A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals by unhealthy snacking
2023-09-15
A quarter of people are undoing the benefits of healthy meals with unhealthy snacks, which increases the risk of strokes and cardiovascular disease.
The findings, published today in the European Journal of Nutrition by researchers from the School of Life Course & Population Sciences and ZOE, details the snacking habits of 854 people from the ZOE PREDICT study.
Researchers found that half of the participants do not match the healthiness of their meals to their snacks and vice versa. This difference has a negative effect on health measures, such as blood sugar and fat levels, and addressing this could be a simple diet strategy to improve ...
Polar experiments reveal seasonal cycle in Antarctic sea ice algae
2023-09-15
In the frigid waters surrounding Antarctica, an unusual seasonal cycle occurs. During winter, from March to October, the sun barely rises. As seawater freezes it rejects salts, creating pockets of extra-salty brine where microbes live in winter. In summer, the sea ice melts under constant daylight, producing warmer, fresher water at the surface.
This remote ecosystem is home to much of the Southern Ocean’s photosynthetic life. A new University of Washington study provides the first measurements of how sea-ice algae and other single-celled life adjust to these seasonal rhythms, offering clues to what might happen as ...
Clever lapwings use cover to hide in plain sight
2023-09-15
Ground-nesting birds called lapwings use the shape of their nests and surroundings to hide from predators, new research shows.
Many ground-nesting species are in decline due to changes in land management and high populations of predators, such as foxes and crows. Conservation projects can fail because too many eggs and chicks are eaten.
The new study, led by the University of Exeter, assessed the visibility of lapwing nests in terms of cover (also called “occlusion”) and camouflage using models that simulate the vision and viewing angles of various predators.
The findings showed that despite nesting in open fields, lapwings can hide their eggs ...
When it comes to starting a family, timing is everything
2023-09-15
The review, conducted jointly with researchers from Oxford University, the Royal Berkshire Hospital in Reading, and the Princess Anne Hospital in Southampton, included seven randomised controlled trials involving 2,464 women or couples who had been trying to conceive.
Each month there is a narrow window for successful conception due to the limited lifespan of the sperm and egg, which begins from around five days before ovulation (egg release) and lasts until several hours afterwards.
The period of a woman’s cycle can be identified by different methods, including urine ovulation tests (dipstick ...
Are us teenagers more likely than others to exaggerate their math abilities?
2023-09-15
A major new study has revealed that American teenagers are more likely than any other nationality to brag about their math ability.
Research using data from 40,000 15-year-olds from nine English-speaking nations internationally found those in North America were the most likely to exaggerate their mathematical knowledge, while those in Ireland and Scotland were least likely to do so.
The study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, used responses from the OECD Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), in which participants took a two-hour maths test alongside a ...
Women receiving inflated risks from genetic testing could undergo unnecessary breast surgery
2023-09-15
Women could be opting to have unnecessary surgery to avoid breast cancer, after being told they are at high risk from genetic test results which do not take family history into account.
The authors of new research led by the University of Exeter have warned that women who discover, outside of a clinical setting, that they carry a disease-causing variant in one of the BRCA genes (BRCA1 or BRCA2) may be told their risk of breast cancer is 60-80 per cent. In fact, the risk could be less than 20 per cent if they do not have a close relative with the condition.
The warning has emerged in a paper published today in the Lancet journal eClinical Medicine. Until recently, women who ...
The Morton Arboretum awarded historic $15 million in federal IRA funds to improve urban forests in underserved Illinois communities
2023-09-14
LISLE, Ill. (September 14, 2023) — The Morton Arboretum in Lisle, Ill., announced it will receive $15 million in federal funding from the U.S. Forest Service through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) to expand and improve the tree canopy in disadvantaged communities throughout Illinois. The funding is part of a historic $1 billion investment to boost the nation’s urban tree cover in communities nationwide. The federal grant funding the Arboretum will receive is the largest award in Illinois, the largest award to a public garden in the country and a historic sum for the nonprofit tree-focused organization.
The U.S. ...
Scientists uncovered mystery of important material for semiconductors at the surface
2023-09-14
A team of scientists with the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has investigated the behavior of hafnium oxide, or hafnia, because of its potential for use in novel semiconductor applications.
Materials such as hafnia exhibit ferroelectricity, which means that they are capable of extended data storage even when power is disconnected and that they might be used in the development of new, so-called nonvolatile memory technologies. Innovative nonvolatile memory applications will pave the way for the creation of bigger and faster computer systems by alleviating the heat generated from the continual ...
