Alternatives to indwelling urinary catheters help patients avoid infections and urethral trauma
2023-08-25
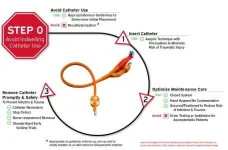
ARLINGTON, Va. (August 25, 2023) — Avoiding the unnecessary use of indwelling catheters and promptly removing catheters that are no longer needed are the first steps in preventing catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals, according to new recommendations developed by five medical societies and published today in the journal Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
“Urinary catheters can be associated with infection and also with non-infectious harms like trauma and obstruction,” said Payal Patel, M.D., an infectious disease physician at Intermountain Health and ...
UCLA researchers say embedding study recruitment in pre-appointment check-in may significantly boost participation
2023-08-25
FINDINGS
UCLA researchers find that they can electronically recruit patients for biomedical research at rates up to 40 times higher than the traditional method of patient portal messages by embedding study recruitment into the pre-appointment preCheck-in page.
BACKGROUND
While patient portal messages are increasingly used to recruit patients for research studies, this method typically results in study enrollment rates of 1-8%. In addition, this method of study recruitment has historically led to ...
New ‘promising medicines’ fund may incentivise commercialisation of high price drugs with weak evidence on clinical benefits
2023-08-25
A new fund to fast-track patient access to potentially valuable new medicines may incentivise the pharmaceutical industry to develop high priced drugs for rare diseases with weak evidence on clinical benefits.
Health economics and policy academics from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, warn that if the NHS England Innovative Medicines Fund (IMF) is not implemented appropriately, it risks disincentivising the generation of essential evidence and could shift the financial burden from the pharmaceutical industry to the public finances.
The IMF operates on similar terms to ...
Certain gut conditions may be early warning signs of Parkinson’s disease
2023-08-25
Certain gut problems, such as constipation, difficulty swallowing, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), may be early warning signs of the neurological condition Parkinson’s disease, suggests research published online in the journal Gut.
Gastrointestinal symptoms are thought to precede the development of cerebrovascular disease, such as stroke or a brain aneurysm, or Alzheimer’s disease, and it has been suggested (Braak’s hypothesis) that gut conditions may precede the development of Parkinson’s disease too.
To ...
Poor lifestyle of over 60s linked to heightened risk of nursing home care
2023-08-25
Over 60s with the unhealthiest lifestyles are significantly more likely to require admission to a nursing home than their peers with the healthiest lifestyles, suggest the findings of a large population study published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Physical inactivity, smoking, poor diet and sleep disorders between the ages of 60 and 64 seemed to be particularly influential: they were associated with a more than doubling in the risk of admission, the findings show.
Modifiable lifestyle risk factors are associated with the development and progression of several long term conditions, ...
Beverage Plant Research indexed in CABI
2023-08-25
We are delighted to announce that the Beverage Plant Research articles are now indexed in CABI specialized databases. This important milestone ensures that articles published in Beverage Plant Research are easily found when searching for beverage plant literature and it enables this journal authors to keep track of how often their article has been cited by others. According to the correspondence made by CABI, the Beverage Plant Research will be indexed from Volume 1, 2021.
About Beverage Plant Research
Beverage Plant Research (e-ISSN: ...
Paper drinking straws may be harmful and may not be better for the environment than plastic versions, researchers warn
2023-08-25
“Eco-friendly” paper drinking straws contain long-lasting and potentially toxic chemicals, a new study has concluded.
In the first analysis of its kind in Europe, and only the second in the world, Belgian researchers tested 39 brands of straws for the group of synthetic chemicals known as poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
PFAS were found in the majority of the straws tested and were most common in those made from paper and bamboo, the study, published ...
Sediment movement during Hurricane Harvey could negatively impact future flooding, prove costly to Houston, UH study finds
2023-08-25
Enormous amounts of sediment, or sand and mud, flowed through Houston waterways during Hurricane Harvey in 2017, due in part to modifications made by humans to bayous, rivers and streams over the past century, that could seriously impact future flooding events and be costly to the City of Houston.
New analysis by geology researchers at the University of Houston found 27 million cubic meters of sediment, or 16 Astrodomes, moved through 12 Houston waterways and Addicks and Barker reservoirs during Harvey, the largest rainfall event in U.S. history. After the storm, up to five feet ...
