SwRI investigates the efficiency impact of smart-technology-enabled vehicles
2023-08-23
SAN ANTONIO — August 23, 2023 — A Southwest Research Institute project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has demonstrated an average of 15% energy savings when vehicles outfitted with connected and automated vehicle systems, or CAVs, are introduced into traffic.
CAVs use wireless smart technology to communicate with other CAVs and traffic infrastructure. SwRI’s eco-driving framework uses custom software and predictive powertrain algorithms to enable human drivers to make more efficient driving ...
Nemours Children’s Health researchers to present at World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
2023-08-23
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (August 23, 2023) – Researchers from Nemours Children’s Health will present a range of studies at the World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery, Aug. 27 – Sept. 1 in Washington D.C., the leading global conference in the field. Nemours Children’s presentations will highlight advances in complex congenital heart disease, prevention, cardiomyopathy in rare diseases, and the benefit of integration with other areas like psychology and telehealth.
"In pediatric cardiac surgery, the Nemours Children’s Cardiac Center has pioneered a number of procedures, and we are pleased to share our new findings with researchers and clinicians ...
Unravelling the water dynamics and structure of water-coordinated metal complexes
2023-08-23
Lanthanide-containing complexes are important compounds for sophisticated nuclear-fuel processing and medical imaging. Moreover, they often have interesting symmetric crystal structures and associated dynamics that render unique properties for practical applications.
The seven-coordinate lanthanide complex Ho(III) aqua-tris(dibenzoylmethane) or Ho-(DBM)3·H2O was first reported in the late 1960s. It has a three-fold symmetric structure with holmium (Ho) at the center of three propeller-shaped dibenzoylmethane (DBM) ligands and a water (H2O) ...
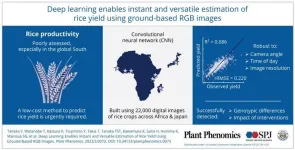
Artificial intelligence can now estimate rice yields, according to new study
2023-08-23
With the rise in global demand for staple crop products projected to substantially increase by 2050 due to population growth, rising per capita income, and the growing use of biofuels, it is necessary to adopt sustainable agricultural intensification practices in existing croplands to meet this demand. However, estimation processes currently employed in the global South remain inadequate. Traditional methods like self-reporting and crop cutting have their limitations, and remote sensing technologies are not fully utilized in this context.
However, recent advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, particularly deep learning with convolutional ...
NIH/National Institute on Aging’s $3 million R01 Grant supports study evaluating probiotic/prebiotic combination’s impact on maintaining bone health of older women
2023-08-23
The NIH/National Institute on Aging has awarded a R01 $3 million grant to study the impact of a probiotic/prebiotic (synbiotic) medical food developed by Solarea Bio on maintaining bone health of older women.
The study will support an 18-month clinical trial of a synbiotic medical food in 220 older women to test whether it maintains lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) with aging.
Grant recipients are Hebrew SeniorLife, USDA HNRCA at Tufts University, Maine Medical Center Research Institute, and Solarea Bio.
“There is an unmet need for safe and effective dietary interventions for the ...
University of South Florida scientist: Barnacles may help reveal location of lost Malaysia Airlines flight MH370
2023-08-23
TAMPA, Fla. (Aug. 23, 2023) – A University of South Florida geoscientist led an international team of researchers to create a new method that can reconstruct the drift path and origin of debris from flight MH370, an aircraft that went missing over the Indian Ocean in 2014 with 239 passengers.
Associate Professor Gregory Herbert was inspired the moment he saw photographs of the plane debris that washed ashore Reunion Island off the coast of Africa a year after the crash.
“The flaperon ...
Heart attack and stroke survivors neglect LDL cholesterol despite increased risk
2023-08-23
DALLAS, August 23, 2023 — A 2023 survey from the American Heart Association conducted by The Harris Poll, found that a majority (70%) of heart attack and stroke survivors are unaware that LDL cholesterol is commonly referred to as 'bad cholesterol.' This matters because LDL cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) significantly contributes to the development of cardiovascular disease, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, ...
FAU lands $4.2 million NIH grant for air quality and Alzheimer’s risks study
2023-08-23
Worldwide, the practice of preparing agricultural fields by burning crop residue contributes large quantities of gaseous pollutants and aerosol particles to the atmosphere and is a known cardiorespiratory health hazard. It has been shown that combustion byproducts in smoke cross the blood-brain barrier causing brain inflammation, and repeated inhalation of smoke can contribute to cognitive decline and dementia among older adults.
Federal efforts to monitor air quality have been focused on population-dense urban communities. As such, impacts of smoke exposure from agricultural fires ...
