Researchers detail methodological approach to creating joint displays of data collection in mixed methods research
2023-07-25
Researchers present a methodology for developing joint displays of integrated mixed data collection. These joint displays provide a framework for supporting integration of a mixed methodology in research. Drawing upon a convergent mixed methods cohort study – the Early Discharge of Febrile Neutropenic Children with Cancer Study – the authors constructed a joint display of integrated mixed data collection from a patient/caregiver mixed methods survey instrument and manual medical chart abstraction. The paper outlines the methodological approach, including iterative ...
Brazilian researchers identify gynecological concerns of caregivers of young girls and women with Down syndrome
2023-07-25
Brazilian researchers conducted a cross-sectional study to explore the concerns of caregivers of Brazilian girls with Down syndrome (DS) regarding gynecological aspects of DS including menstruation, contraception and sexual practices. The study included 100 caregivers of females aged 9 years or older with DS who had reached menarche. Participating caregivers completed a questionnaire about their concerns around puberty, menstruation, sexuality and contraceptive methods.
Caregivers commonly expressed concerns around menstrual bleeding. Most caregivers ...
Meta-analysis of research on acne reveals that oral isotretinoin, followed by topical antibiotic, benzoyl peroxide and retinoid, are most effective treatments
2023-07-25
In their comprehensive meta-analysis (comprising 221 randomized controlled trials involving 65,601 patients), researchers investigated the effectiveness of various pharmacological therapies for acne vulgaris across diverse age groups and genders. The articles described 37 interventions, with a median patient age of 20 years old and median duration of treatment of 12 weeks. The median total, inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesion counts were 71.5, 27 and 44, respectively.
The study revealed that oral isotretinoin was the most effective treatment (mean difference 48.41; p-score 1.00), followed in efficacy by a triple therapy containing ...
Survey suggests geographic inequalities in patient registration versus primary care physician density can exclude patients from comprehensive care access
2023-07-25
French researchers conducted a large, simulated study to examine the relationship between the presence of primary care physicians (PCPs) and the ability of patients to register with a PCP. The study aimed to analyze local PCP supply based on various indicators, including PCP presence, patient registration availability for office visits, and patient registration availability for home visits. Out of 5,188 census blocks, 55.4% had at least one PCP, with 38.6% of those blocks allowing registration for office visits and 19.46% allowing registration for home ...
Greater primary care continuity among older people is associated with fewer inappropriate prescriptions and prescribing omissions
2023-07-25
Researchers from the Netherlands conducted an observational study to determine the association between personal continuity and potentially inappropriate prescriptions (PIPs) by family physicians in older patients. PIPs can be categorized as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and potential prescribing omissions (PPOs). The study utilized anonymized routine care data from 269,478 patients, receiving care in 48 Dutch family practices, from 2013 to 2018. They included all patients 65 and older with five or more contacts with their practice in six years, giving them a sample of 25,854 individuals. ...
Primary care clinics that improved patient access, identified at-risk patients and expanded services experienced reductions in acute hospitalizations
2023-07-25
Researchers from Mathematica studied high-performing Comprehensive Primary Care Plus (CPC+) sites to identify key strategies that contributed to significant reductions in acute hospitalization rates. Researchers identified CPC+ practice sites with the highest likelihood of achieving substantial reductions in Medicare acute hospitalization rates between 2016 and 2018, and referred to them as "Acute Hospitalization Rate (AHR) high-performers." Afterwards, they conducted telephone interviews and within- and cross-case comparative analyses of 14 of these primary care practice sites, ...
Primary care doctors face barriers in treating alcoholism
2023-07-25
Researchers explored how primary care physicians who have some familiarity with medications for alcohol use disorder (MAUD) make prescribing decisions and identify reasons for the underuse of MAUD in primary care. They interviewed 19 primary care physicians who had recently prescribed MAUD to patients in an outpatient setting. These physicians were selected from a large online database of medical professionals. Participating physicians reported several challenges in prescribing MAUD: (1) they had somewhat negative personal beliefs about the effectiveness of medications and the likelihood of patient ...
Family medicine physicians receive lowest HPV vaccine cost reimbursements compared to pediatricians, internal medicine doctors, nurse practitioners and other specialists
2023-07-25
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination coverage has improved in the United States, but privately insured adolescents have lower initiation and completion rates compared to those under public insurance programs. One of the contributing factors to this disparity is the higher cost of the HPV vaccine compared to other routinely recommended adolescent vaccines. While private payers typically reimburse the cost of the HPV vaccine at or above the CDC list price (i.e., $210.99 in 2017-2018), it remains below ...
