New ACS report finds smoking rates, alcohol use, physical inactivity decreased during COVID-19; worsening trends in obesity, cervical cancer screening
2023-05-02
ATLANTA, May 2, 2023 – In a new report, American Cancer Society (ACS) researchers discovered both favorable and unfavorable changes in major cancer risk factors, preventive behaviors and services, and screenings in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic. Between 2019 and 2021, current smoking, physical inactivity, and heavy alcohol consumption declined, and human papillomavirus vaccination and stool testing for colorectal cancer screening uptake increased. In contrast, obesity prevalence increased, while cervical cancer screening declined during the same timeframe. Additionally, disparities by racial/ethnic and socioeconomic status persisted.
The findings were released ...
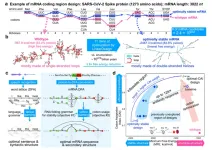
New AI algorithm boosts COVID-19 mRNA vaccine antibody response by 128 times
2023-05-02
A team of researchers from Baidu Research has developed an AI algorithm that can rapidly design highly stable COVID-19 mRNA vaccine sequences that were previously unattainable. The algorithm, named LinearDesign, represents a major leap in both stability and efficacy for vaccine sequences, achieving a 128-fold increase in the COVID-19 vaccine’s antibody response.
“This research can apply mRNA medicine encoding to a wider range of therapeutic proteins, such as monoclonal antibodies and anti-cancer drugs, promising broad applications and far-reaching impact,” said Dr. He Zhang, Staff Software Engineer ...
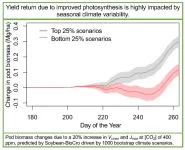
RIPE researchers model ‘link’ between improved photosynthesis and increased yield
2023-05-02
A team from the University of Illinois has modeled improving photosynthesis through enzyme modification and simulated soybean growth with realistic climate conditions, determining to what extent the improvements in photosynthesis could result in increased yields.
“There’s a complex relationship between photosynthesis improvement and actual yield, having higher photosynthesis doesn’t necessarily mean you have higher yield. The yield return is highly impacted by seasonal climate conditions” said Yufeng He, a postdoctoral researcher at Illinois, who led this work for a research project called Realizing Increased ...
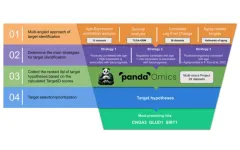
Dual-purpose therapeutic targets for aging and glioblastoma identified with PandaOmics
2023-05-02
“[...] AI-powered algorithms, such as PandaOmics, may accelerate subsequent gene target discovery not only for GBM but for a broader range of age-associated diseases.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 2, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Identification of dual-purpose therapeutic targets implicated in aging and glioblastoma multiforme using PandaOmics - an AI-enabled biological target discovery platform.”
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive and most ...
Flagship report of the North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation, Taking Stock, examines where 5 billion kg of industrial pollutants go every year in North America
2023-05-02
Montreal — The North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) today released a new report compiling and analyzing data reported by approximately 24,000 industrial facilities in Canada, Mexico and the United States to their respective national pollutant release and transfer registers. The report reveals important gaps in the reporting and tracking of transfers to disposal across the region due to differing reporting requirements, shared responsibilities across agencies and jurisdictions, and the lack of information about the fate of waste pollutants when they are transferred to third parties (such as waste management service providers) or across national ...
Cedars-Sinai Cancer appoints new biobank director
2023-05-02
Cedars-Sinai Cancer welcomes Karine Sargsyan, MD, formerly director of one of the world’s largest clinical biobanks, as scientific director of its OncoBiobank. Sargsyan is charged with leading biobank development and creating new strategies for the optimal deployment and use of the Cedars-Sinai Cancer Molecular Twin Precision Oncology Platform for both research and clinical practice. She will work collaboratively with Nicholas Tatonetti, PhD, associate director of Computational Oncology, on the ...
Upcycling method turns textile trash to functional coatings
2023-05-02
ITHACA, N.Y. - In an effort to make textiles more sustainable, a new method allows researchers to break old clothing down chemically and reuse polyester compounds to create fire resistant, anti-bacterial or wrinkle-free coatings that could then be applied to clothes and fabrics.
The proof-of-principle study provides hope for unsustainable textile, apparel and footwear industries that together generate 20% of global solid waste. Many so-called recyclers end up illegally dumping textiles as trash in countries in Asia and Africa.
“We think that our clothes are recycled or reprocessed, but most ...
Joyful music could be a game changer for virtual reality headaches
2023-05-02
Joyful music could be a game changer for virtual reality headaches
Listening to music could reduce the dizziness, nausea and headaches virtual reality users might experience after using digital devices, research suggests.