Study connects neural gene expression differences to functional distinctions
2023-08-23
Figuring out how hundreds of different kinds of brain cells develop from their unique expression of thousands of genes promises to not only advance understanding of how the brain works in health, but also what goes wrong in disease. A new MIT study that precisely probes this “molecular logic” in two neuron types of the Drosophila fruit fly, shows that even similar cells push and pull many levers to develop distinct functions.
In the study in Neuron, a team of neurobiologists at The Picower Institute for Learning and ...
Toppling siloes to link electronic dental and health records
2023-08-23
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study from researchers at Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Dentistry reports on linking electronic health records and electronic dental records to provide better care and outcomes for individuals with Sjögren's disease, an autoimmune disorder that can affect the entire body, including teeth. Their work may have implications for other systemic autoimmune diseases, including lupus and possibly rheumatoid arthritis.
Sjögren’s is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disorder affecting four million Americans ...
AI recommendation vs. user subscription: analyzing in-feed digital advertising performance on platforms like Twitter, Google News, and TikTok
2023-08-23
Researchers from Lehigh University, University of Hong Kong, and Wuhan University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines in-feed advertising’s performance across subscription versus AI recommended news feeds.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Tales of Two Channels: Digital Advertising Performance Between AI Recommendation and User Subscription Channels” and is authored by Beibei Dong, Mengzhou Zhuang, Eric (Er) Fang, and Minxue Huang.
How ...
Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, FACP, named new CEO of National Comprehensive Cancer Network; Robert W. Carlson, MD, retiring after 10+ years leading global oncology nonprofit
2023-08-23
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [August 23, 2023] — Today the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a not-for-profit alliance of leading academic cancer centers—announced Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, FACP, as incoming Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Dr. Denlinger—who is currently NCCN’s Senior Vice President, Chief Scientific Officer—is being promoted to lead the global guidelines organization following a national search to replace the retiring longtime CEO, Robert W. Carlson, MD.
Dr. Denlinger has a long history of global cancer care leadership with NCCN and beyond. She was named an ...
Matthew Sfeir named 2023 Moore Foundation Experimental Physics Investigator
2023-08-23
NEW YORK, August 23, 2023 — Physicist Matthew Sfeir is among 21 innovative mid-career scientists who will each receive $1.25 million from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to pursue experimental physics research with the promise of significantly transforming understanding of physics and facilitating next-generation technological breakthroughs.
The five-year Experimental Physics Investigator Award will allow Sfeir—a Photonics Initiative professor with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) ...
Despite fears to the contrary, Canadian wildfire smoke exposure was not much worse than a bad pollen day in New York City
2023-08-23
New Yorkers can apparently breathe a sigh of relief, at least for now. Their exposure to the smoke in June 2023 from Canadian wildfires led to only a slightly higher bump in visits to New York City hospital emergency departments for breathing problems or asthma attacks than what is seen on days when pollen counts are high. However, authors of a new study say other possible health effects, such as possible heart attacks and stroke, still need to be investigated.
For the study, researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine analyzed daily levels of air pollution, as measured ...
Rare kidney disease is genetically decoded
2023-08-23
When Dr. Bodo Beck first saw the three children of a family who had fled Syria sitting in his consultation room at University Hospital Cologne, the human geneticist was surprised. His genetic analysis diagnosed Bartter syndrome type 3, but never before had he seen such severe joint changes in patients with this rare disease.
The kidney disease is hereditary – affected individuals lack the CLCNKB gene, which is responsible for a specific chloride channel. The electrolyte balance becomes disrupted because the kidneys cannot reabsorb important nutrients and salts back into ...
Which is better—casts or surgery—for older adults with arm fractures?
2023-08-23
A recent study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research found that cast immobilization is as effective as surgery for treating older patients with bone fractures near the wrist.
The study included 276 patients aged 70–89 years who suffered a distal radius fracture that didn’t penetrate the skin and that was treated conservatively or surgically between August 2018 and January 2022. Cast immobilization was used on 213 patients, whereas the other 63 had plates or pins placed during different types of surgery.
Nineteen patients experienced complications within the first year, with the most common being complex regional pain syndrome (5 patients who ...
Is research adequately assessing mental health interventions for children in low- and middle-income countries?
2023-08-23
It is estimated that, globally, mental disorders affect about one in seven children and adolescents aged 10–19 years. A recent analysis of published studies indicates that most research on child and adolescent mental health and psychological interventions in low- and middle-income countries is reactive rather than proactive, focusing on treating rather than preventing mental health problems or promoting mental health.
For the analysis, which is published in Campbell Systematic Reviews, investigators searched a wide range of bibliographic databases, libraries, and websites for relevant studies published between 2010 and ...
