Special Issue: Australia
2023-08-10
In this Special Issue of Science, three Reviews, a Policy Forum, and a Perspective highlight Australia’s exceptional exposure to the risks of climate change and ecosystem degradation. Australia is home to Earth’s most ancient ecosystems and oldest continuous indigenous cultures, which have survived for more than 60,000 years. However, the continent’s unique ecosystems and cultural history have proved vulnerable to waves of European colonization and its associated social and environmental impacts. Ongoing climate change and the ...
Global ecosystem water use efficiency has stalled since 2001
2023-08-10
Increases in global ecosystem water use efficiency – the ratio between carbon assimilation to water evapotranspiration – have stalled since 2001 due to a rising vapor pressure deficit, according to a new study. The findings highlight one way that the adverse effects of our warming climate may undermine human reliance on nature-based climate solutions to achieve carbon neutrality. The rapid rise of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) has led to substantial changes in global terrestrial carbon and water cycles. One of these impacts has been a generalized increase in ecosystem water use efficiency (WUEeco). On a global scale, WUEeco plays ...
A climate-orchestrated early human love story
2023-08-10
A new study published in the journal Science by an international team finds that past changes in atmospheric CO2 and corresponding shifts in climate and vegetation played a key role in determining when and where early human species interbred.
Modern-day people carry in their cells a small quantity of DNA deriving from other human species, namely the Neanderthals and the elusive Denisovans. Back in 2018, scientists announced to the world the discovery of an individual [Figure 1], later nicknamed Denny, who lived 90,000 years ago and who was identified as a daughter to a Denisovan father and a Neanderthal mother [Slon et al. 2018]. Denny, along with fellow mixed-ancestry ...
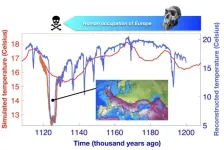
How a massive North Atlantic cooling event disrupted early human occupation in Europe
2023-08-10
A new study published in the journal Science finds that around 1.12 million years ago a massive cooling event in the North Atlantic and corresponding shifts in climate, vegetation and food resources disrupted early human occupation of Europe.
The study published by an international group of scientists from the UK, South Korea and Spain presents observational and modelling evidence documenting that unprecedented climate stress changed the course of early human history.
Archaic humans, known as Homo erectus moved from Africa into central Eurasia around 1.8 million years. From there on they spread towards western Europe, reaching the Iberian peninsula around 1.5 million ...
Global consortium creates large-scale, cross-species database and universal ‘clock’ to estimate age in all mammalian tissues
2023-08-10
Scientists at UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and UCLA Health led an international research team that published two articles detailing changes in DNA – changes that researchers found are shared by humans and other mammals throughout history and are associated with life span and numerous other traits.
“We've discovered that the life spans of mammals are closely associated with chemical modifications of the DNA molecule, specifically known as epigenetics, or more accurately, methylation. In essence, mammals with longer life spans exhibit more pronounced DNA methylation landscapes, whereas those ...
Extreme cooling ended the first human occupation of Europe
2023-08-10
Paleoclimate evidence shows that around 1.1 million years ago, the southern European climate cooled significantly and likely caused an extinction of early humans on the continent, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
Published in the journal Science, the team of researchers discovered the occurrence of previously unknown extreme glacial conditions around 1.1 million years ago. The glacial cooling pushed the European climate to levels beyond what archaic humans could tolerate, emptying the continent of human populations.
The oldest known human remains in ...
An unexpected way to upcycle: Plastic waste transforms into soap
2023-08-10
A team led by Virginia Tech researchers has developed a new method for upcycling plastics into high-value chemicals known as surfactants, which are used to create soap, detergent, and more.
Plastics and soaps tend to have little in common when it comes to texture, appearance, and, most importantly, how they are used. But there is a surprising connection between the two on a molecular level: The chemical structure of polyethylene — one of the most commonly used plastics in the world today — is strikingly similar ...
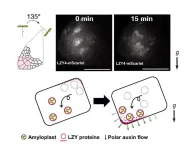
The positional transmitter of statoliths unveiled: It keeps plants from getting lazy
2023-08-10
Plants orient their organs in response to the gravity vector, with roots growing towards gravity and shoots growing in the opposite direction. The movement of statoliths responding to the inclination relative to the gravity vector is employed for gravity sensing in both plants and animals. However, in plants, the statolith takes the form of a high-density organelle, known as an amyloplast, which settles toward gravity within the gravity sensing cell. Despite the significance of this gravity sensing mechanism, the exact process behind it has eluded scientists ...
City of Hope researchers develop a CAR T cell therapy for advanced ovarian cancer
2023-08-10
LOS ANGELES — There are currently few effective treatment options for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer and other solid tumors, but City of Hope researchers are trying to change that.
