Immunotherapy drug combo helps extend the lives of patients with metastatic melanoma
2023-08-17
A research team co-led by UCLA investigators has shown that an immunotherapy drug combination can be an effective second-line therapy for patients with an aggressive and deadly type of melanoma that is resistant to the widely used immunotherapy drugs known as PD-1 inhibitors.
In clinical trials, the investigators found that the combination therapy can extend the amount of time patients live without their cancer worsening, known as progression-free survival, and helps overcome resistance to prior immunotherapies, allowing more patients to benefit from the treatment.
The ...
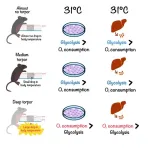
Towards organ preservation: Animal resistance to cold reflected in stem cells
2023-08-17
Researchers led by Genshiro Sunagawa at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) in Japan have shown that an animal’s stem cells possess the same level of cold resistance as the animal itself. Published August 17 in Cell Reports, the study focuses on mice with different hibernation-like characteristics, showing that those with the best resistance to cold temperatures have stems cells that generate energy differently than others. Beyond these immediate findings, the study establishes mouse stem cells as a practical model ...
Anti-obesity drug improves associative learning in people with obesity
2023-08-17
To control our behaviour, the brain must be able to form associations. This involves, for example, associating a neutral external stimulus with a consequence following the stimulus (e.g., the hotplate glows red - you can burn your hand). In this way, the brain learns what the implication of our handling of the first stimulus are. Associative learning is the basis for forming neural connections and gives stimuli their motivational force. It is essentially controlled by a brain region called the dopaminergic midbrain. This region ...
Association between health insurance and primary care vision testing among children and adolescents
2023-08-17
About The Study: In this survey study, the primary care physician vision testing rate was low and differed by insurance status among persons ages 3 to 17. Despite recommendations of yearly testing for children ages 3 to 5, less than half of those with private insurance received testing, with lower rates among those without private insurance.
Authors: Olivia J. Killeen, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.3644)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional ...
Augmented reality for perioperative anxiety in patients undergoing surgery
2023-08-17
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial that included 95 patients, a preoperative walkthrough of a patient’s day of surgery using augmented reality decreased preoperative anxiety compared with traditional perioperative education and handouts, but there was no significant effect on postoperative anxiety, pain levels, or narcotic use. These findings suggest that augmented reality may serve as an effective means of decreasing preoperative patient anxiety.
Authors: Michael G. Rizzo Jr., M.D., of the University of Miami, is the corresponding author.
To ...
To improve solar and other clean energy tech, look beyond hardware
2023-08-17
To continue reducing the costs of solar energy and other clean energy technologies, scientists and engineers will likely need to focus, at least in part, on improving technology features that are not based on hardware, according to MIT researchers. They describe this finding and the mechanisms behind it in Nature Energy.
While the cost of installing a solar energy system has dropped by more than 99 percent since 1980, this new analysis shows that “soft technology” features, such as the codified permitting practices, supply chain management techniques, and system design processes that go into deploying a solar energy plant, contributed only 10 to 15 percent of total ...
New breast cancer susceptibility genes
2023-08-17
Québec City, August 17, 2023 – A large-scale international collaborative study lead by Professor Jacques Simard from Université Laval and Professor Douglas Easton at the University of Cambridge, UK, has identified new genes associated with breast cancer that could eventually be included in tests to identify women at increased risk.
Current genetic tests for breast cancer only consider a few genes, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2. However, these only explain a minority of the genetic risk, suggesting that more genes remain to be identified.
The study found evidence for at least four new breast cancer risk genes, with suggestive evidence for many others. ...
Cutting-edge imaging technique shines light on how DNA strands stack up
2023-08-17
In a new study, researchers at the Department of Biochemistry, Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have used a novel imaging technique to pinpoint how strongly adjacent bases – the building blocks of DNA – stack up on top of each other in a single strand. The findings open up possibilities for building complex DNA nanodevices and unravelling fundamental aspects of DNA structure.
Behind the seamless running of every living cell lies DNA – the hereditary vehicle carrying information for its growth, functioning and reproduction. Each DNA strand is usually made up of four nucleotide bases – Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) and Cytosine ...
Chung-Ang University study validates the simple view of reading for enhancing second and foreign language learners’ experience
2023-08-17
The simple view of reading (SVR) is a widely accepted theory that attempts to define the skills that contribute to early reading comprehension. It attributes a person’s reading comprehension ability to two skills—word recognition (decoding) and language comprehension. This theory has been tested in the context of second as well as foreign languages. However, SVR is known to have some limitations, especially for complex reading, such as second and foreign language (SFL). Recent reading research indicates that SVR needs to be expanded upon to include cognitive factors which may have an ...