SwRI’s Wyrick named GSA Fellow
2023-07-25
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The Geological Society of America (GSA) has elected Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Danielle Wyrick as a Fellow, recognizing her exemplary scientific achievements, support of young geoscientists and excellent service to GSA. She has played a significant role in GSA’s Planetary Geology Division leadership and committees.
“During my tenure on the board of GSA’s Planetary Geology Division, we adopted the motto ‘when one planet just isn’t enough,’ ...
Physics informed supervised learning framework could make computational imaging faster
2023-07-25
BOSTON - Computational imaging techniques are growing more popular, but the large number of measurements they require often lead to slow speeds or damage to biological samples. A newly developed physics-informed variational autoencoder (P-VAE) framework could help speed up computational imaging by using supervised learning to jointly reconstruct many light sources, each with sparse measurements.
Vidya Ganapati, Assistant Professor of Engineering, Swarthmore College, will present this research at the Optica Imaging Congress. The hybrid meeting will take place 14 – 17 August 2023 in ...
Bacterial testing in kids with sinusitis could slash antibiotic use
2023-07-25
In children with suspected sinusitis, a nasal swab to test for three types of bacteria can tell whether antibiotics are likely to be effective or not, according to a new JAMA study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC.
“Five million kids in the U.S. get prescribed antibiotics for sinusitis each year,” said lead author Nader Shaikh, M.D., pediatrician at UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh and professor of pediatrics and clinical and translational science at Pitt. “Our study suggests that only half of these kids see an improvement in symptoms with antibiotic use, so ...
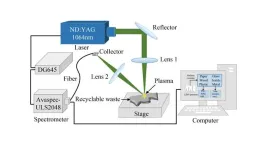
Improving recyclable waste classification with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
2023-07-25
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2023 – Managing and classifying waste accurately for reuse is a growing challenge in environmental protection. Addressing this issue, researchers at Hefei University of Technology in China have embarked on a quest to innovate in the realm of waste management, seeking effective methods that can simplify and improve the identification and classification of recyclable waste.
Delving into the intricacies of waste management, the researchers explored the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technology for the identification ...
State restrictions and geographic access to gender-affirming care for transgender youth
2023-07-25
About The Study: State restrictions were associated with significantly increased estimated drive times for youths seeking gender-affirming care. With more than 1 in 4 gender clinics located in states with restrictions, it is unknown whether existing clinics may have capacity to meet the increased need of out-of-state patients.
Authors: Kevin C. Chung, M.D., M.S., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.11299)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
New robot boosts solar energy research
2023-07-25
Researchers have created a robot capable of conducting experiments more efficiently and sustainably to develop a range of new semiconductor materials with desirable attributes. The researchers have already demonstrated that the new technology, called RoboMapper, can rapidly identify new perovskite materials with improved stability and solar cell efficiency.
“RoboMapper allows us to conduct materials testing more quickly, while also reducing both cost and energy overhead – making the entire process more sustainable,” ...
Only 60% of at-risk women report getting counseled on heart health at their postpartum visit
2023-07-25
Heart disease risk factors (being overweight, having diabetes or high blood pressure) increased among birthing adults between 2016 and 2020
Postpartum visits are crucial for checking mom’s heart health after delivery
Each year, 90% of women in the U.S. attend at least one postpartum visit
‘We must take advantage of this prime opportunity when we have a captive audience’
CHICAGO --- Despite having risk factors for heart disease, only 60% of women reported receiving counseling on optimizing their heart health, which includes healthy eating, exercise and losing weight gained during pregnancy at their six-week ...
Vegetarian dietary patterns and cardiometabolic risk in people with or at high risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-07-25
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that consuming a vegetarian diet may modestly but significantly improve cardiometabolic outcomes beyond standard pharmacological therapy in individuals at high risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), highlighting the potential protective and synergistic effects of vegetarian diets for the primary prevention of CVD.
Authors: Tian Wang, A.P.D., R.D., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25658)
Editor’s ...
DNA testing before tissue diagnosis and time to treatment in lung cancer
2023-07-25
About The Study: The use of plasma circulating tumor DNA testing before tissue diagnosis among patients with suspected advanced lung cancer may expedite biomarker testing and accelerate time to treatment.
