignin could help spin wheat straw into gold. Lignin produced using the new method was color-neutral, odorless and homogenous, an advance that could make this carbon-neutral material a more viable candidate for development of high-value products.
Reporting in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the Washington State University researchers extracted up to 93% lignin with up to 98% purity from wheat straw, producing a significant amount of material in a uniform way that could make ...
Hydrogen sulfide shows promise as healthy ageing therapeutic when specifically targeted within cells
2023-07-31
Future therapies to help people live healthy lives for longer could be developed from drugs that release tiny amounts of the gas hydrogen sulfide (H2S), new research has indicated.
A study from the University of Exeter, funded by the US Army and charity The United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation, found that targeting tiny amounts of H2S to specific areas of cells in adult worms using a H2S-releasing molecule called AP39, greatly improved health and activity as they aged. The research, published in PNAS, concludes that targeting ...
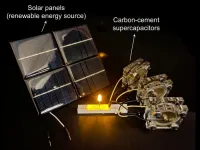
MIT engineers create an energy-storing supercapacitor from ancient materials
2023-07-31
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Two of humanity's most ubiquitous historical materials, cement and carbon black (which resembles very fine charcoal), may form the basis for a novel, low-cost energy storage system, according to a new study. The technology could facilitate the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and tidal power by allowing energy networks to remain stable despite fluctuations in renewable energy supply.
The two materials, the researchers found, can be combined with water to make a supercapacitor — an alternative to batteries — ...
How flies develop sight: Scientists use single-cell sequencing to identify cell types in the visual system
2023-07-31
New York University researchers have discovered new cell types in the visual system of flies, made possible by their creation of a tool that finds and labels neurons during development.
The study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), combines single-cell sequencing data with a novel algorithm to identify pairs of genes that point to previously unknown cells in the brains of fruit flies.
Fruit flies (also known as Drosophila) have long been used as a model organism to study fundamental ...
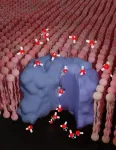
Study reveals long-debated makeup of the molecules that help organize your cells
2023-07-31
For years, we’ve known that a special kind of molecular assembly known as a “polyelectrolyte complex” helps your cells keep themselves organized. These complexes are very good at forming interfaces to keep two liquids separated: your cells use them to create compartments. These abilities have led scientists to consider them for technological applications, including filtering water, better batteries, and even underwater glue, as well as for better pharmaceutical drugs.
But for decades, no one knew exactly ...
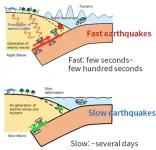
How to distinguish slow and fast earthquakes
2023-07-31
Researchers from the University of Tokyo and Stanford University show what differentiates slow and fast earthquakes and how their magnitudes vary with time.
Normally, earthquakes last up to a few minutes and radiate strong seismic waves. But around 23 years ago, scientists discovered an unusual slow-slip phenomena called slow earthquakes. Slow earthquakes last days or even months. Though they involve significant tectonic movement, you may never feel them. Since slow earthquakes could indicate future fast earthquakes, monitoring and ...
Research shows filter tip stent retrievers may allow neurointerventionalists to remove blood clots on the first try during stroke treatment
2023-07-31
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: July 31, 2023, 12:00 P.M. PDT
CONTACT: Camille Jewell
cjewell@vancomm.com or 202-248-5460
Research Shows Filter Tip Stent Retrievers May Allow Neurointerventionalists to Remove Blood Clots on the First Try During Stroke Treatment
SAN DIEGO—Research presented today at the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery’s (SNIS) 20th Annual Meeting shows that different types of stent retriever tips may result in improved patient outcomes when performing mechanical thrombectomy to treat stroke.
Ischemic stroke, one of the most common types of strokes, happens ...
Nuclear spin's impact on biological processes uncovered
2023-07-31
A research team led by Prof. Yossi Paltiel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem with groups from HUJI, Weizmann and IST Austria new study reveals the influence of nuclear spin on biological processes. This discovery challenges long-held assumptions and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in biotechnology and quantum biology.
Scientists have long believed that nuclear spin had no impact on biological processes. However, recent research has shown that certain isotopes behave differently due to their nuclear spin. The team focused on stable oxygen isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) and found ...
Researchers use geospatial mapping to assist burn patients
2023-07-31
University of Texas at Dallas researchers are using geospatial mapping techniques to identify social and environmental obstacles in communities that might impede burn injury survivors’ reentry into society.
The project is designed to help patients with burn injuries better adapt to their lives after medical discharge, including improving patient access to transportation, employment, food and other necessities.