USC-supported startup receives major grant for clinical trial of a promising eye treatment
2023-08-24
A stem cell patch developed by USC researchers for patients with macular degeneration will soon be tested in a phase 2b clinical trial.
This latest milestone in the patch’s development was made possible by a combined $21 million in support from a state organization, a nonprofit foundation and the university. Last month, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) awarded an estimated $12.4 million to the USC-supported startup Regenerative Patch Technologies (RPT) to test the safety and efficacy ...
New detector paves the way to large-scale optical neural networks
2023-08-24
For the first time, researchers have used a surface normal nonlinear photodetector (SNPD) to improve the speed and energy efficiency of a diffractive optical neural network (ONN). The new device lays the groundwork for large-scale ONNs, which can perform high-speed processing at the speed of light in an extremely energy efficient manner.
Farshid Ashtiani from Nokia Bell Labs will present this research at Frontiers in Optics + Laser Science (FiO LS), which will be held 9 – 12 October 2023 at the Greater Tacoma Convention ...
The right combo: Getting the most health benefits from fruit smoothies
2023-08-24
Smoothies can be a tasty and convenient way to get the important fruits and vegetables you need for a healthy diet. But is a banana and blueberry smoothie the best combo? Researchers at the University of California, Davis, suggest that blending certain ingredients in smoothies can influence whether your body is getting a nutritional boost.
The study, published today in the Royal Society of Chemistry’s journal Food and Function, used smoothies to test how various levels of polyphenol oxidase, an enzyme in many fruits and vegetables, affects the levels of flavanols in food to be absorbed by the body. Flavanols ...
$12 million grant funds foundational research on early liver transplantation
2023-08-24
Alcohol-associated liver disease accounts for 50% of liver-related deaths, and its rates are rising worldwide. But one of the best treatment options, early liver transplantation (ELT)—transplants done with no mandatory period of abstinence from alcohol—is also one of the most controversial, partly because of concerns that patients will relapse to alcohol after transplantation.
Part of the problem is that livers for transplants are in short supply, and researchers lack data to determine who will benefit most from ELT. Studies show that decisions about who gets a transplant can, at times, be influenced by bias or unsystematic. ...
Study shows technology boosts public health programs
2023-08-24
An examination of the SCALE-UP Counts program was recently published in the journal Pediatrics. This analysis, led by Yelena Wu, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and associate professor in the department of dermatology at the University of Utah (the U), and David Wetter, PhD, MS, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor in the department of population health sciences at the U, received support from RADx-Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) and funding from the National Institute of Health (NIH).
The SCALE-UP Counts program was designed to promote COVID-19 testing through collaboration ...
A global observatory to monitor Earth's biodiversity
2023-08-24
At a time of nature crisis driven by unparalleled rates of biodiversity loss, a new interconnected system to monitor biodiversity around the world is urgently needed to direct and focus conservation action.
"The lethal combination of habitat loss, the exploitation of natural populations, pollution, and climate change is causing species extinction rates not seen since the last mass extinction 65 million years ago," said Prof. Andrew Gonzalez, Liber Ero Chair in Conservation Biology at McGill University, and co-Chair of GEO BON. "We lack the means to monitor these impacts ...
High drug price associated with decreased treatment retention for patients with chronic liver disease
2023-08-24
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/24/2023) — Researchers from the University of Minnesota Medical School and College of Pharmacy have found that high costs for hepatic encephalopathy treatment in patients with end-stage liver disease were associated with decreased treatment retention for patients. The study results were recently published in Hepatology Communications.
Hepatic encephalopathy is the loss of brain function that occurs in people with severe liver disease. The condition is associated with high morbidity and mortality. ...
Optimizing tobacco cessation treatment with lung cancer screening
2023-08-24
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (08/24/2023) —Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer in the United States, and 80% of lung cancer deaths are linked to one risk factor: smoking. While lung cancer screenings are a critical part of prevention and treatment for the disease and 15 million Americans qualify for yearly screenings, over half those eligible for screenings are still actively smoking. Without standard smoking cessation measures in place, the benefits of the screenings have not been fully realized.
New ...
New quantum device generates single photons and encodes information
2023-08-24
A new approach to quantum light emitters generates a stream of circularly polarized single photons, or particles of light, that may be useful for a range of quantum information and communication applications. A Los Alamos National Laboratory team stacked two different, atomically thin materials to realize this chiral quantum light source.
