New and updated resources published to help guide oncology care in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
2023-08-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [August 16, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today announced that a library of resources for improving cancer care in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) has been updated and expanded in collaboration with regional experts. The United States-based non-profit has worked with the King Abdulaziz Medical City in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, since 2015 to standardize cancer treatment based on the latest evidence and expert-consensus, as part of the MENA-NCCN Regional Coordinating Center. Their efforts have led to the ...
Gray wolf recovery is a success—is that a problem?
2023-08-16
Over the past 30 years, efforts to recover gray wolf populations in the United States have been broadly successful, with many regions now sporting robust populations of the charismatic carnivore. Writing in BioScience, wolf experts David E. Ausband and L. David Mech describe the conservation landscape and also the obstacles that wolves face as their populations expand into their historical ranges.
"Remarkable wolf conservation success yields remarkable challenges," ...
Common wristbands ‘hotbed’ for harmful bacteria including E. coli, staphylococcus
2023-08-16
The COVID-19 pandemic took disinfecting to new heights. Now, a new study examining a commonly used item might convince you not to let your guard down just yet.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science tested wristbands of various textures to determine their risk for harboring potentially harmful pathogenic bacteria. Despite being worn daily, routine cleaning of wristbands is generally overlooked or simply ignored.
For the study, researchers tested plastic, rubber, cloth, leather ...
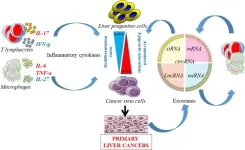
What is the next step in preventative therapies for treating liver cancer?
2023-08-16
Primary liver cancers ranked as the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancers and the third leading cause of cancer-related death in 2020. Among all primary liver cancers, HCC is the most common cancer, accounting for more than 80% of cases with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10% in Western countries. Despite significant progress in diagnosis and treatments, HCC, often diagnosed at late stages, remains a life-threatening disease with an increasing incidence. Therefore, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms triggering the early steps of tumorigenesis represents a great interest to predict and propose more effective therapeutic ...
Layered and traditional semiconductors heterogenous integration open door for post Moore era
2023-08-16
Scientists in NEXT Lab, Tsinghua University have revealed the fabrication and engineering techniques of TMDs and provided a comparative view between TMDs and traditional semiconductors, demonstrating the benefit of combining TMDs with traditional semiconductors.
The research, published in IJEM, shows how to fabricate layered semiconductors modulated with various methods, including phase engineering, defect engineering, doping, and alloying. Then the authors discuss various possibilities to combine layered semiconductors with traditional semiconductors.
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) with suitable ...
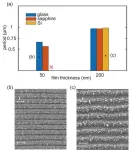
Novel lateral data storage: Two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor memory with a bottom contact 100 nm channel using in-plane polarization
2023-08-16
Traditional memory technologies face limitations in terms of speed, scalability, and power consumption, making them unsuitable for future data-intensive applications. Ferroelectric memory has garnered immense interest in recent years due to its potential for non-volatile storage, enabling data retention even when the power is turned off. The development of two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals material α-In2Se3 has also opened new opportunities for advancing memory technologies.
Interestingly, ferroelectric memory takes a giant step forward by incorporating the remarkable properties ...
Professor Ibrahim Abubakar awarded 2023 Roux Prize
2023-08-16
SEATTLE, Wash. August 16, 2023–Distinguished global health leader Ibrahim Abubakar is the recipient of the 2023 Roux Prize for his dedication to improve health outcomes over the last three decades.
Now in its 10th year, the Roux Prize has been recognizing individuals all over the globe who have leveraged evidence-based health data to improve population health. The Roux Prize is awarded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington’s School of Medicine.
“Prof. Abubakar has been steadfast in his contributions to global health. His expertise and advocacy have directly affected policy implementation and ...
Genetically modified neural stem cells developed by CityU and HKUMed researchers show promising therapeutic potential for spinal cord injury
2023-08-16
A research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant advancement in spinal cord injury treatment by using genetically modified human neural stem cells (hNSCs). They found that specifically modulating a gene expression to a certain level in hNSCs can effectively promote the reconstruction of damaged neural circuits and restore locomotor functions, offering great potential for new therapeutic opportunities for patients with spinal cord injury.
Traumatic spinal cord injury ...