Cybersickness – a type of motion sickness from virtual reality experiences such as computer games – significantly reduces when joyful music is part of the immersive experience, the study found.
The intensity of the nausea-related symptoms of cybersickness was also found to substantially decrease with both joyful and calming music.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh assessed the effects of music ...
Study shows governments escape blame by contracting services such as prisoner transport
2023-05-02
LAWRENCE — Governments and private contractors work together on countless functions, but when something goes wrong, who is to blame?
Zach Mohr, associate professor of public affairs & administration at the University of Kansas, is involved in a series of studies to examine how people determine blame and hold those in power accountable.
While research has shown deaths in prisons have increased in recent years, there is little public data available about how those deaths occur in specific ...
New research reveals that most child victims of gun violence are innocent bystanders
2023-05-02
A University of Missouri School of Medicine researcher examining the circumstances behind pediatric firearm assaults found that most child shooting victims were shot outdoors for unknown reasons and were likely not intentionally targeted.
Firearm injuries surpassed motor vehicle accidents as the leading cause of child deaths in 2020. Assault has become the most common cause of firearm injury among American children and adolescents, surpassing firearm suicide and accidental firearm injuries. However, very little research exists examining the circumstances ...
National trends in mental health–related emergency department visits among youth
2023-05-02
About The Study: Over the last 10 years, the proportion of pediatric emergency department visits for mental health reasons have approximately doubled, including a 5-fold increase in suicide-related visits. These findings underscore an urgent need to improve crisis and emergency mental health service capacity for young people, especially for children experiencing suicidal symptoms.
Authors: Greg Rhee, Ph.D., of the University of Connecticut School of Medicine in Farmington, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
USPSTF recommendation statement on screening for latent tuberculosis infection in adults
2023-05-02
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in populations at increased risk. Populations at increased risk for LTBI based on increased prevalence of active disease and increased risk of exposure include persons who were born in, or are former residents of, countries with high tuberculosis prevalence and persons who live in, or have lived in, high-risk congregate settings (e.g., homeless shelters or correctional facilities). The precise prevalence rate of LTBI in the U.S. is difficult to determine; however, estimated prevalence is about 5.0%, or up to 13 million persons. ...
Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potential
2023-05-02
WASHINGTON, May 2, 2023 – Cancer cells that initiate metastasis, or the spread of the disease from its primary location, are different from cancer cells that stay in the original tumor. Distinguishing metastasis-initiating cell types can determine the severity of cancer and help medical practitioners decide on a course of treatment.
In APL Machine Learning, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Texas Tech University developed a deep learning model to classify cancer cells by type. The tool requires only a simple microscope and a ...
COVID-19 Mortality by race and ethnicity in metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas
2023-05-02
About The Study: This study found that most of the national decrease in racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortality between the initial and Omicron waves was explained by increased mortality among non-Hispanic white adults and changes in the geographic spread of the pandemic. These findings suggest that despite media reports of a decline in disparities, there is a continued need to prioritize racial health equity in the pandemic response.
Authors: Andrew C. Stokes, Ph.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Anti-poverty programs may help reduce disparities in brain development and mental health symptoms in children
2023-05-02
States that provide stronger social safety nets have lower socioeconomic disparities in the brain development and mental health of children 9 to 11 years old, according to research supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) at the National Institutes of Health. The disparity in brain structure between children from high- versus low-income households was more than a third lower in states with greater cash assistance than in those offering less, and the disparity in mental health symptoms was reduced by nearly a half.
The study, published in Nature Communications, ...
Ibogaine inspires new compounds to treat addiction, depression
2023-05-02
Scientists have developed two new drug candidates for potentially treating addiction and depression, modeled on the pharmacology of a traditional African psychedelic plant medicine called ibogaine. At very low doses, these new compounds were able to blunt symptoms of both conditions in mice.
The findings, published on May 2 in Cell, took inspiration from ibogaine’s impact on the serotonin transporter (SERT), which is also the target of SSRI antidepressants like fluoxetine (Prozac). A team of scientists from UCSF, Yale and Duke universities virtually screened 200 million molecular structures to find ones that blocked SERT in the same way ...
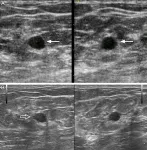
AI helpful in triaging breast masses in low-resource areas
2023-05-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can analyze breast mass images from low-cost portable ultrasound machines and accurately identify cancer, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). This could prove useful for triage in low-resource settings.
Breast lumps are often found accidentally, during breast self-exam or during a breast exam by a medical professional. Breast cancer screening can find cancers in the breast before the lump can be felt.