RIT researcher receives award to advance study of cortical blindness
2023-09-14
Rochester Institute of Technology’s Gabriel Diaz, associate professor in the Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science, has earned the Research to Prevent Blindness/Lions Clubs International Foundation Low Vision Research Award (LVRA), in collaboration with researchers at the University of Rochester.
The award is given annually to provide funding for innovative research, which demonstrates out-of-the-box thinking, focuses on the visual system that is damaged, and seeks greater understanding of how the visual system and brain respond to severe and chronic visual ...
$8.7M to vector-borne disease center funds training, evaluation
2023-09-14
ITHACA, N.Y. -- To help respond to emerging and established vector-borne threats, the Northeast Regional Center for Excellence in Vector-Borne Diseases (NEVBD), led by Cornell, has received a five-year, $8.7 million award from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to train and educate current and future vector-borne disease professionals and to evaluate the effectiveness of community and regional prevention strategies.
The award, effective as of July, follows $10 million in ...
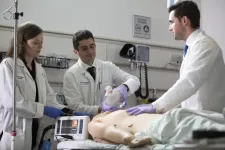
New device rapidly controls postpartum hemorrhage
2023-09-14
NEW YORK, NY, Sept. 14, 2023--A study led by Columbia obstetricians has shown that a new intrauterine device can rapidly control postpartum hemorrhage, a major cause of severe maternal morbidity and death, in real-world situations.
“Our findings show that the device is an important new tool in managing postpartum bleeding,” says Dena Goffman, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and senior author of the study.
“We had ...
Grant funds study of video game for preventing unintended teen pregnancies
2023-09-14
Weill Cornell Medicine has been awarded a five-year, $5 million grant from the United States Department of Health and Human Services through the Office of Population Affairs under the Teen Pregnancy Prevention Program to conduct a randomized trial testing whether a bilingual video game called “No Baby No (No Bebé No)” can increase the use of contraception among sexually active Black and Hispanic adolescents.
“Nine out of ten teens play video games. No Baby No empowers Black and Hispanic adolescents to learn about contraception, and the potential consequences of not using it, in a risk-free virtual ...
New evidence indicates patients recall death experiences after cardiac arrest
2023-09-14
Philadelphia, September 14, 2023 – Up to an hour after their hearts had stopped, some patients revived by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) had clear memories afterward of experiencing death and had brain patterns while unconscious linked to thought and memory, report investigators in the journal Resuscitation, published by Elsevier.
In a study led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, in cooperation with 25 mostly US and British hospitals, some survivors of cardiac arrest described lucid death experiences that occurred while they were seemingly unconscious. Despite immediate treatment, fewer than 10% of the 567 patients studied, ...
Clinical whole genome sequencing test developed at JAX
2023-09-14
Until quite recently, it was extremely difficult to detect the variants underlying many genetic disorders. In the absence of a defined cause, clinicians have little to guide treatment for those left without a genetic diagnosis, forcing patients and families to embark on a diagnostic odyssey with no guarantee of finding answers.
A decade ago, sequencing centers began offering clinical whole exome sequencing, but these only cover the portion of the genome that codes for proteins – approximately 1.5 percent of the entire genome. While relatively successful, the diagnostic yield for most clinical exome sequencing programs is roughly 25 percent, leaving 75 percent of cases without ...
UCI researchers announce publication of an open-label clinical trial suggesting that N-acetylglucosamine restores neurological function in Multiple Sclerosis patients
2023-09-14
Irvine, CA – Sept. 14, 2023 – UCI researchers have found that a simple sugar, N-acetylglucosamine, reduces multiple inflammation and neurodegeneration markers in people who suffer from multiple sclerosis (MS). In addition, they also found this dietary supplement improved neurological function in 30% of patients.
According to the World Health Organization, MS affects more than 1.8 million people, and while there are treatments to prevent relapses and improve quality of life, there is no cure.
The study, N-acetylglucosamine ...
Vocal learning linked to problem solving skills and brain size
2023-09-14
The European starling boasts a remarkable repertoire. Versatile songbirds that learn warbles, whistles, calls, and songs throughout their lives, starlings rank among the most advanced avian vocal learners. Now a new study published in Science finds that starlings, along with other complex vocal learners, are also superior problem solvers.
“There is a long-standing hypothesis that only the most intelligent animals are capable of complex vocal learning,” says Jean-Nicolas Audet, a research ...
Study finds spiritual coping behaviors may be key to enhanced trauma recovery of Black men who survive firearm injury
2023-09-14
PHILADELPHIA (September 14, 2023) – High rates of firearm injury among urban Black men in the U.S. can lead to long physical and psychological recovery times, worsened by limited access to mental health services. In the face of firearm injury, urban Black men may feel they have lost control over their lives, leading to fear, paranoia, lack of forgiveness, and different dimensions of mental health challenges, which can be difficult to overcome.