Coronavirus: Researchers develop new rapid and reliable detection method
2023-08-16
Commercially available mass spectrometers can reliably detect the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. In the journal "Clinical proteomics" researchers from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) present a new method which employs equipment that is already being used in hospitals and laboratories to detect bacterial and fungal infections. It takes just two hours from swab to result. According to the team, the approach can also be easily adapted to detect other pathogens and could thus help in future ...
Spectrum of apps shrinks after ban on personalized ads
2023-08-16
A ban on using apps to collect data in order to personalize advertising would significantly reduce the spectrum of available apps and the number of updates, according to a study by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) based on the ban concerning Android apps for children. The findings can assist companies in defining their business models and policymakers when regulating targeted advertising.
Most smartphone apps are free. The providers finance them with advertising, often with what is referred to as targeted advertising: The apps evaluate data such as usage behavior and the user's location and even photos and messages ...
Sugars affect brain ‘plasticity,’ helping with learning, memory, recovery
2023-08-16
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — Can you recognize someone you haven’t seen in years, but forget what you had for breakfast yesterday? Our brains constantly rearrange their circuitry to remember familiar faces or learn new skills, but the molecular basis of this process isn’t well understood. Today, scientists report that sulfate groups on complex sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) affect “plasticity” in the brains of mice. Determining how GAGs function could help us understand ...
Clever coating turns lampshades into indoor air purifiers
2023-08-16
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — Indoor air pollution may have met its match. Today, scientists will report that they have designed catalyst-coated lampshades that transform indoor air pollutants into harmless compounds. The lampshades work with halogen and incandescent light bulbs, and the team is extending the technology so it will also be compatible with LEDs.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person ...
What makes those pandemic-era sourdoughs so deliciously, uniquely, sour?
2023-08-16
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — A few years ago, amid lockdown boredom, it seemed like everyone was perfecting their sourdoughs. A simple, fermented mixture of flour and water, the bread is powered by microbes that provide its one-of-a-kind tangy flavor. For over a hundred years, sourdough bread has been synonymous with San Francisco, where today, scientists will report that they’ve identified and quantified 21 key chemical compounds that make this bread taste and smell so unique. They’ve also compared the levels of the compounds in different breads.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society ...
Cleaning water with ‘smart rust’ and magnets (video)
2023-08-16
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — Pouring flecks of rust into water usually makes it dirtier. But researchers have developed special iron oxide nanoparticles they call “smart rust” that actually makes it cleaner. Smart rust can attract many substances, including oil, nano- and microplastics, as well as the herbicide glyphosate, depending on the particles’ coating. And because the nanoparticles are magnetic, they can easily be removed from water with a magnet along with the pollutants. Now, the team is reporting that they’ve ...
Tubing and swimming change the chemistry and microbiome of streams
2023-08-16
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 16, 2023 — With Labor Day approaching, many people are preparing to go tubing and swimming at local streams and rivers. These delightful summertime activities seem innocuous, but do they have an impact on these waterways? Today, scientists report preliminary results from the first holistic study of this question, which shows that recreation can alter the chemical and microbial fingerprint of streams, but the environmental and health ramifications are not yet known.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2023 is a hybrid meeting ...
Experiencing pain after a heart attack may predict long-term survival
2023-08-16
Research Highlights:
Experiencing pain – even pain not associated with heart disease – a year after having a heart attack is common, and people who had moderate or extreme pain were more likely to die within the next 8 years compared to adults who did not have any post-heart attack pain.
When recommending treatment and making prognoses for people who have had a heart attack, health care professionals should consider if the patients are experiencing moderate or extreme pain.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Aug. 16, 2023
DALLAS, ...
Racism, poverty, and illiteracy increase the risk of contracting and succumbing to AIDS in Brazil
2023-08-16
Social determinants of health —the social conditions in which people grow up, live and work— can influence the risk of contracting AIDS and the mortality associated with the disease. This is the main conclusion of a new study carried out by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and published in The Lancet Regional Health.
The research team evaluated a cohort of 28.3 million people, representative of the low-income Brazilian population, based on data collected between 2007 and 2015. This is the largest evaluation of social determinants of health ...
Harnessing big data reveals birds’ coexisting tactics
2023-08-16
Birds likely hold smart insights about coexisting in popular habitats– especially as climate change looms. But tapping into that knowledge has a big hurdle: knowing where and how numerous birds live successfully in vast environments.
In today’s biological research journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, scientists at Michigan State University (MSU) peeled back layer upon layer of big data to tease out real-life answers that until now have been explored mostly in small-scale experiments.