“Our study looks at how people who survive burn injuries reenter the community,” said Dr. Richard Scotch, program head of sociology and a professor of public policy and political economy in the School of ...
Diving deep: Unveiling the secrets of microalgae to cope with environmental challenges.
2023-07-31
Environmental change, such as ocean warming, alters resource competition and biodiversity. Thus, it is essential to understand how organisms respond to increased competition because changes in their size and metabolism affect the productivity of ecosystems.
Competition has long been recognized as a driving force behind rapid evolution. Still, until now, a mechanistic framework for identifying the specific traits that evolve and their trajectories has yet to be developed. Researchers at Gulbenkian and Monash University turned to metabolic theory, which explicitly predicts how competition shapes the evolution of metabolism ...
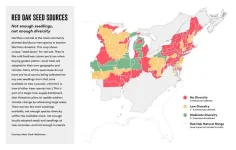
Plans to plant billions of trees threatened by massive undersupply of seedlings
2023-07-31
The REPLANT Act provides money for the US Forest Service to plant more than a billion trees in the next nine years. The World Economic Forum aims to help plant a trillion trees around the world by 2030. Many US cities have plans to shade their streets with millions of trees. Major government and private funding is being invested in planting trees as a powerful tool to fight climate change, protect water, clean air, and cool cities. In short, trees are hot.
But new research shows a troubling bottleneck that could threaten these efforts: U.S. ...
Hollings director honored as fellow of Royal College of Physicians
2023-07-31
Raymond N. DuBois, M.D., Ph.D., director of MUSC Hollings Cancer Center, has been inducted as a fellow into the Royal College of Physicians (RCP).
DuBois traveled to London, England, for the ceremony in July. He had been elected to the prestigious body prior to the COVID pandemic, which delayed the induction ceremony.
The Royal College of Physicians was established in 1518 by a royal charter from King Henry VIII. The college's founding aim was to professionalize physicians through an academic body that required a degree and an exam before ...
NIH launches long COVID clinical trials through RECOVER Initiative, opening enrollment
2023-07-31
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Monday, July 31, 2023
Noon EDT
Contact
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
NIH launches long COVID clinical trials through RECOVER Initiative, opening enrollment
Today, the National Institutes of Health launched and is opening enrollment for phase 2 clinical trials that will evaluate at least four potential treatments for long COVID, with additional clinical trials to test at least seven more treatments expected in the coming months. Treatments ...
Johnson-Matthews receives funding for conference: VL/HCC 2023 Graduate Consortium
2023-07-31
Brittany Johnson-Matthews, Assistant Professor, Computer Science, received funding from the National Science Foundation for: "Conference: VL/HCC 2023 Graduate Consortium."
This award will support the Graduate Consortium at this year's IEEE Conference on Visual Languages and Human-Centric Computing (VL/HCC), which will be held in Washington, D.C. October 2-6, 2023.
Johnson-Matthews said, "This funding will support the ability for students across the country to come together, network, share their research, and curate advice on completing their PhD from senior members of the VL/HCC community."
VL/HCC ...
Wang conducting finite temperature simulation of non-Markovian quantum dynamics
2023-07-31
Wang Conducting Finite Temperature Simulation Of Non-Markovian Quantum Dynamics
Fei Wang, Assistant Professor, Chemistry and Biochemistry, received funding from the National Science Foundation for the project: "Finite temperature simulation of non-Markovian quantum dynamics in condensed phase using quantum computers."
For this research, Wang will develop efficient quantum algorithms to perform condensed phase quantum dynamics simulations on quantum computers.
Many important physical and chemical processes occur in the condensed phase, spanning chemical reactions in solutions, charge transfer at semiconductor interfaces, ...
Study demonstrates efficacy of new short-term resistant TB treatment
2023-07-31
(Boston) – Tuberculosis (TB) disproportionately affects vulnerable populations including those with limited economic resources, HIV patients, those whose diet is deficient in nutrients and others. Resistant TB (MDR TB) does not respond to first line medications and is difficult to treat, requiring long regimens of 15-20 months that are associated with significant side effects and poor outcomes.
Recently, new six-month regimens have been shown to have better results than the long-term treatments, with improved quality of life and health equity. But these novel regimens have not yet been adopted widely in the United States. ...
[1] ... [1765]
[1766]
[1767]
[1768]
[1769]
[1770]
[1771]
[1772]
1773
[1774]
[1775]
[1776]
[1777]
[1778]
[1779]
[1780]
[1781]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.