In a pilot study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing ...
In the “I” of the beholder: People believe self-relevant artwork is more beautiful
2023-09-14
People have fairly consistent preferences when it comes to judging the beauty of things in the real world—it’s well known, for example, that humans prefer symmetrical faces. But our feelings about art may be more personal, causing us to prefer art that speaks to our sense of self, research in Psychological Science suggests.
“When there is personal meaning in an image, that can dominate your aesthetic judgments way more than any image feature,” said Edward A. Vessel (The City College of New York) in an interview. Though self-relevant ...
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotrophic fungus that can cause serious life-threatening invasive infections in immunocompromised individuals
2023-09-14
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotrophic fungus that can cause serious life-threatening invasive infections in immunocompromised individuals; by constructing a recombination map, this study shows that A. fumigatus produces the highest number of crossovers per chromosome ever described (~30 per chromosome pair).
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002278
Article Title: The human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus can produce ...
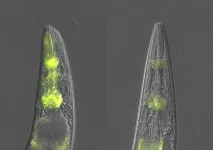
During failure of core protein quality control in the nematode C. elegans, a specialized anti-aggregation mechanism relying on pathogen response factors and lysosomal mediated degradation is triggered
2023-09-14
During failure of core protein quality control in the nematode C. elegans, a specialized anti-aggregation mechanism relying on pathogen response factors and lysosomal mediated degradation is triggered, promoting tissue-specific resilience to age-dependent protein aggregation and its proteotoxicity.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002284
Article Title: A safety mechanism enables tissue-specific resistance to protein aggregation during aging in C. ...
How a molecule deletes neural chat might help treat Angelman syndrome
2023-09-14
Researchers from the University of Tokyo reveal how the presynaptic Ube3a E3 ligase, a causal factor in Angelman syndrome, eliminates neural chat. The study helps find a better drug target for the Angelman syndrome treatment.
Neurons chat through electrical signals, transmitting information via connection sites between neurons—the synapses. After birth, the number of synapses increases. During childhood, the brain starts to mature and removes many unnecessary synapses. But sometimes, the development of the nervous system goes awry, leading to developmental disorders.
Kotaro ...
In songbirds, complex vocal learning predicts problem-solving abilities and brain size
2023-09-14
Vocal learning complexity, or the ability to imitate sounds, is associated with better problem-solving abilities and larger brains in songbird species, according to a new study. Whether vocal learning complexity was linked with such cognitive phenotypes was previously unknown. The approach used in the study, to study a lineage of birds, serves as a model for testing similar patterns in other vocal learning species. Complex vocal learning – the ability to imitate heard sounds – is a crucial component of human spoken language and has been assumed to be associated with more advanced cognitive abilities. Outside of humans, it has ...
Governance reforms could strengthen the Sustainable Development Goal implementation
2023-09-14
In a Policy Forum, Frank Biermann and colleagues outline demanding – yet realistic – policy reforms to strengthen the governance and implementation of the United Nations’ (UN) ambitious Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In 2015, the UN General Assembly agreed on 17 SDGs with 169 targets intended to be achieved by 2030. However, recent research has shown that the political impact of these goals has been limited and has not yet succeeded in reorienting political systems, institutions, or societies ...
Switching off the cytokine storm
2023-09-14
Constant exposure of cells to stressing agents, such as pathogens, may disturb an organism’s normal functioning. To fight stress, cells have developed several coping mechanisms, including the inflammatory response.
While inflammation is necessary, too much of it can impair cell and organ function. This is the case with cytokine storms – inflammatory cascades during an infection that can spiral out of control and lead to severe disease and even death, as recently highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a new paper published in Science, EMBL Grenoble and University ...
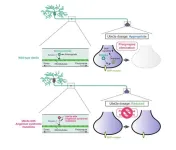
Specialised gut immune cells pinpointed that can limit progression of inflammatory bowel disease
2023-09-14
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute, King’s College London and Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust have characterised a specialised type of immune cell, which plays a key role in protecting and repairing the cells in the healthy human gut.
These protective immune cells are depleted in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), leaving patients vulnerable to disease progression and severe complications. The findings could lead to better clinical management and treatment options for people living ...
[1] ... [1687]
[1688]
[1689]
[1690]
[1691]
[1692]
[1693]
[1694]
1695
[1696]
[1697]
[1698]
[1699]
[1700]
[1701]
[1702]
[1703]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.