Sam Ayebare, a PhD candidate from Uganda, has led the work that is the first steps to understanding how so many birds can coexist in the vast Albertine ...
Six strategies could boost NY City housing by 300,000 units over decade
2023-08-16
Six policies aimed boosting residential housing construction in New York City could spark the production of roughly 300,000 additional new housing units over a decade, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
The additional housing units would represent more than a 160% increase over recent annual housing production levels in the city, according to the report.
Researchers say the surge in housing supply likely would lead to increased affordability through greater competition among landlords for tenants in the short term and an increase in naturally occurring ...
The Journal of Scientific Exploration publishes special issue on the Shakespeare authorship question
2023-08-16
In the issue, ten historians and literary scholars present evidence that casts serious doubts about who actually authored the monumental works credited to William Shakespeare. Suggesting that the name is actually a pseudonym for someone else, this position has been endorsed by numerous artists and scholars over the decades ranging from Walt Whitman and Mark Twain to Sigmund Freud, Tyrone Guthrie (founder of Canada’s Stratford Shakespeare Festival) and Mark Rylance founding Artistic Director of the reconstructed Globe Theatre in London.
Tradition credits a businessman from an essentially ...
In-school occupational therapy creates positive education experiences for kids with autism
2023-08-16
Strong parent-school relationships are central to a child’s learning, development, and wellbeing, yet when it comes to children with autism (ASD), it seems positive relationships are few and far between say UniSA researchers.
In Australia, an estimated 200,000 people are autistic, with autism the largest primary disability group served by the NDIS. Globally, about one in 100 children are autistic.
Lead researcher, UniSA’s Dr Kobie Boshoff, says support is urgently needed in schools to support the learning needs of children with ...
Team compares reanalysis datasets with Advanced Himawari Imager measurements over East Asia
2023-08-16
Today’s weather satellites provide scientists with a unique opportunity to evaluate the abilities of various reanalysis datasets to depict multilayer tropospheric water vapor. So a research team undertook a study to assess multilayer water vapor depiction in six representative reanalysis datasets against the measurements from the Advanced Himawari Imager over East Asia. Because water vapor is important in the formation of clouds and precipitation, it is vital for scientists to better understand water vapor and the biases among various datasets.
Their work is published in the journal Advances in Atmospheric Science on July 29, 2023.
Scientists produce reanalysis datasets when ...
Controlling the source of electromagnetic waves enables control of the period of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS)
2023-08-16
Since the scientists at Bell Labs invented the world’s first transistor in December 1947, a revolution in microelectronics technology has profoundly affected lifestyles worldwide. As electronics get smaller and smaller, it is a challenge to find an easy, fast, and low-cost way to fabricate micro-nano components. Traditional direct writing fabrication methods such as mechanical scribing, focused ion beam etching, electron beam lithography, multiphoton polymerization, and thermal scanning probe etching are inefficient. Although methods such as nanoimprinting, photolithography, plasma etching, and ...
Immigration slowed in COVID-19 pandemic, but migrant jobs not filled by U.S.-born
2023-08-16
A prevailing narrative about immigration is that migrants displace U.S.-born residents in the workforce, but new research from University of California, Davis, economists shows that’s not the case.
The study, published in the Journal of Population Economics, details how the COVID-19 pandemic led to a decrease in immigration to the U.S. and how jobs often filled by migrants were not filled by U.S.-born residents.
“We found that this drop in immigrants corresponded also to a drop in employment in some specific types of occupations, including accommodation ...
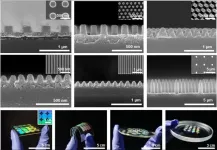
Advancing metasurface manufacturing with water-soluble mold
2023-08-16
When will the protruding rear camera on smartphones become obsolete? The implementation of a metasurface, which completely disregards the properties of light, promises to reduce the thickness of a camera lens to 1/10,000 of a conventional lens. However, despite this advancement, challenges still persist due to high production costs and intricate processes. Nonetheless, a recent study unveiled a “mold” that dissolves in water, enhancing the efficiency of the fabrication process.
A collaborative team led by Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department ...
[1] ... [1734]
[1735]
[1736]
[1737]
[1738]
[1739]
[1740]
[1741]
1742
[1743]
[1744]
[1745]
[1746]
[1747]
[1748]
[1749]
[1750]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.