Researchers with City of Hope, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the nation, have published preclinical research in Nature Communications demonstrating that a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cell therapy worked against ovarian cancer in the laboratory and in preclinical models.
“City of Hope’s ...
Threatened grey-necked rockfowl's habitat even smaller than expected, study finds
2023-08-10
SAN DIEGO (AUG. 10, 2023) — A new study on gray-necked rockfowl has found a much smaller range of suitable habitat for this elusive African bird than was previously assumed, and may warrant a downgrade in its conservation status.
Scientists from the Cameroon Biodiversity Association (CAMBIO) in Cameroon, in partnership with San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, set out to better understand how much suitable habitat remains for the rockfowl, and where the birds can still be found.
Understanding suitable habitat and its extent is crucial for protecting species. However, scientists have limited knowledge ...
Louisiana Obesity Society to host inaugural conference on Aug. 12 in New Orleans
2023-08-10
Physicians, psychologists, advanced practice providers, dietitians, and others who are committed to treating and preventing obesity in Louisiana have come together to formally launch the Louisiana Obesity Society, a new statewide professional organization. The Louisiana Obesity Society will be hosting its inaugural annual conference in conjunction with the Louisiana Chapter of American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery on Saturday, Aug. 12, at the Renaissance New Orleans Arts Warehouse District Hotel in New Orleans.
The Louisiana Obesity Society was created to support providers treating obesity through education and networking. The society will also advocate ...
Poverty alleviation breakthrough: How a switch to a 'growth mindset' empowers entrepreneurs in developing nations
2023-08-10
Although millions are spent each year on entrepreneurship training that is intended to help alleviate poverty and elevate the quality of life of entrepreneurs in developing nations, these programs often fail to make an impact.
Brigham Young University professors Shad Morris and Chad Carlos, along with three other colleagues, were invited by the Tanzania Social Action Fund (“TASAF”) to see if they could help figure out why TASAF’s entrepreneurship trainings were not producing the results they were hoping for.
In order to assist TASAF, Morris, Carlos, and colleagues Geoff Kistruck, Elly Tumsifu and Bob Lount, carried out an extensive ...
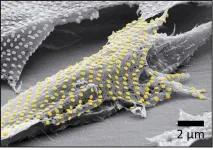
Tattoo technique transfers gold nanopatterns onto live cells
2023-08-10
For now, cyborgs exist only in fiction, but the concept is becoming more plausible as science progresses. And now, researchers are reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters that they have developed a proof-of-concept technique to “tattoo” living cells and tissues with flexible arrays of gold nanodots and nanowires. With further refinement, this method could eventually be used to integrate smart devices with living tissue for biomedical applications, such as bionics and biosensing.
Advances in electronics have enabled manufacturers ...
Long COVID symptoms can emerge months after infection
2023-08-10
Long COVID can persist for at least a year after the acute illness has passed, or appear months later, according to the most comprehensive look yet at how symptoms play out over a year.
The multicenter study, a collaboration between UC San Francisco, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and seven other sites, expands knowledge of post-COVID-19 conditions, describing trends in more detail than previous research and highlighting significant impacts the epidemic has had on the U.S. health care system.
The study appears Aug. 10, 2023, in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), ...
PeerJ announce Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte as Co-Editors-in-Chief of forthcoming new journal, PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science
2023-08-10
Open Access publisher PeerJ have announced their second Editor-in-Chief partnership for the Open Advances series of journals. Professors Ute Roessner and Luis E. Eguiarte have agreed to take on the leadership of PeerJ Open Advances in Plant Science as Co-Editors-in-Chief.
Professors Roessner and Eguiarte are highly respected, award-winning scientists working at the forefront of their fields. As Co-Editors-in-Chief they will provide the scientific leadership for the journal, starting with recruiting an Editorial Board who will ...
NIH zebrafish research included in US Postal Service’s “Life Magnified” stamps
2023-08-10
A microscopy image created by National Institutes of Health researchers is part of the “Life Magnified” stamp panel issued today by the United States Postal Service (USPS®). The NIH zebrafish image, which was taken to understand lymphatic vessel development in the brain, merges 350 individual images to reveal a juvenile zebrafish with a fluorescently tagged skull, scales and lymphatic system.
“Zebrafish are used as a model for typical and atypical human development. It is surprising how much we have in common with ...
Novel socio-environmental vulnerability index pinpoints sustainability issues in Brazilian river basins
2023-08-10
Brazilian researchers combined environmental physical, social and economic indicators to create an index that measures a region’s vulnerability and used it to analyze the basins of the Parnaíba River and São Francisco River in the Northeast of Brazil. The index is named SEVI (for Socio-Environmental Vulnerability).