Authors: Natasha B. Leighl, M.D., of the University Health Network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.25332)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article ...
Origins of glioma brain cancer found to be in the epigenome
2023-07-25
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: Modeling Epigenetic Lesions that Cause Gliomas
Publication: Cell, Tuesday, July 25, 2023 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.022)
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Authors: Gilbert J. Rahme, PhD; Nauman M. Javed, MD, PhD; Kaitlyn L. Puorro; Volker Hovestadt, PhD; Sarah E. Johnstone, MD, PhD; Bradley E. Bernstein, MD, PhD
Summary:
While cancers often originate from mutations and other alterations of cells' DNA, researchers in the Bernstein Laboratory at Dana-Farber and the Broad ...
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century
2023-07-25
Gloomy climate calculation: Scientists predict a collapse of the Atlantic ocean current to happen mid-century.
Important ocean currents that redistribute heat, cold and precipitation between the tropics and the northernmost parts of the Atlantic region will shut down around the year 2060 if current greenhouse gas emissions persist. This is the conclusion based on new calculations from the University of Copenhagen that contradict the latest report from the IPCC.
Contrary to what we may imagine about the impact ...
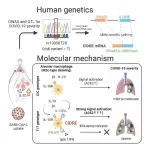
CiDRE renders alveolar macrophages susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 invasion
2023-07-25
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that alveolar macrophages expressing the readthrough transcript CiDRE are stimulated by interleukin-10 to express ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, and promote cytokine storm in patients with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Despite intensive research since the pandemic began, much remains unknown about COVID-19, particularly why it can be so severe in some cases and relatively mild in others. Now, researchers from Japan have identified a genetic quirk that could make some patients more likely to experience severer ...
Robotic hand rotates objects using touch, not vision
2023-07-25
Inspired by the effortless way humans handle objects without seeing them, a team led by engineers at the University of California San Diego has developed a new approach that enables a robotic hand to rotate objects solely through touch, without relying on vision.
Using their technique, the researchers built a robotic hand that can smoothly rotate a wide array of objects, from small toys, cans, and even fruits and vegetables, without bruising or squishing them. The robotic hand accomplished these tasks using only information based on touch.
The work could aid in the development of robots that can manipulate objects in the ...
AI as a leader? A conversation we need to have!
2023-07-25
How can an AI become the boss? Already during the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen how crucial digital technologies have become for leadership. Without Microsoft Teams, Zoom, and related programs, leaders would not have been able to reach their employees easily. These tools continue to enjoy a secured place in the office today.
There is no surprise there. Anything that can be considered a competitive advantage will be utilized as such, and digital options are often quicker, more cost-efficient, or simply more convenient. Indeed, in the future, leadership as a whole is going to make giant leaps toward digitalization. The next phase is therefore only logical: digitally supported leadership, that ...
Mount Sinai receives significant funding to study which coronary revascularization procedure best improves survival and quality of life for women and underserved minority groups
2023-07-25
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will help lead and launch the first clinical trial focusing on women and minority populations to determine which coronary revascularization procedure best improves their survival and quality of life. This trial will be funded through $29.9 million from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute Award to the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Weill Cornell Medicine.
“While there have been many trials comparing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), most have enrolled ...
Large PCORI award funds study of surgical options for coronary artery disease in underrepresented patient populations
2023-07-25
A multi-institutional team of scientists led by Dr. Mario Gaudino, the Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Professor in Cardiothoracic Surgery and assistant dean for clinical trials at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been approved for a nearly $30 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). The award will fund the first study among women and Black and Hispanic patients comparing the effectiveness of two revascularization options used to treat coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease, a narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, is the leading ...
Offsetting or reducing CO2: This is what consumers want
2023-07-25
Whether it’s recycled aluminum at Apple’s MacBook Air or compensation payments from Microsoft for emissions over the life of an Xbox, climate-friendly products are becoming more and more popular. But do consumers also pay attention to how a neutral climate balance is created? Companies use two ways to accomplish this goal: reducing emissions directly or compensating them afterward. “Both approaches can make a product climate-neutral and have a positive impact on the environment, while compensatory measures are being discussed more and more critically in the public. To this end, the consumers in our study were ...
[1] ... [1768]
[1769]
[1770]
[1771]
[1772]
[1773]
[1774]
[1775]
1776
[1777]
[1778]
[1779]
[1780]
[1781]
[1782]
[1783]
[1784]
... [8816]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.