While cancer screening has been the focus in Western countries, low- and middle-income ...
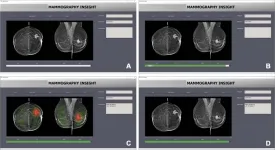
AI bias may impair radiologist accuracy on mammogram
2023-05-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Incorrect advice by an AI-based decision support system could seriously impair the performance of radiologists at every level of expertise when reading mammograms, according to a new study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Often touted as a “second set of eyes” for radiologists, AI-based mammographic support systems are one of the most promising applications for AI in radiology. As the technology expands, there are concerns that it may make radiologists susceptible to automation bias—the tendency of humans ...
Machine translation for cuneiform tablets
2023-05-02
An AI model has been developed to automatically translate Akkadian text written in cuneiform into English. Hundreds of thousands of clay tablets from ancient Mesopotamia, written in cuneiform and dating back as far as 3,400 BCE, have been found by archeologists, far more than could easily be translated by the limited number of experts who can read them. Shai Gordin and colleagues present a new machine learning model that can automatically translate Akkadian cuneiform into English. Two versions of the model were trained. One version translates the Akkadian from representations of the cuneiform signs in Latin ...
Climate reasoning, prior beliefs, and partisanship
2023-05-02
A popular explanation for climate denialism is that humans will adopt beliefs that accord with their political orientation, using their cognitive abilities to explain away identity-inconsistent information in a process called “motivated reasoning.” To test this hypothesis, Bence Bago and colleagues challenged volunteers’ ability to think rationally using time pressure and cognitive loads of varying intensity. The team recruited American participants from Lucid, a website that connects academics with online survey participant pools. The authors found that people who had the ability to deliberate free of cognitive load or time ...
SwRI, UTSA researchers develop new method to synthesize antimalarial drug
2023-05-02
SAN ANTONIO – May 2, 2023 - Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) have developed a method to synthesize the highly potent antimalarial drug artemisinin, which could lead to a more cost-effective treatment for malaria. The work, recently featured on the cover of the scientific journal Organic Letters, was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation as well as a grant from the Connecting through Research Partnerships (Connect) program, a joint effort by SwRI and UTSA to enhance scientific collaboration between the two institutions.
In 2021, 247 million cases of malaria led to 619,000 deaths worldwide. The most effective ...
ASBMB calls for better wages and benefits for postdocs
2023-05-02
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations to the National Institutes of Health on April 14 to improve working conditions for postdocs.
The society recommended that the NIH:
Ensure a livable wage, benefits, etc. for postdocs
Require that principle investigators help postdocs craft a training plan
Require that principal investigators complete mentor training programs
Expand programs to create more academic staff scientist positions
Collect data on postdoc career outcomes
“Many of our members who run labs are struggling to recruit and retain qualified postdocs,” Sarina Neote, public affairs director ...
Cooperation benefits from peer-punishment
2023-05-02
A multi-lab replication of a 2006 study supports the role of peer sanction in promoting human cooperation. Cooperation is imperative for society to successfully solve complex problems, including climate change. One approach many groups have adopted is a system of peer sanctions for noncooperators. Such a system incurs costs to participants, who must impose the sanctions, but can allow cooperators to feel more secure that their investments in the shared project will be matched by others. A 2006 study suggested that groups with peer sanctions outgrew and outperformed groups without a peer-sanctioning institution. In light ...
Recycling of valuable metals from spent lithium ion batteries using spinning reactors
2023-05-02
In a world that is slowly distancing itself from carbon-based energy, there has been a meteoric rise in the use of lithium-ion batteries as a next-generation energy storage solution. However, this has resulted in another problem - an increase in the amount of lithium battery waste. Lithium-ion batteries degrade slowly over their lifetime, losing anywhere from 12% to 24% of their total capacity over 500 charging and discharging cycles. The electrolyte and other materials inside the battery can also degrade, causing a decrease in capacity over time. The disposal of lithium batteries ...
PCORI offers up to $452 million through new health research funding opportunities on high-priority topics
2023-05-02
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today began inviting proposals for new studies and implementation projects through nine funding opportunities. These PCORI Funding Announcements (PFAs) include four offering up to $452 million for comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) studies comparing health care approaches to help patients and their caregivers make better-informed health choices given their particular circumstances. Additional PFAs offer funding for a range of projects that support and advance patient-centered CER and use of PCORI-funded research results.
“With ...
[1] ... [1957]
[1958]
[1959]
[1960]
[1961]
[1962]
[1963]
[1964]
1965
[1966]
[1967]
[1968]
[1969]
[1970]
[1971]
[1972]
[1973]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.