Study assesses lifestyle behaviors and cardiometabolic diseases in diverse group of US young adults
2023-08-23
Research published in the Journal of the American Heart Association reveals that many US young adults have poor lifestyle factors and cardiometabolic diseases—such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension—with varying rates based on race and ethnicity.
The study included 10,405 individuals aged 18–44 years whose information was available from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2018. The prevalence of lifestyle risk factors ranged from 16.3% for excessive drinking to 49.3% for poor diet quality. The prevalence of cardiometabolic ...
Does deafness alter brain circuits supporting social skills?
2023-08-23
Hearing impairment may cause difficulties in social interactions, but new research indicates that social struggles experienced by deaf individuals are likely not due to brain alterations but rather due to non-supportive environments. The findings, which are published in Human Brain Mapping, suggest that deafness does not affect the mechanisms and brain circuits supporting social skills.
For the research, investigators analyzed published neuroimaging studies focusing on social perception in deaf versus hearing participants. Results indicated that both deaf and hearing participants recruited the ...
Does catheter ablation lower dementia and mortality risks in all groups of older adults with atrial fibrillation?
2023-08-23
Previous studies have shown a link between catheter ablation and a lower risk of dementia and premature death for patients with atrial fibrillation. This procedure involves a flexible wire that is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin and guided to the heart where it destroys tissue that is causing rapid and irregular heartbeats. It’s unclear if the associations between catheter ablation and lower dementia and mortality risks hold among different subgroups of patients stratified by age, sex, co-morbidities, and medication use.
Now, a large study in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society including more ...
What’s the best way to prevent tuberculosis transmission from wildlife to cattle?
2023-08-23
An analysis of relevant published studies indicates that cattle face a hypothetically high risk of getting tuberculosis from wildlife—such as deer, foxes, and wild boar—through indirect interactions, with a much lower risk from direct interactions.
In the analysis, which is published in Mammal Review, data from 31 studies using various methods to assess wildlife-cattle interactions around the world revealed that direct interaction rates were low (an average of 0.03 interactions per month per species pair). In contrast, indirect interaction rates were 154 times higher (an average of 4.63 interactions per month per species pair). Indirect interaction ...
Sedentary time in children linked with heart damage in young adulthood
2023-08-23
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 23 Aug 2023: Hours of inactivity during childhood could be setting the stage for heart attacks and strokes later in life, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2023.1 The study found that sedentary time accumulated from childhood to young adulthood was associated with heart damage – even in those with normal weight and blood pressure.
“All those hours of screen time in young people add up to a heavier heart, which we know from studies in adults raises the likelihood of heart attack and stroke,”2 said study author Dr. Andrew Agbaje ...
People taking adult education classes run lower risk of dementia
2023-08-23
How can we best keep our brain fit as we grow older? It’s well known that regular cognitive activity, for example brainteasers, sudokus, or certain video games in middle and old age tends to protect against cognitive decline and dementias like Alzheimer’s. But many of us regularly engage in adult education classes, for example learning a language or a new skill. Is such adult education likewise associated with a lower risk of cognitive decline and dementia?
Yes, according to researchers from the Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer of Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan who have shown for the first time, in a new study in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.
“Here ...
Firearm injuries and the pandemic: Lower opportunity neighborhoods are disproportionately affected
2023-08-23
During a time when hospitals were overrun with COVID-19 patients and ventilators were in high demand, the nation’s
focus was not on firearm-related injuries. With our attention elsewhere, it may have seemed that these injuries
appeared to decrease and mass shootings seemed to disappear. But that doesn’t mean firearm injuries went away. In
fact, for one group of children in particular, firearm trauma rates grew. In a new study, investigators at Children’s
Hospital Los Angeles reveal that ...
Dramatic reductions in malaria cases and deaths continue over five years with seasonal malaria vaccine-drug combination
2023-08-23
Final results of landmark study confirm two-thirds reduction in cases of malaria, including cases of severe malaria, and deaths from malaria, for RTS,S-drug combination over either intervention given alone in settings of highly seasonal malaria transmission.
RTS,S vaccine has similar high efficacy to drugs in preventing malaria in highly seasonal transmission settings.
Overall reduction in malaria incidence likely “tops” 90% among children protected by bednets, vaccines, and drugs.
Seattle and London, August 22, 2023—The final results of a landmark study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases ...
[1] ... [1720]
[1721]
[1722]
[1723]
[1724]
[1725]
[1726]
[1727]
1728
[1729]
[1730]
[1731]
[1732]
[1733]
[1734]
[1735]
[1736]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.