Moffitt awarded $5.5 million to study virus-associated tumors among those living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa
2023-08-17
TAMPA, Fla. — The Center for Immunization and Infection Research in Cancer at Moffitt Cancer Center is expanding its viral infection research in Africa. The cancer center has received a $5.5 million, five-year specialized research center grant (U54CA277834) from the National Cancer Institute to investigate virus-associated tumors that disproportionately impact men and women living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa.
Two-thirds of people living with HIV call sub-Saharan Africa home. Their immunosuppression from the virus that causes AIDS leaves them susceptible to infections that cause cancer and makes it more difficult to control viral infections, such as human papillomavirus ...
NIH establishes Maternal Health Research Centers of Excellence
2023-08-17
The National Institutes of Health has awarded $24 million in first-year funding to establish Maternal Health Research Centers of Excellence. Part of NIH’s Implementing a Maternal health and PRegnancy Outcomes Vision for Everyone (IMPROVE) initiative, the centers will develop and evaluate innovative approaches to reduce pregnancy-related complications and deaths and promote maternal health equity. The grants are expected to last seven years and total an estimated $168 million, pending the availability of funds.
Compared to other high-income countries, the United States has a high rate of maternal deaths, with more than 1,200 such deaths occurring in 2021, the most recent year ...
Philosopher: Mindfulness rests on dubious philosophical foundations
2023-08-17
Recent years have seen an explosive growth in mindfulness, which has been adapted from Buddhist meditation practices: in schools, the health services and workplaces, different forms of therapy based on mindfulness are on offer, and meditation apps such as Headspace and Ten Percent Happier are downloaded by millions of people all over the world.
In other words, there is no doubt that mindfulness is fulfilling a need and that many feel that they are being helped by the techniques it offers. But according to PhD Odysseus Stone from the University of Copenhagen, many of the philosophical ...
Marijuana and hallucinogen use, binge drinking reached historic highs among adults 35 to 50
2023-08-17
Past-year use of marijuana and hallucinogens by adults 35 to 50 years old continued a long-term upward trajectory to reach all-time highs in 2022, according to the Monitoring the Future (MTF) panel study, an annual survey of substance use behaviors and attitudes of adults 19 to 60 years old. Among younger adults aged 19 to 30, reports of past-year marijuana and hallucinogen use as well as marijuana and nicotine vaping significantly increased in the past five years, with marijuana use and vaping at their highest historic levels for this age group in 2022. The MTF study is funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, ...
Scientists proposed to adapt a Mars ISRU system to the changing Mars environment
2023-08-17
Human missions to Mars will require a substantial launch vehicle to ascend from Mars to rendezvous with a waiting Earth return vehicle in Mars orbit. For an ascending crew of 6, the current best estimate of oxygen propellants required for ascent is about 30 metric tons. Producing oxygen for ascent propellants and possibly life support from the indigenous CO2 on Mars, rather than bringing oxygen to Mars from Earth, is of significant benefit. The oxygen production is accomplished through a process known generically as in situ resource utilization (ISRU). ...
Lesser-known brain cells may be key to staying awake without cost to cognition, health
2023-08-17
SPOKANE, Wash. – New animal research suggests that little-studied brain cells known as astrocytes are major players in controlling sleep need and may someday help humans go without sleep for longer without negative consequences such as mental fatigue and impaired physical health.
Published in the Journal of Neuroscience, the study found that activating these cells kept mice awake for hours when they would normally be resting, without making them any sleepier.
“Extended wakefulness normally increases sleep time and intensity, but what we saw in this study was that despite hours of added wakefulness these mice did not differ from well-rested ...
Endocrine Society honors endocrinology field’s leaders with 2024 Laureate Awards
2023-08-17
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society today announced it has chosen 14 leading endocrinologists as winners of its prestigious 2024 Laureate Awards, the top honors in the field.
Endocrinologists are scientists and medical doctors who specialize in unravelling the mysteries of hormone disorders to care for patients and cure diseases. These professionals have achieved breakthroughs in scientific discoveries and clinical care benefiting people with hundreds of conditions, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, obesity, hormone-related cancers, growth problems, osteoporosis and infertility.
Established in 1944, the Society’s Laureate ...
Without aggressive climate action, U.S. property values will take a hit from escalating wildfire risk and tree mortality, study finds
2023-08-17
Earth’s rapidly changing climate is taking an increasingly heavy toll on landscapes around the world in the form of floods, rising sea levels, extreme weather, drought and wildfire.