The Parnaíba and São Francisco basins are considered crucial to agricultural expansion and biodiversity conservation. They contain more than 780 municipalities and part of the semi-arid Caatinga and savanna-like Cerrado biomes, which are threatened ...
Mayo Clinic ‘mini-brain’ study reveals possible key link to autism spectrum disorder
2023-08-10
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Using human "mini-brain" models known as organoids, Mayo Clinic and Yale University scientists have discovered that the roots of autism spectrum disorder may be associated with an imbalance of specific neurons that play a critical role in how the brain communicates and functions. The specific cells are known as excitatory cortical neurons.
The new study is published in Nature Neuroscience.
Findings
The team found an abnormal imbalance of excitatory ...
Muon g-2 doubles down with latest measurement, explores uncharted territory in search of new physics
2023-08-10
Batavia, Ill., Aug. 10, 2023 – Physicists now have a brand-new measurement of a property of the muon called the anomalous magnetic moment that improves the precision of their previous result by a factor of 2.
An international collaboration of scientists working on the Muon g-2 experiment at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory announced the much-anticipated updated measurement on Aug. 10. This new value bolsters the first result they announced in April 2021 and sets up a showdown between theory and experiment over 20 years in the making.
“We’re really probing new territory. We’re determining ...
Making molecules dance to our tune reveals what drives their first movements
2023-08-10
Bringing ultrafast physics to structural biology has revealed the dance of molecular ‘coherence’ in unprecedented clarity.
How molecules change when they react to stimuli such as light is fundamental in biology, for example during photosynthesis. Scientists have been working to unravel the workings of these changes in several fields, and by combining two of these, researchers have paved the way for a new era in understanding the reactions of protein molecules fundamental for life.
The large international research team, led by Professor ...
Gut microbiome can increase risk, severity of HIV, EBV disease
2023-08-10
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Over the past decade, the gut microbiome has gained significant interest by scientists and non-scientists alike. Recent research has shown that the bacteria and other microbes in our gut play a supporting role in immunity, metabolism, digestion, and the fight against "bad bacteria" that try to invade our bodies.
However, new research published in Nature Biotechnology by Angela Wahl, PhD, Balfour Sartor, MD, J. Victor Garcia, PhD, and UNC School of Medicine colleagues others has revealed that the microbiome may not as always be protective against human pathogens.
Using a first-of-its-kind ...
YALE EMBARGOED NEWS: Yale scientists reveal two paths to autism in the developing brain
2023-08-10
New Haven, Conn. — Two distinct neurodevelopmental abnormalities that arise just weeks after the start of brain development have been associated with the emergence of autism spectrum disorder, according to a new Yale-led study in which researchers developed brain organoids from the stem cells of boys diagnosed with the disorder.
And, researchers say, the specific abnormalities seem to be dictated by the size of the child’s brain, a finding that could help doctors and researchers to diagnosis and treat autism in the future.
The findings were ...
Before reaching the skies, the Himalayas had a leg up, new study shows
2023-08-10
Mountain ranges play a key role in global climate, altering weather and shaping the flora and fauna that inhabit their slopes and the valleys below. As warm air rises windward grades and cools, moisture condenses into rain and snow. On the leeward side, it’s quite the opposite. Deserts prevail, a phenomenon known as rain shadow. Thus, the way mountain ranges form is a matter of intense interest among those who study and model climates of the past.
That debate will soon grow more heated with a new paper in the journal Nature Geoscience. A team of researchers ...
Scientists harness the power of AI to shed light on different types of Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-10
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 16:00hrs BST 10 August 2023
Peer reviewed
Observational study
Cells
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, working with technology company Faculty AI, have shown that machine learning can accurately predict subtypes of Parkinson’s disease using images of patient-derived stem cells.
Their work, published today in Nature Machine Intelligence, has shown that computer models can accurately classify four subtypes of Parkinson’s disease, with one reaching an accuracy of 95%. This could pave the way for personalised medicine and targeted drug discovery.
Parkinson’s ...
Researchers discover a potential application of unwanted electronic noise in semiconductors
2023-08-10
Random Telegraph Noise (RTN), a type of unwanted electronic noise, has long been a nuisance in electronic systems, causing fluctuations and errors in signal processing. However, a team of researchers from the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), South Korea has made an intriguing breakthrough that can potentially harness these fluctuations in semiconductors. Led by Professor LEE Young Hee, the team reported that magnetic fluctuations and their gigantic RTN signals can be generated in a vdW-layered semiconductor by introducing vanadium in ...
[1] ... [1755]
[1756]
[1757]
[1758]
[1759]
[1760]
[1761]
[1762]
1763
[1764]
[1765]
[1766]
[1767]
[1768]
[1769]
[1770]
[1771]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.