“Our research shows that it is possible for a monolayer semiconductor to emit circularly polarized light without the help of an external magnetic field,” ...
Making materials more durable through science
2023-08-24
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories developed a molecule that helps change the way some materials react to temperature fluctuations, which makes them more durable. It’s an application that could be used in everything from plastic phone cases to missiles.
Polymers, which include various forms of plastics, are made up of many smaller molecules, bonded together. This bond makes them especially strong and an ideal product to be used to protect delicate components in a wide variety of items. But with time, use and exposure to different environments, all materials begin to deteriorate.
Hot ...
New framework for oceanographic research provides potential for broader access to deep sea scientific exploration
2023-08-24
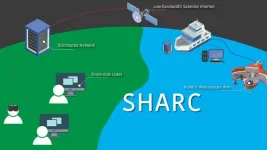
Woods Hole, Mass. (August 23, 2023) -- Scientific exploration of the deep ocean has largely remained inaccessible to most people because of barriers to access due to infrastructure, training, and physical ability requirements for at-sea oceanographic research.
Now, a new and innovative framework for oceanographic research provides a way for shore-based scientists, citizen scientists, and the general public to seamlessly observe and control robotic sampling processes.
The Shared Autonomy for Remote Collaboration (SHARC) framework “enables remote participants to conduct shipboard operations and control ...
How pre-eclampsia accelerates aging in women
2023-08-24
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Pre-eclampsia, a life-threatening surge in blood pressure, is an enigmatic condition. Each year, it causes the deaths of more than 70,000 women worldwide. Because scientists do not know what causes it, they lack targeted strategies to treat it.
Delivery, the only available therapy, is not the cure it is often made out to be, according to Vesna D. Garovic, M.D., Ph.D., a nephrologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who has devoted her career to studying this common pregnancy complication.
"Even after delivery, women ...
Sweet corn yield at the mercy of the environment, except for one key factor
2023-08-24
URBANA, Ill. — A new analysis from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the USDA-Agricultural Research Service (ARS) has identified the top factors accounting for yield variability in processing sweet corn (used for canned and frozen products), including one within the control of processors.
“We used a very robust approach to account for sweet corn yield with field-level data across some 16,000 fields and 27 years. Year and production region were the two most important variables, which makes ...
Cambridge and ISPA scientists create a tool to identify individuals at risk of developing different myeloid leukemias
2023-08-24
Scientists have created a new test for identifying people at risk of developing acute myeloid leukaemia and related cancers, years before they do. The new platform, ‘MN-predict’, will allow doctors and scientists to identify those at risk and to design new treatments to prevent them from developing these potentially lethal cancers.
Researchers at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute (CSCI), the University of Cambridge’s Department of Haematology, and Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria del Principado de Asturias (ISPA) analysed data from more than 400,000 individuals participating ...
Repairing broken brain circuits may offer path to new Parkinson’s treatments
2023-08-24
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (August 24, 2023) — Van Andel Institute scientists have identified a series of processes that help the brain adapt to damage caused by breakdowns in circuits that govern movement, cognition and sensory perception.
Because such breakdowns contribute to Parkinson’s disease, the findings may one day help researchers optimize current treatments or develop new ones that repair or bypass the broken circuits.
A study describing the findings published this week in the journal Science Advances.
“Our work highlights the importance ...
MSK Research Highlights, August 24, 2023
2023-08-24
New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) and the Sloan Kettering Institute — a hub for basic science and translational research within MSK — suggests a method for revealing DNA repair “scars” could help make treatment decisions in BRCA1- and BRCA2-deficient cancers; modified a bacteria-made compound to target mutant KRAS-driven cancers; and shed new light on brain metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.
New method for revealing DNA repair “scars” ...
Study uncovers genetic risk factors for heart failure
2023-08-24
In a new study co-led by investigators at the United States Department of Veterans Affairs and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, a global team of scientists conducted one of the largest genetic association studies on heart failure to date. Using genomic data from over 90,000 heart failure patients and more than a million controls, the team identified 39 genetic mutations associated with heart failure, 18 of which had not been reported previously.
The researchers also pinpointed seven druggable proteins that, when targeted with specially ...
[1] ... [1728]
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
[1734]
[1735]
1736
[1737]
[1738]
[1739]
[1740]
[1741]
[1742]
[1743]
[1744]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.