Also at growing risk are the values of property where these hazards are projected to worsen, according to a new study by University of Utah scholars. The research team, led by biology professor William Anderegg, attempted, for the first time, to quantify the value of U.S. property at risk in forested areas exposed ...
Bigger and better quantum computers possible with new ion trap, dubbed the Enchilada
2023-08-17
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Sandia National Laboratories has produced its first lot of a new world-class ion trap, a central component for certain quantum computers. The new device, dubbed the Enchilada Trap, enables scientists to build more powerful machines to advance the experimental but potentially revolutionary field of quantum computing.
In addition to traps operated at Sandia, several traps will be used at Duke University for performing quantum algorithms. Duke and Sandia are research partners through the Quantum Systems Accelerator, one of five U.S. National Quantum Information Science Research Centers funded by the Department of Energy’s ...
Is data justice the key to climate justice?
2023-08-17
Bias in the collection of data on which Artificial Intelligence (AI) computer programmes depend can limit the usefulness of this rapidly growing tool for climate scientists predicting future scenarios and guiding global action, according to a new paper by researchers at the University of Cambridge published in Nature’s npj |Climate Action series.
AI computer programmes used for climate science are trained to trawl through complex datasets looking for patterns and insightful information. However, missing information from certain locations on the planet, time periods or societal dynamics create “holes” ...
AI model developed by Brigham researchers could help screen for heart defect
2023-08-17
The AI model was more efficient at detecting signatures of atrial septal defect (ASD) in electrocardiograms (ECG) than traditional methods.
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, and Keio University in Japan have developed a deep learning artificial intelligence model to screen electrocardiogram (ECG) for signs of atrial septal defects (ASD). This condition can cause heart failure and is underreported due to a lack of symptoms before irreversible complications arise. Their results are published in eClinicalMedicine.
"If we can deploy our model on a population-level ECG screening, ...
Child Development Journal Q&A: How do youth view gang violence is shaping their communities?
2023-08-17
How do children and adolescents evaluate and reason about acts of physical violence in the context of chronic violence that impacts their communities? Previous studies have used situations that correspond with a single act of interpersonal harm void of broader conditions of violence shaping the context in question. A new study released in Child Development examined how youth exposed to gangs known as maras (e.g., MS 13) in Honduras morally deliberate about conditions of gang violence compared with youth not exposed to gangs in Nicaragua, where there are very few maras ...
Can children recognize sick faces?
2023-08-17
According to the World Health Organization, globally, infectious disease is a leading cause of death among children. Furthermore, children are more likely than adults to contract infectious illnesses. However, there’s a gap in research measuring children’s responses to sick faces. It is important to understand how children’s ability to recognize and avoid sickness emerges and develops to help improve children’s health and public health more broadly. Previous research has only reported that adults can use faces to recognize if someone is sick and make judgments about whether to approach or avoid them.
Researchers from the University ...
Lorazepam treatment may be linked to worse outcomes for pancreatic cancer patients
2023-08-17
PHILADELPHIA – Patients with pancreatic cancer who took the benzodiazepine lorazepam (Ativan), commonly prescribed to treat anxiety during cancer treatment, had a shorter progression-free survival than patients who did not, according to results published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
In contrast, patients who took the benzodiazepine alprazolam (Xanax) had a significantly longer progression-free survival than patients who did not.
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that suppress the activity of the central nervous system, which can relieve ...
A healthy diet, reading, and doing sports promote reasoning skills in children
2023-08-17
Reasoning skills are crucial skills in learning, academic performance, and everyday problem-solving. According to a recent study conducted at the University of Eastern Finland, improved overall diet quality and reduced consumption of red meat, as well as increased time spent in reading and organised sports enhanced reasoning skills among children over the first two school years.
“Children with healthier eating habits showed greater cognitive development than other children. Specifically, better overall diet quality, ...
Heredity and environment account for people’s love of nature
2023-08-17
Humans have a positive view of nature. But is this due to an approach we have learned while growing up, or is it something we are born with? The answer is ‘Both’, according to researchers at the University of Gothenburg and the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Our love of nature is highly individual and should influence how we plan our cities, say the researchers.
It is well known that nature has a positive effect on people. In cities in particular, studies have shown that trees and other greenery contribute to people’s wellbeing. However, experts do not agree on the reasons behind this phenomenon, known ...
[1] ... [1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
[1734]
[1735]
[1736]
[1737]
1738
[1739]
[1740]
[1741]
[1742]
[1743]
[1744]
[1745]
[1746]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.